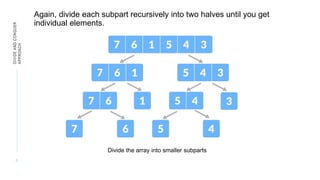
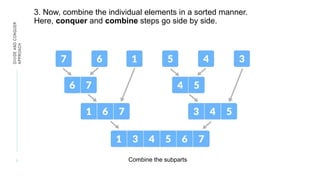
This document discusses the divide and conquer algorithmic approach. It begins with an acknowledgement and then outlines the contents to be covered, which includes an introduction to divide and conquer, the procedure involving dividing the problem into subproblems, conquering the subproblems, and combining the results. An example of applying divide and conquer to merge sort is provided. The algorithm is presented along with advantages like solving difficult problems and allowing for parallelism. Disadvantages involving recursion overhead are also discussed. The document concludes that divide and conquer is a recursive problem-solving approach that breaks problems into smaller subproblems to reduce time complexity.