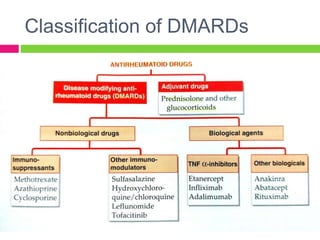
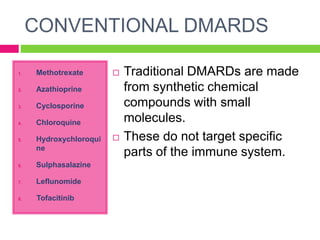
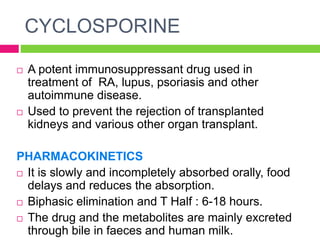
The document discusses rheumatoid arthritis (RA), its pathophysiology, and the roles of various medications including NSAIDs, DMARDs, and adjuvant drugs like corticosteroids. It categorizes DMARDs into conventional and biological agents, detailing individual drugs such as methotrexate, azathioprine, and others, along with their pharmacokinetics, dynamics, and side effects. Recent advances in RA treatment include the approval of new biological agents and JAK inhibitors.