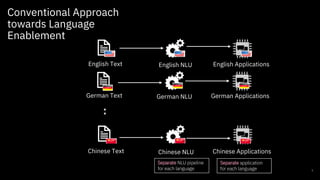
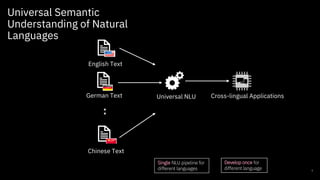
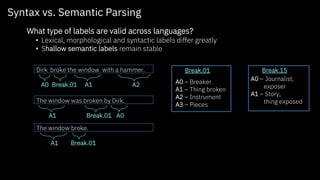
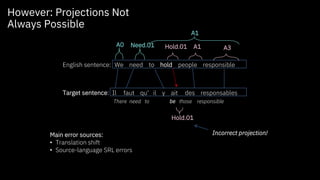
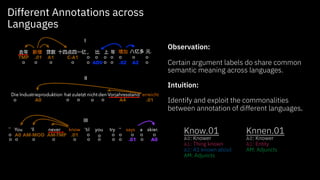
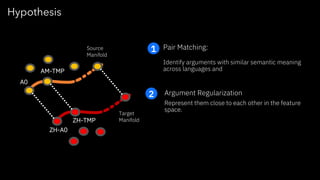
The document discusses challenges and approaches for developing universal semantic understanding across languages. It describes generating semantic role labeling resources for many languages using parallel corpora and crowdsourcing techniques. The goal is to develop cross-lingual models and representations that can understand the semantics of text in different languages.




![The Challenges
7
Models
– Low-frequency exceptions
– Built for one task at a time
Training Data
– High quality labeled data is
required but hard to obtain
Meaning Representation
– Different meaning
representation
• for different languages
• for the same languages
- Data: Auto-generation + crowd-
in-the-loop [ACL’15, EMNLP’16, EMNLP’17,
EMNLP’20 Findings]
- Training: Cross-Lingual transfer
[EMNLP’20 Findings]
Unified Meaning Representation
[ACL’15, ACL’16, ACL-DMR’19]
– Instance-based learning
[COLING’16]
– Deep learning + instance-based
learning [In Submission]
– Human-machine co-creation
[ACL’19, EMNLP’20]
Our Research
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-7-320.jpg)
![The Challenges
8
Models
– Low-frequency exceptions
– Built for one task at a time
Training Data
– High quality labeled data is
required but hard to obtain
Meaning Representation
– Different meaning
representation
• for different languages
• for the same languages
- Data: Auto-generation + crowd-
in-the-loop [ACL’15, EMNLP’16, EMNLP’17,
EMNLP’20 Findings]
- Training: Cross-Lingual transfer
[EMNLP’20 Findings]
Unified Meaning Representation
[ACL’15, ACL’16, ACL-DMR’19]
– Instance-based learning
[COLING’16]
– Deep learning + instance-based
learning [In Submission]
– Human-machine co-creation
[ACL’19, EMNLP’20]
Our Research
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-8-320.jpg)



![The Challenges
13
Models
– Low-frequency exceptions
– Built for one task at a time
Training Data
– High quality labeled data is
required but hard to obtain
Meaning Representation
– Different meaning
representation
• for different languages
• for the same languages
- Data: Auto-generation + crowd-
in-the-loop [ACL’15, EMNLP’16, EMNLP’17,
EMNLP’20 Findings]
- Training: Cross-Lingual transfer
[EMNLP’20 Findings]
Unified Meaning Representation
[ACL’15, ACL’16, ACL-DMR’19]
– Instance-based learning
[COLING’16]
– Deep learning + instance-based
learning [In Submission]
– Human-machine co-creation
[ACL’19, EMNLP’20]
Our Research
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-13-320.jpg)



![Filtered Projection &
Bootstrapping
Two-step process
– Filters to detect translation shift, block
projections (more precision at cost of
recall)
– Bootstrap learning to increase recall
– Generated 7 universal proposition banks
from 3 language groups
• Version 1.0: https://github.com/System-
T/UniversalPropositions/
• Version 2.0 coming soon
[ACL’15] Generating High Quality Proposition Banks for Multilingual Semantic Role Labeling.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-18-320.jpg)
![Multilingual Aliasing
• Problem: Target language frame lexicon
automatically generated from alignments
– False frames
– Redundant frames
• Expert curation of frame mappings
[COLING’16] Multilingual Aliasing for Auto-Generating Proposition
Banks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-19-320.jpg)
![Low-resource Languages
Apply approach to low-resource languages
Bengali, Malayalam, Tamil
– Fewer sources of parallel data
– Almost no NLP: No syntactic parsing,
lemmatization etc.
