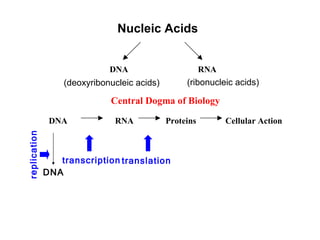
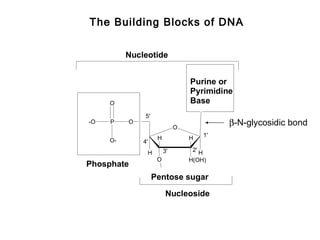
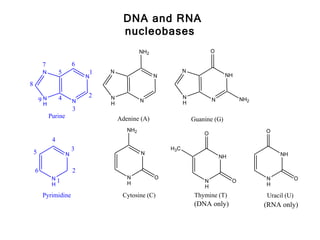
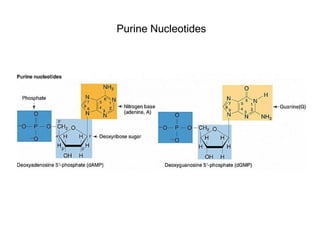
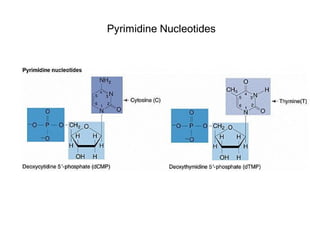
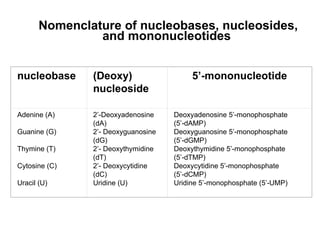
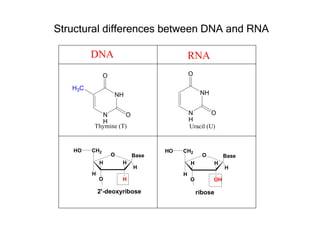
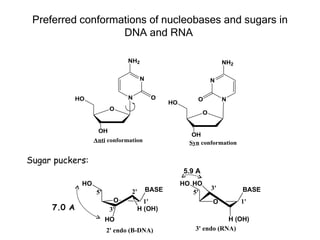
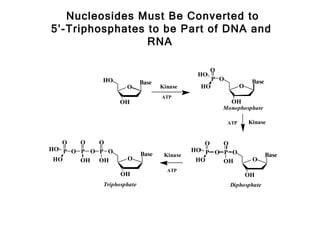
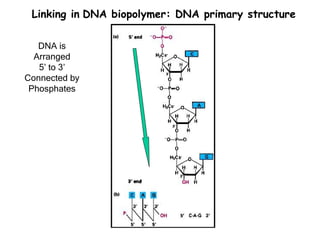
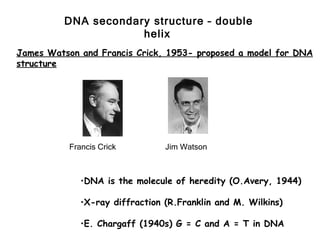
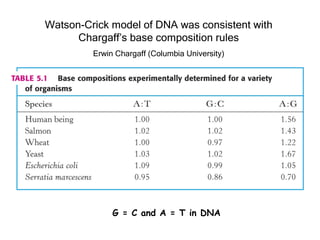
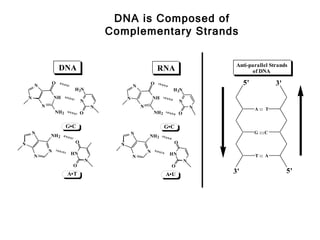
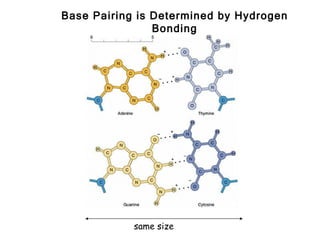
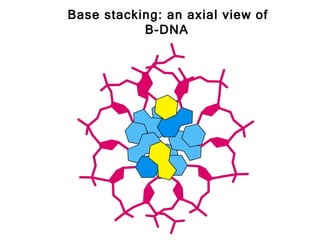
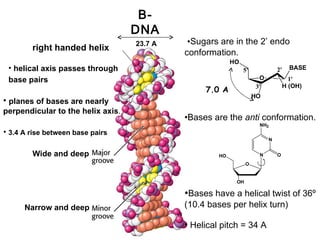
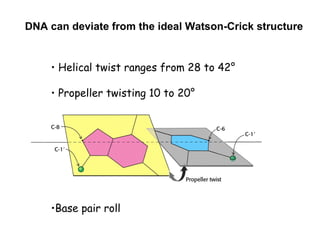
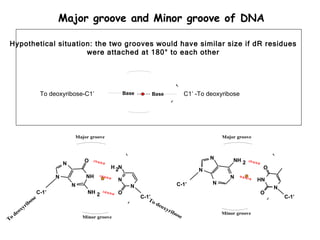
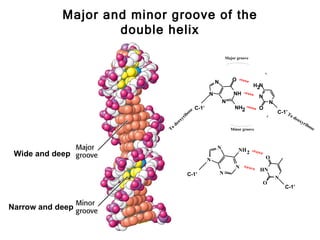
