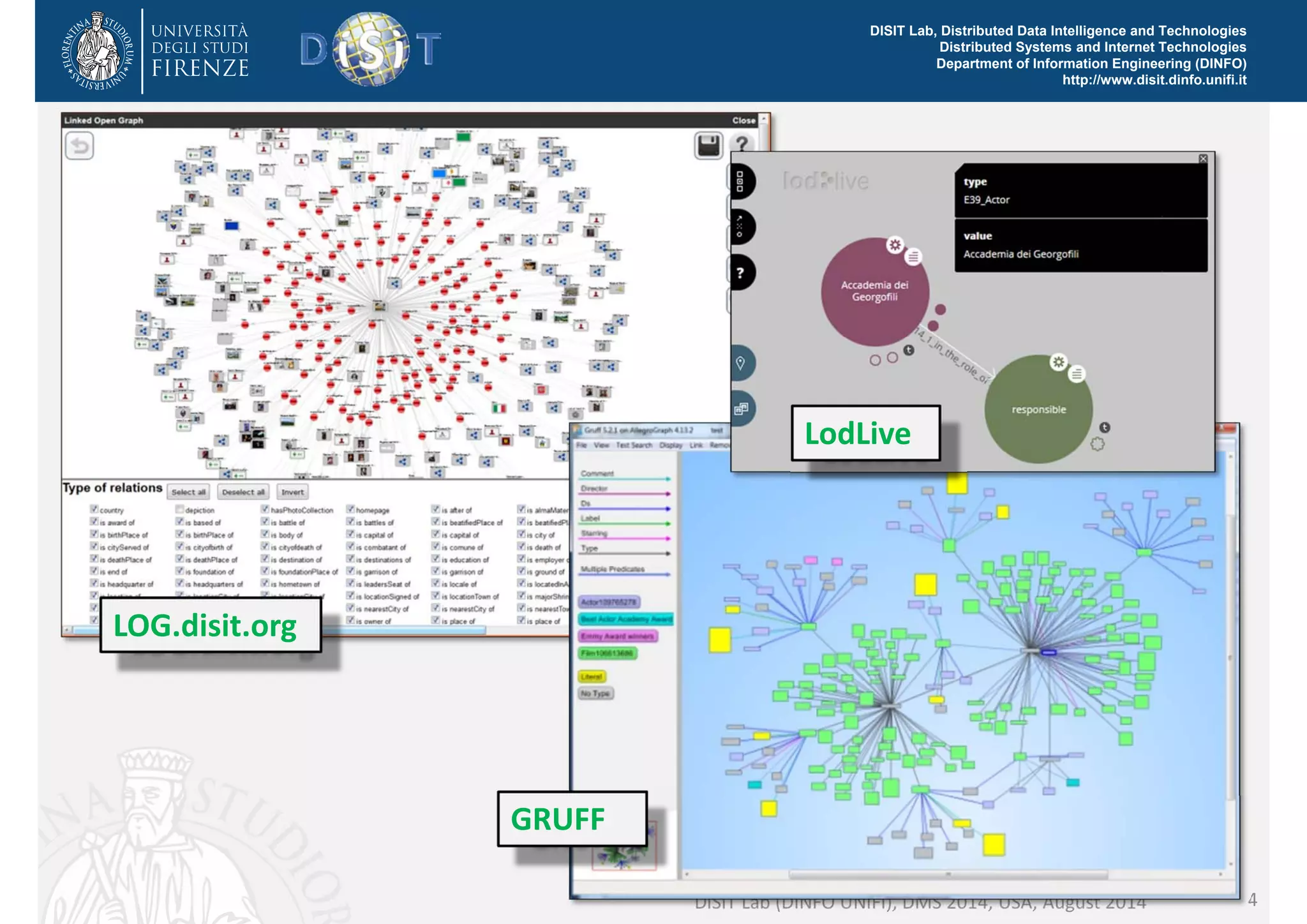
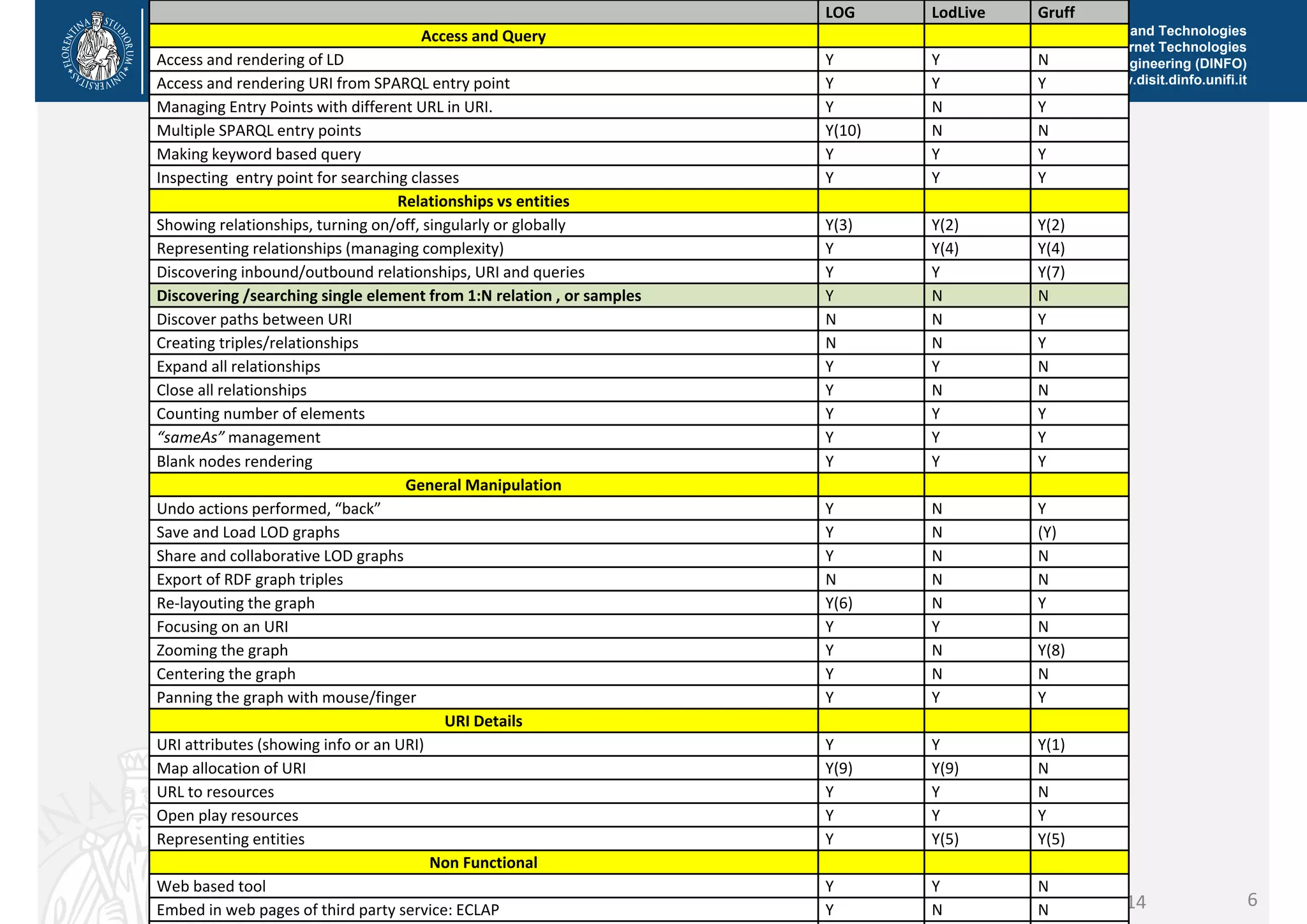
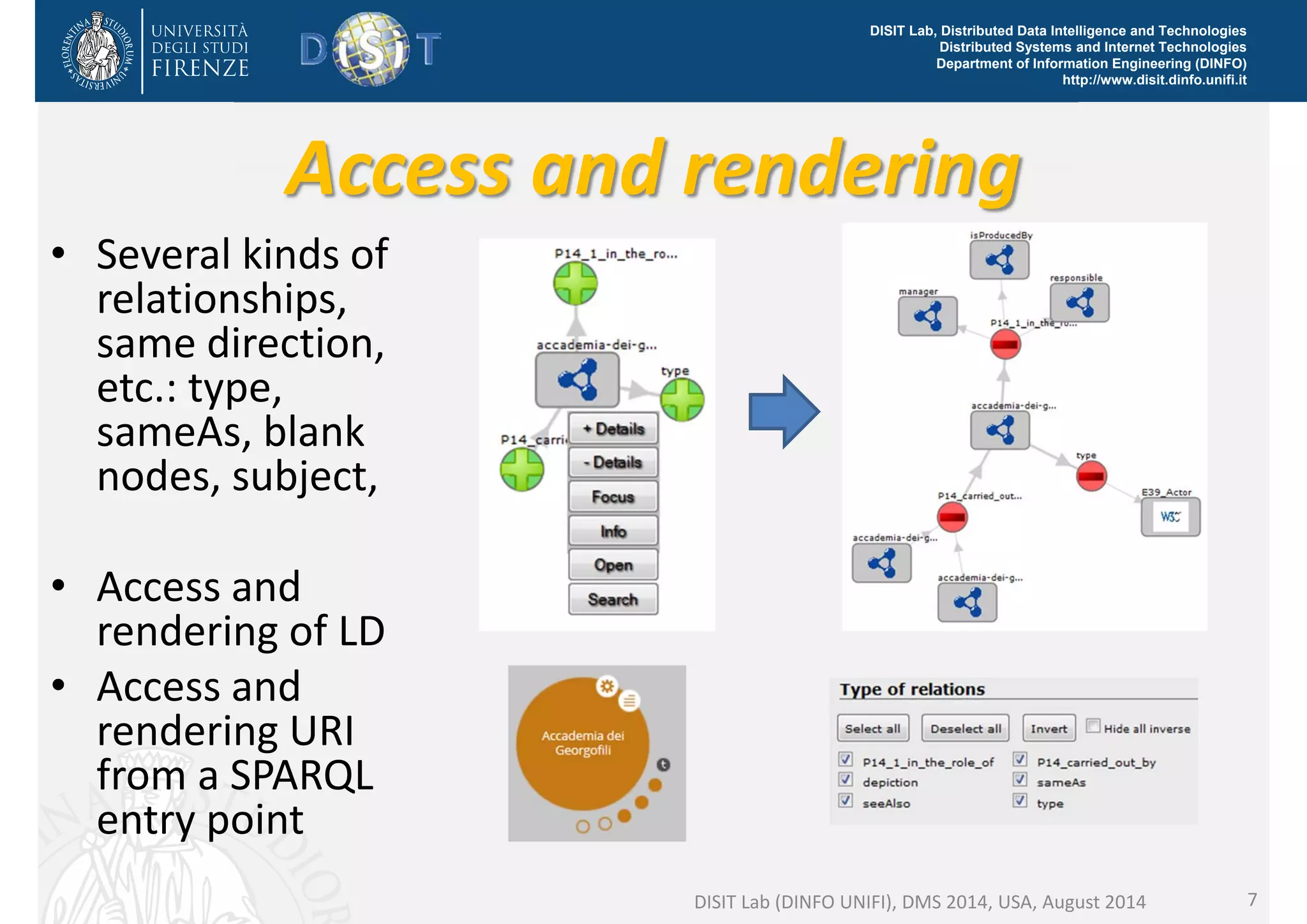