Crowdsourcing for data curation
[EMNLP’16] Towards Semi-Automatic Generation of Proposition Banks for Low-
Resource Languages](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-20-320.jpg)
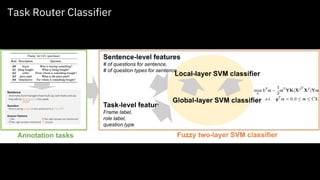
![Annotation
Tasks (all)
Task
Routerraw text
Corpus
predicted
annotations
Corpus
curated
annotations
Corpus
Easy tasks are curated by crowd
Difficult tasks are curated by experts
Crowd-in-the-Loop Curation
[EMNLP’17] CROWD-IN-THE-LOOP: A Hybrid Approach for Annotating Semantic Roles](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-21-320.jpg)
![9pp F1
improvement over SRL
results
Effectiveness of Crowd-in-
the-Loop
¯66.4pp
expert efforts
10pp F1
improvement over SRL
results
¯87.3pp
expert efforts
Latest: Filter à Select à Expert
[Findings of EMNLP’20] A Novel Workflow for Accurately and Efficiently Crowdsourcing Predicate Senses and Argument Labels](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-23-320.jpg)
![The Challenges
24
Models
– Low-frequency exceptions
– Built for one task at a time
Training Data
– High quality labeled data is
required but hard to obtain
Meaning Representation
– Different meaning
representation
• for different languages
• for the same languages
- Data: Auto-generation + crowd-
in-the-loop [ACL’15, EMNLP’16, EMNLP’17,
EMNLP’20 Findings]
- Training: Cross-Lingual transfer
[EMNLP’20 Findings]
Unified Meaning Representation
[ACL’15, ACL’16, ACL-DMR’19]
– Instance-based learning
[COLING’16]
– Deep learning + instance-based
learning [In Submission]
– Human-machine co-creation
[ACL’19, EMNLP’20]
Our Research
24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-24-320.jpg)
![WhatsApp was bought by Facebook
Facebook hat WhatsApp gekauft
Facebook a achété WhatsApp
buy.01
Facebook WhatsApp
Buyer Thing bought
Cross-lingual representation
Multilingual input text
Buy.01 A0A1
Buy.01A1A0
Buy.01A0 A1
Cross-lingual Meaning
Representation
Cross-lingual extraction
Task: Extract who bought what
[NAACL’18] SystemT: Declarative Text Understanding for Enterprise
[ACL’16] POLYGLOT: Multilingual Semantic Role Labeling with Unified Labels
[COLING’16] Multilingual Information Extraction with PolyglotIE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-25-320.jpg)



![The Challenges
32
Models
– Low-frequency exceptions
– Built for one task at a time
Training Data
– High quality labeled data is
required but hard to obtain
Meaning Representation
– Different meaning
representation
• for different languages
• for the same languages
- Data: Auto-generation + crowd-
in-the-loop [ACL’15, EMNLP’16, EMNLP’17,
EMNLP’20 Findings]
- Training: Cross-Lingual transfer
[EMNLP’20 Findings]
Unified Meaning Representation
[ACL’15, ACL’16, ACL-DMR’19]
– Instance-based learning
[COLING’16]
– Deep learning + instance-based
learning [In Submission]
– Human-machine co-creation
[ACL’19, EMNLP’20]
Our Research
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-32-320.jpg)



![Instance-based Learning kNN: k-Nearest Neighbors classification
Find the k most similar instances in training data
Derive class label from nearest neighbors
A0
A1
A1
A2
A1
A1
A1
A1
A1
A0
A0
A1
A0
A2
A2
A2
A2
A1
A2
?
