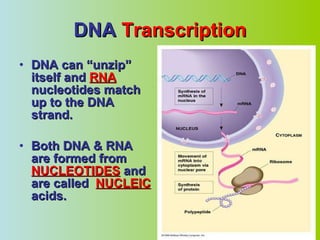
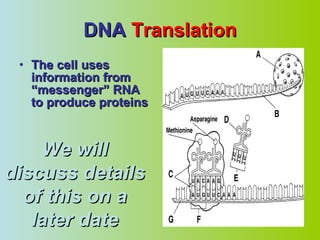
1. DNA contains the genetic instructions that determine traits and control cell functions by serving as a template for protein structure.
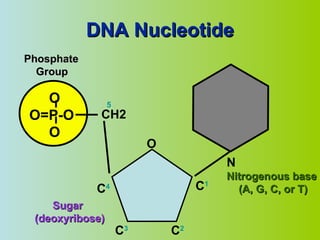
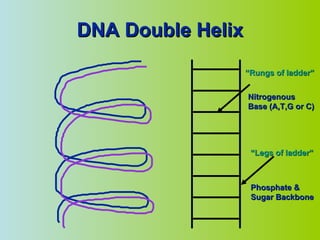
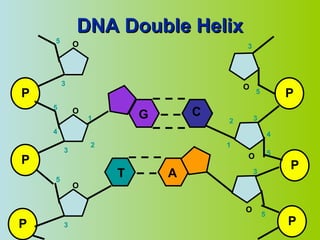
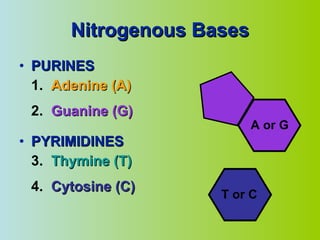
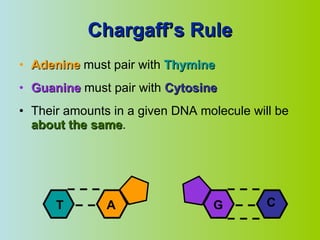
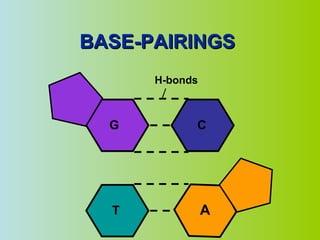
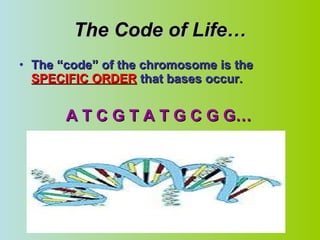
2. DNA is made up of nucleotides that pair together in a double helix structure, with adenine pairing with thymine and cytosine pairing with guanine.
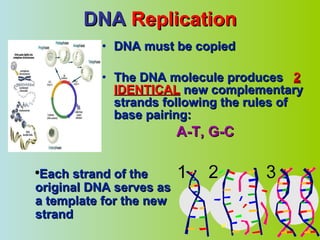
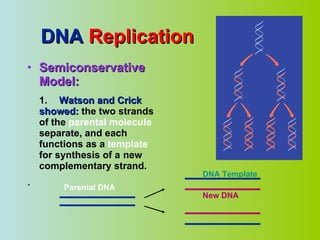
3. DNA must be replicated before cell division so that each new cell contains the exact genetic information of the original cell. The double helix unwinds and each strand acts as a template for a new complementary strand.