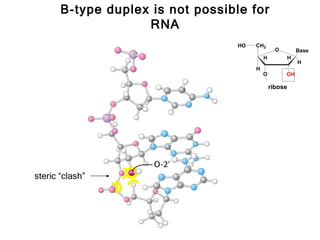
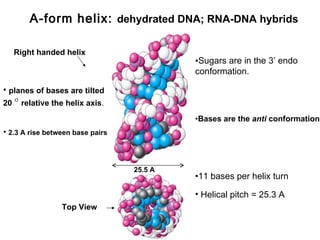
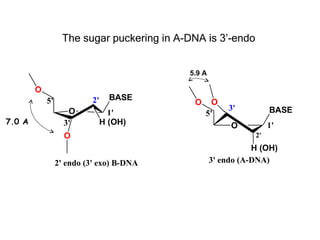
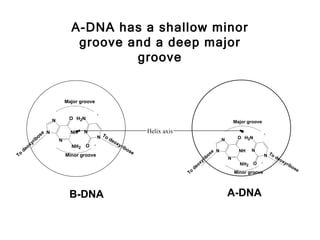
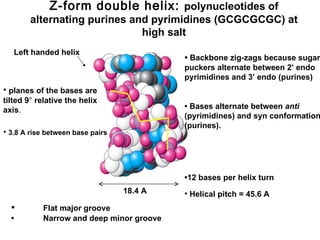
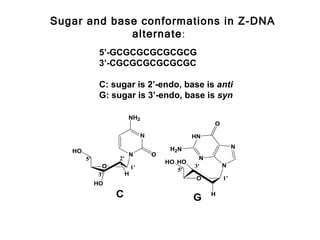
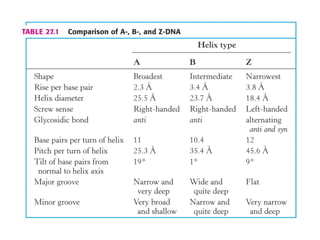
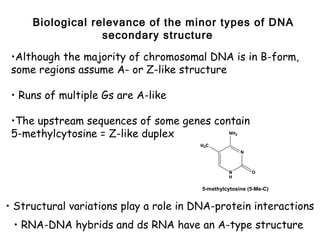
This document provides an overview of DNA structure and the different forms it can take. It discusses the primary structures of DNA including nucleotides, nucleosides, and bases. It then describes the canonical B-DNA double helical structure proposed by Watson and Crick, including base pairing, base stacking, and the forces that stabilize the structure. Finally, it briefly discusses alternative A-form and Z-form double helical structures and their biological relevance.