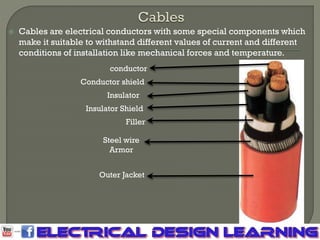
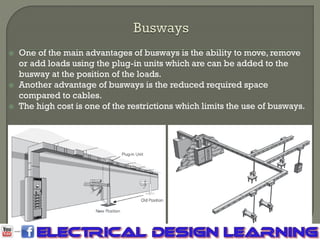
The document outlines the current carrying components of distribution systems, including cables, wires, busways, and overhead transmission lines, detailing their characteristics and installation conditions. Cables are used in both medium voltage (MV) and low voltage (LV) parts, while wires are simpler and deliver current to final loads. Busways are advantageous for long distances and future load additions but are limited by their high cost, while overhead lines are used in rural areas where underground installation is challenging.