1 2 3 ndistance
Creditors were told to hold off.
SBJ
ORPD
VC
IM PRT
“creditor” passive subject of TELL.01
noun passive subject of TELL.01
COMPOSITE FEATURE DISTANCE
1
2
.
.
.
.
.
.
any passive subject of any agentive verb n
?
Main idea: Back off to composite feature seen at least k times
[COLING 2016] K-SRL: Instance-based Learning for Semantic Role Labeling](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-37-320.jpg)
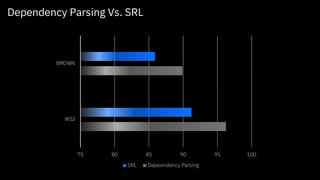
![Results
In-domain Out-of-domain
• Significantly outperform previous approaches
– Especially on out-of-domain data
• Small neighborhoods suffice (k=3)
• Fast runtime 1.4pp F1
In-Domain
5.1pp F1
Out-of-Domain
Latest results (improvement over SoAT.
with DL + IL, in submission)
[In Submission] Deep learning + Instance-based Learning
[COLING 2016] K-SRL: Instance-based Learning for Semantic Role Labeling](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-38-320.jpg)
![The Challenges
39
Models
– Low-frequency exceptions
– Built for one task at a time
Training Data
– High quality labeled data is
required but hard to obtain
Meaning Representation
– Different meaning
representation
• for different languages
• for the same languages
- Data: Auto-generation + crowd-
in-the-loop [ACL’15, EMNLP’16, EMNLP’17,
EMNLP’20 Findings]
- Training: Cross-Lingual transfer
[EMNLP’20 Findings]
Unified Meaning Representation
[ACL’15, ACL’16, ACL-DMR’19]
– Instance-based learning
[COLING’16]
– Deep learning + instance-based
learning [In Submission]
– Human-machine co-creation
[ACL’19, EMNLP’20]
Our Research
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-39-320.jpg)
![WhatsApp was bought by Facebook
Facebook hat WhatsApp gekauft
Facebook a achété WhatsApp
buy.01
Facebook WhatsApp
Buyer Thing bought
Cross-lingual representation
Multilingual input text
Buy.01 A0A1
Buy.01A1A0
Buy.01A0 A1
Crosslingual Information
Extraction
Sentence Verb Buyer Thing bought
1 buy.01 Facebook WhatsApp
2 buy.01 Facebook WhatsApp
3 buy.01 Facebook WhatsApp
Crosslingual extraction
Task: Extract who bought what
[NAACL’18] SystemT: Declarative Text Understanding for Enterprise
[ACL’16] POLYGLOT: Multilingual Semantic Role Labeling with Unified Labels
[COLING’16] Multilingual Information Extraction with PolyglotIE https://vimeo.com/180382223](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-40-320.jpg)
![Transparent Linguistic Models for Contract Understanding
41
[NAACL-NLLP’19] Transparent Linguistic Models for Contract Understanding and Comparison https://www.ibm.com/cloud/compare-and-comply](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-41-320.jpg)
![Transparent Model Design
Purchaser will
purchase the Assets
by a cash payment.
Element
Obligation for
Purchaser
[NAACL-NLLP’19] Transparent Linguistic Models for Contract Understanding and Comparison https://www.ibm.com/cloud/compare-and-comply](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-42-320.jpg)
![Transparent Model Design
Purchaser will
purchase the Assets
by a cash payment.
