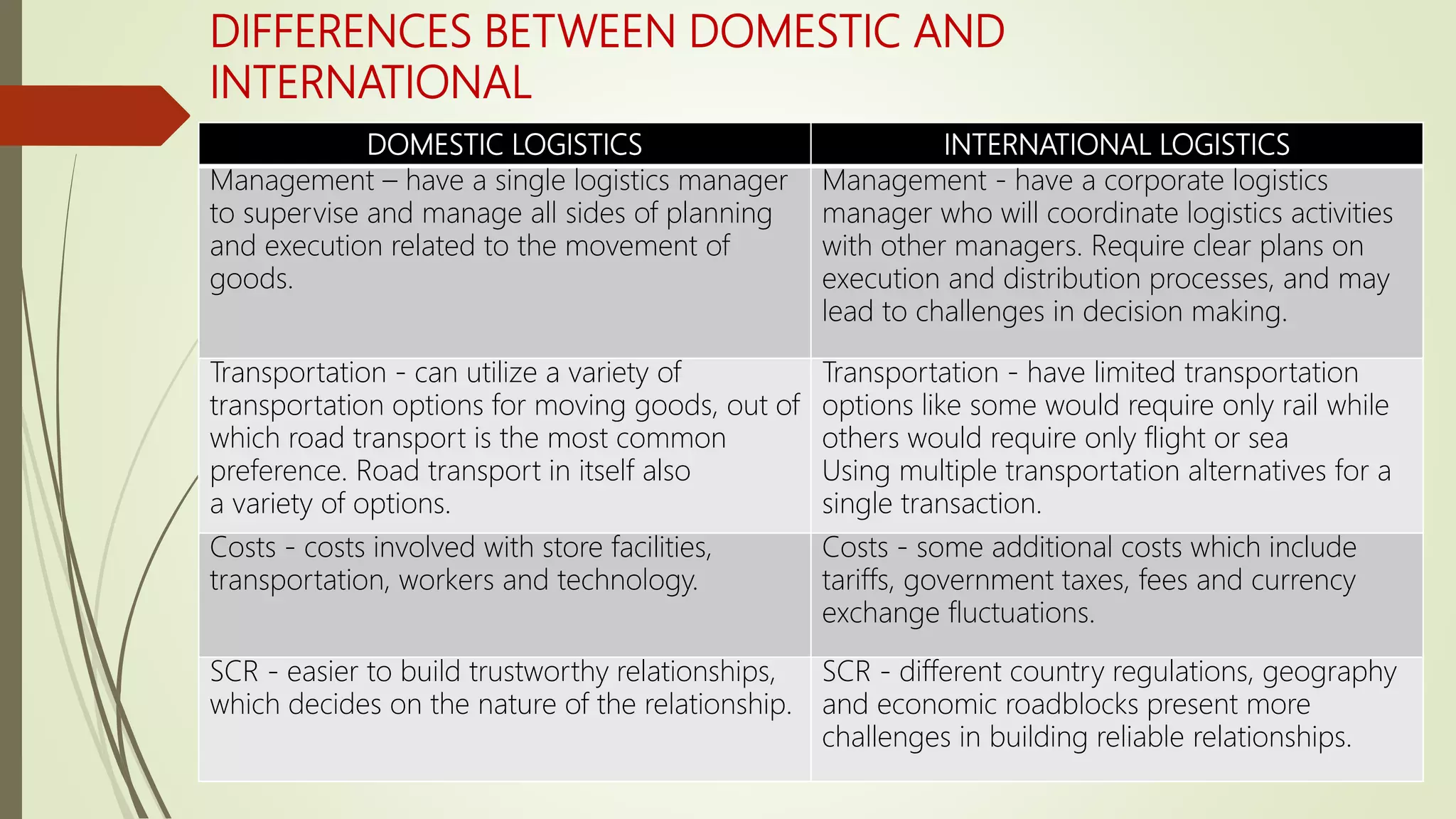
The document discusses domestic and international logistics and supply chain management. It defines logistics, domestic logistics, and international logistics. Domestic logistics involves distribution within a country while international logistics involves distribution across international borders. Managing logistics internationally is more complex due to factors like multiple transportation options, additional costs like tariffs, and challenges building relationships across countries. The document also discusses transportation types, warehouse types, facility location decisions, and evaluating locations using models like weighted factor and break even.