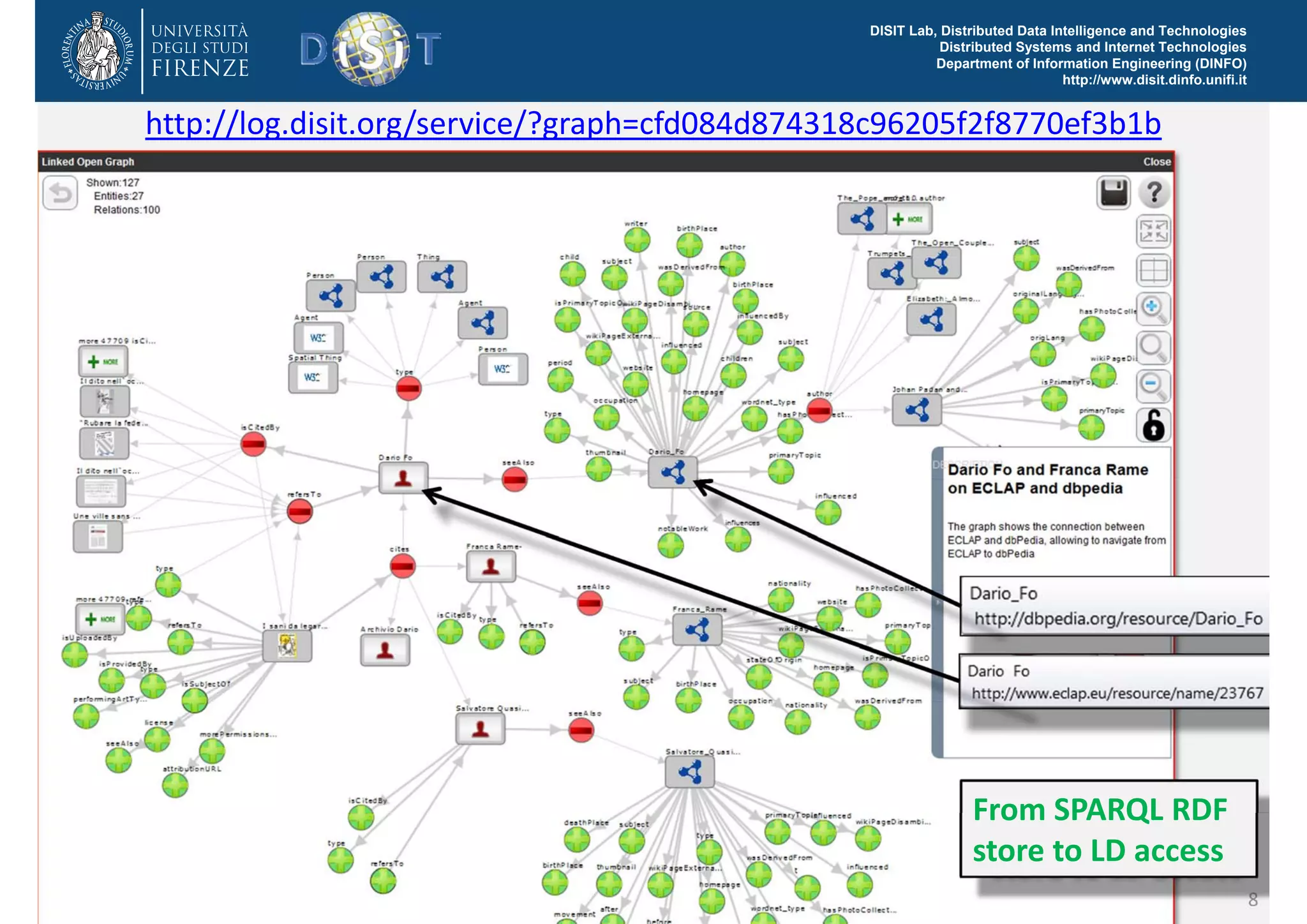
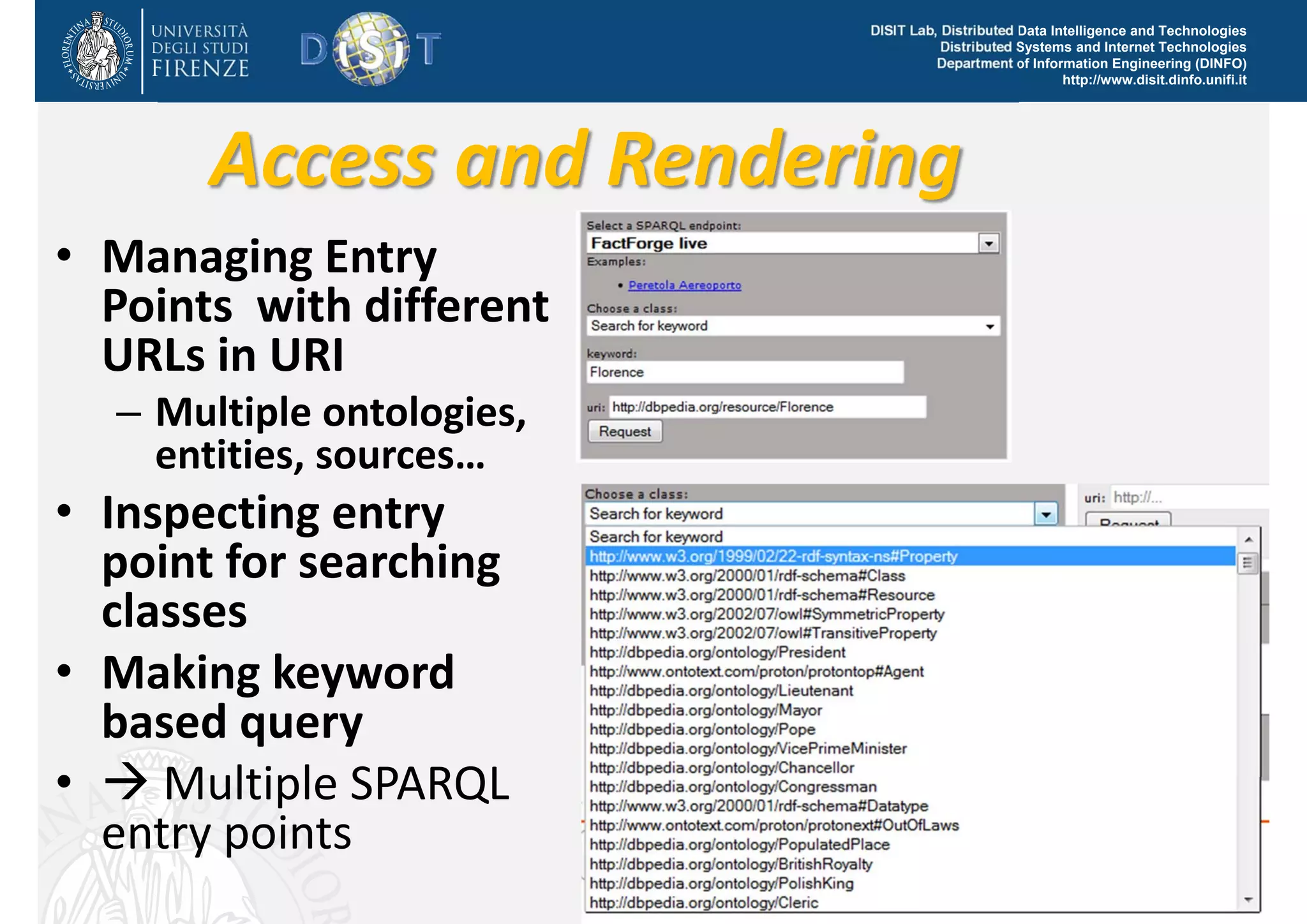