Element
[Purchaser]A0
[will]TENSE-FUTURE
purchase
[the Assets]A1
[by a cash payment]ARGM-MNR
Core NLP Understanding
Core NLP Primitives &
Operators
Provided by SystemT
[ACL '10, NAACL ‘18]
Semantic NLP Primitives
[NAACL-NLLP’19] Transparent Linguistic Models for Contract Understanding and Comparison https://www.ibm.com/cloud/compare-and-comply](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-43-320.jpg)
![Transparent Model Design
Purchaser will
purchase the Assets
by a cash payment.
Element Legal Domain LLEs
[Purchaser]ARG0
[will]TENSE-FUTURE
purchase
[the Assets]ARG1
[by a cash payment]ARGM-MNR
LLE1:
PREDICATE ∈ DICT Business-Transaction
∧ TENSE = Future
∧ POLARITY = Positive
→ NATURE = Obligation ∧ PARTY =
ARG0
LLE2:
…........
Domain Specific Concepts
Business transact. verbs
in future tense
with positive polarity
Core NLP Primitives &
Operators
Semantic NLP Primitives
[NAACL-NLLP’19] Transparent Linguistic Models for Contract Understanding and Comparison https://www.ibm.com/cloud/compare-and-comply](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-44-320.jpg)
![Transparent Model Design
Purchaser will
purchase the Assets
by a cash payment.
Element Model Output
[Purchaser]ARG0
[will]TENSE-FUTURE
purchase
[the Assets]ARG1
[by a cash payment]ARGM-MNR
Obligation for
Purchaser
Nature/Party:
Domain Specific Concepts
Core NLP Primitives &
Operators
LLE1:
PREDICATE ∈ DICT Business-Transaction
∧ TENSE = Future
∧ POLARITY = Positive
→ NATURE = Obligation ∧ PARTY =
ARG0
LLE2:
…........
Legal Domain LLEsSemantic NLP Primitives
[NAACL-NLLP’19] Transparent Linguistic Models for Contract Understanding and Comparison https://www.ibm.com/cloud/compare-and-comply](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-45-320.jpg)
![Human & Machine Co-Creation
Labeled
Data
Evaluati
on
Results
Productio
n
Deep
Learning
Learned Rules
(Explainable)
Modify Rules
Machine performs heavy lifting to abstract out patterns Humans verify/
transparent model
Evaluation & Deployment
Raises the abstraction level for domain experts to interact with
[EMNLP’20] Learning Explainable Linguistic Expressions with Neural Inductive Logic Programming for Sentence Classification](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-46-320.jpg)
![Label being assigned
Various ways of
selecting/ranking
ranking rules
Center panel lists all rules
HEIDL Demo
Rule-specific performance
metrics
[ACL’19] HEIDL: Learning Linguistic Expressions with Deep Learning and Human-in-the-Loop](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-47-320.jpg)
![HEIDL Demo
Examples available at the
click of a button
[ACL’19] HEIDL: Learning Linguistic Expressions with Deep Learning and Human-in-the-Loop](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-48-320.jpg)
![Center panel lists all rules
HEIDL Demo
Playground mode allows
adding and dropping of
predicates from a rule
[ACL’19] HEIDL: Learning Linguistic Expressions with Deep Learning and Human-in-the-Loop](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-49-320.jpg)
![User Study: Human+Machine
Co-Created Model
Performance
User study
– 4 NLP Engineers with 1-2 year experience
– 2 NLP experts with 10+ years experience
Key Takeaways
– Explanation of learned rrules: Visualization tool is very
effective
– Reduction in human labor: Co-created model created within
1.5 person-hrs outperforms black-box sentence classifier
– Lower requirement on human expertise: Co-created model is
at par with the model created by Super-Experts
Ua Ub Uc Ud
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
F-measure
RuleNN+Human
BiLSTM
[ACL’19] HEIDL: Learning Linguistic Expressions with Deep Learning and Human-in-the-Loop](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsuniversallanguageunderstanding-2-201202181619/85/Towards-Universal-Language-Understanding-2020-version-50-320.jpg)