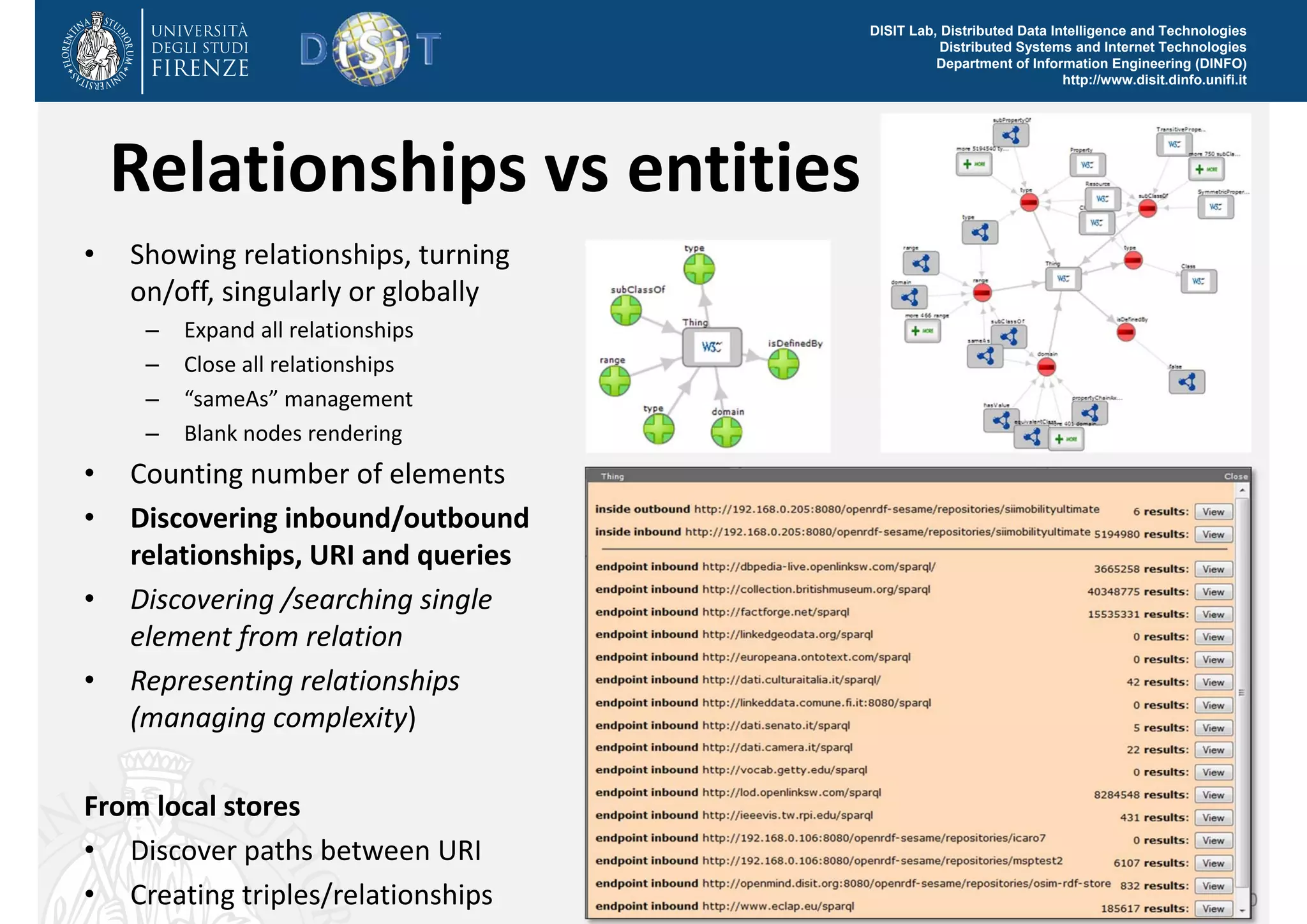
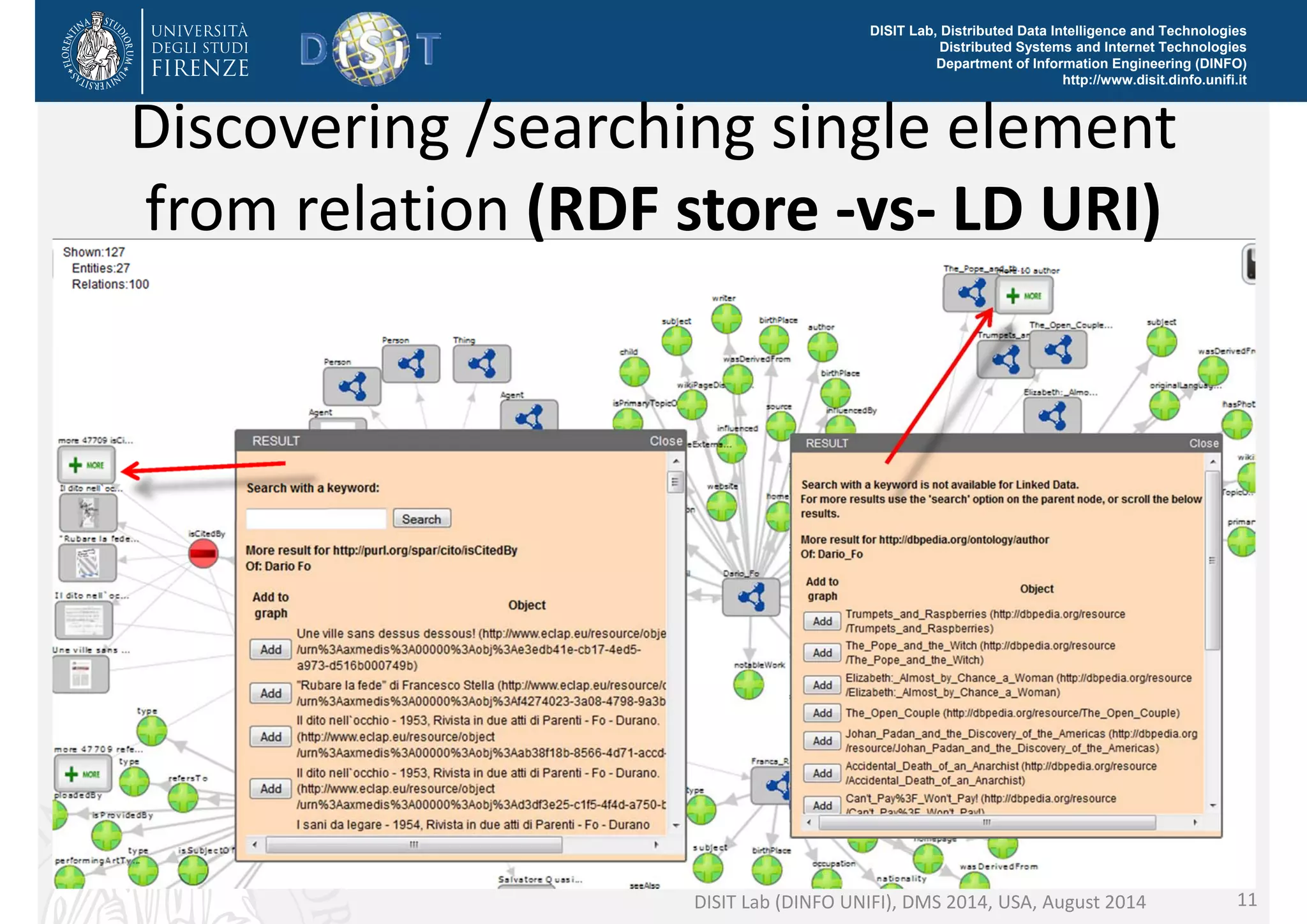
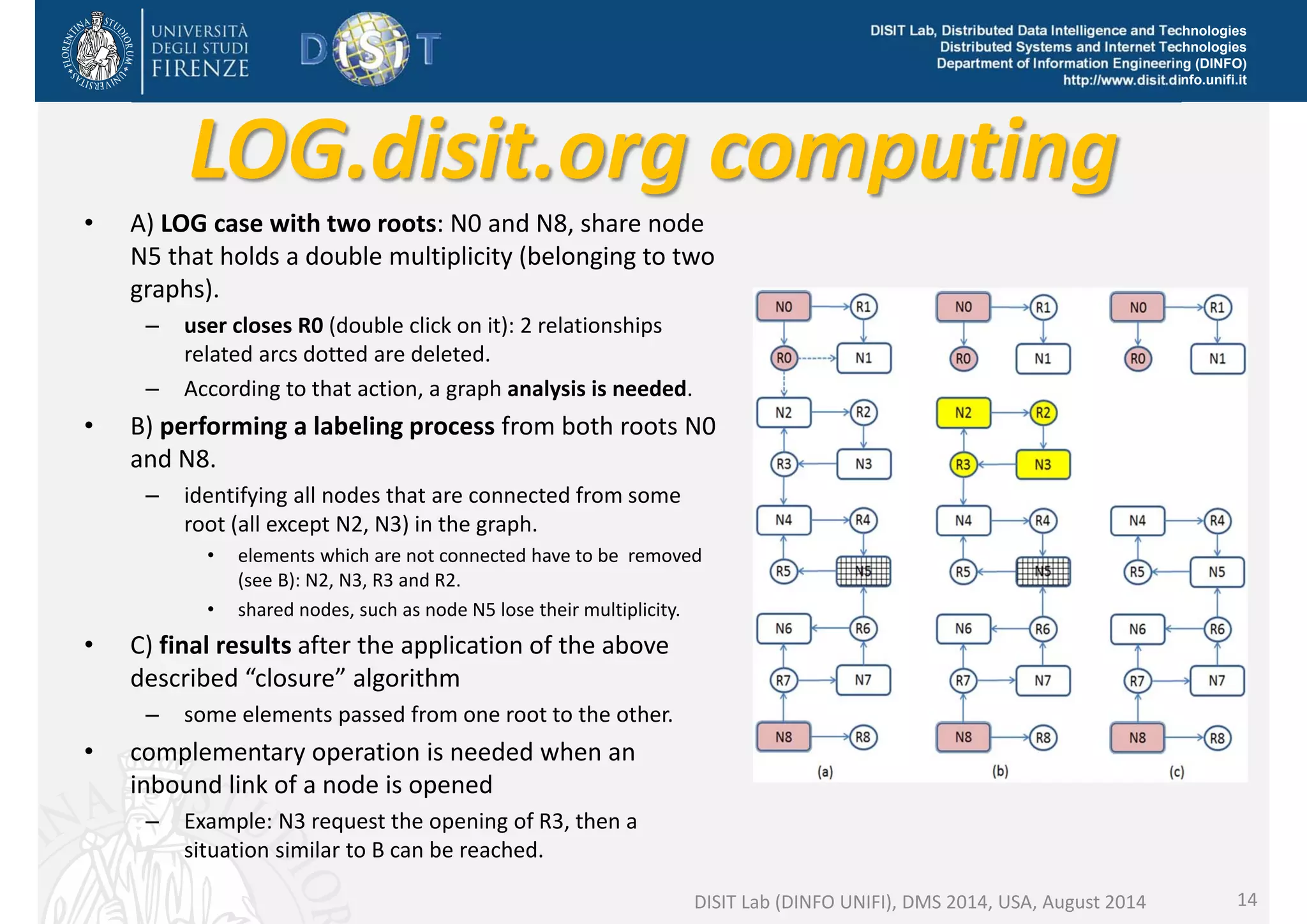
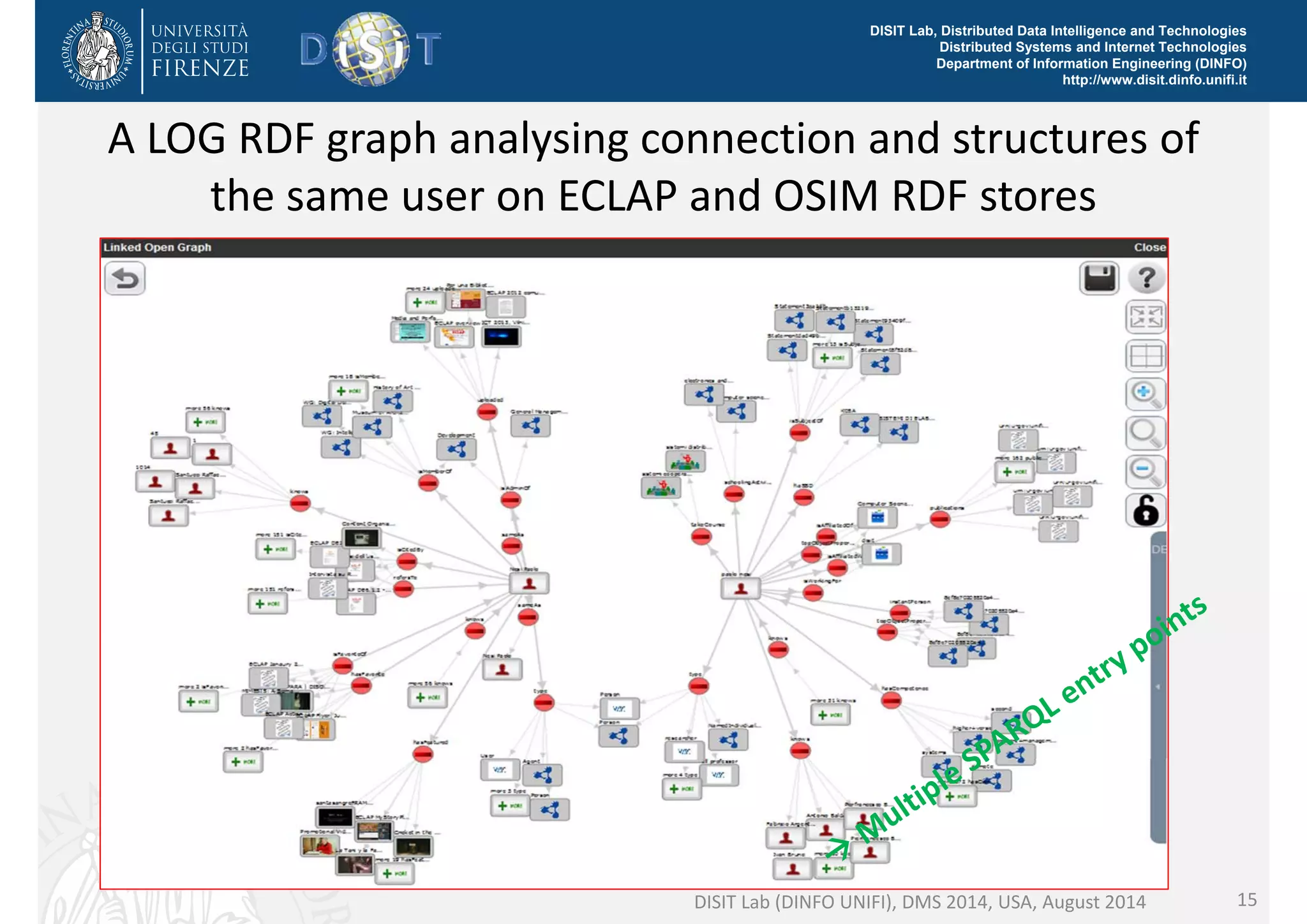
The document discusses the development of a distributed knowledge base (KB) leveraging Linked Open Data (LOD) and RDF technologies through SPARQL entry points. It outlines major features for accessing, querying, and manipulating linked data and emphasizes the integration and comparison of multiple data sources for enhanced understanding and exploration. The proposed model, log.disit, aims to support collaborative work, progressive browsing, and advanced querying capabilities in the domain of semantic web applications.