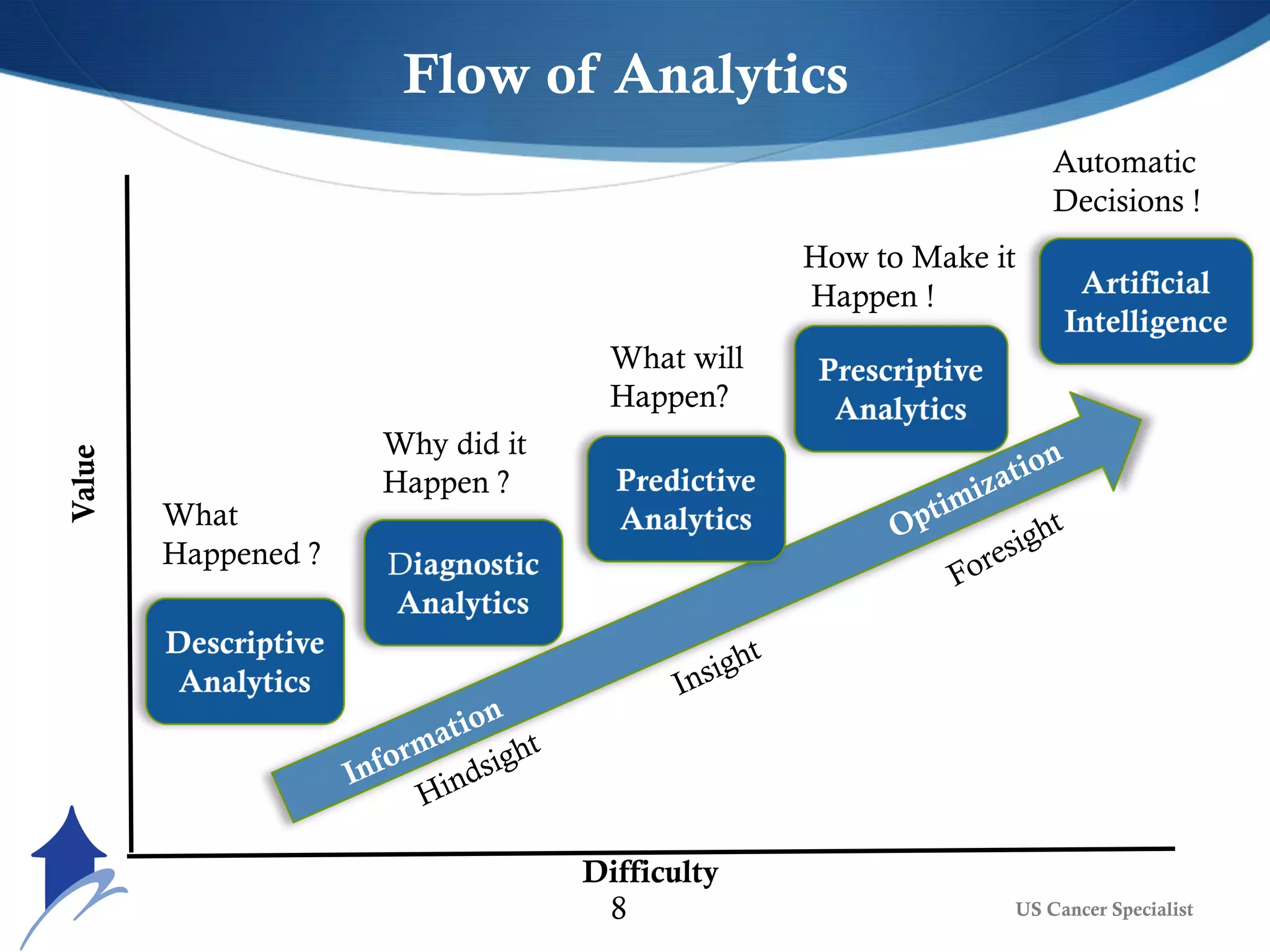
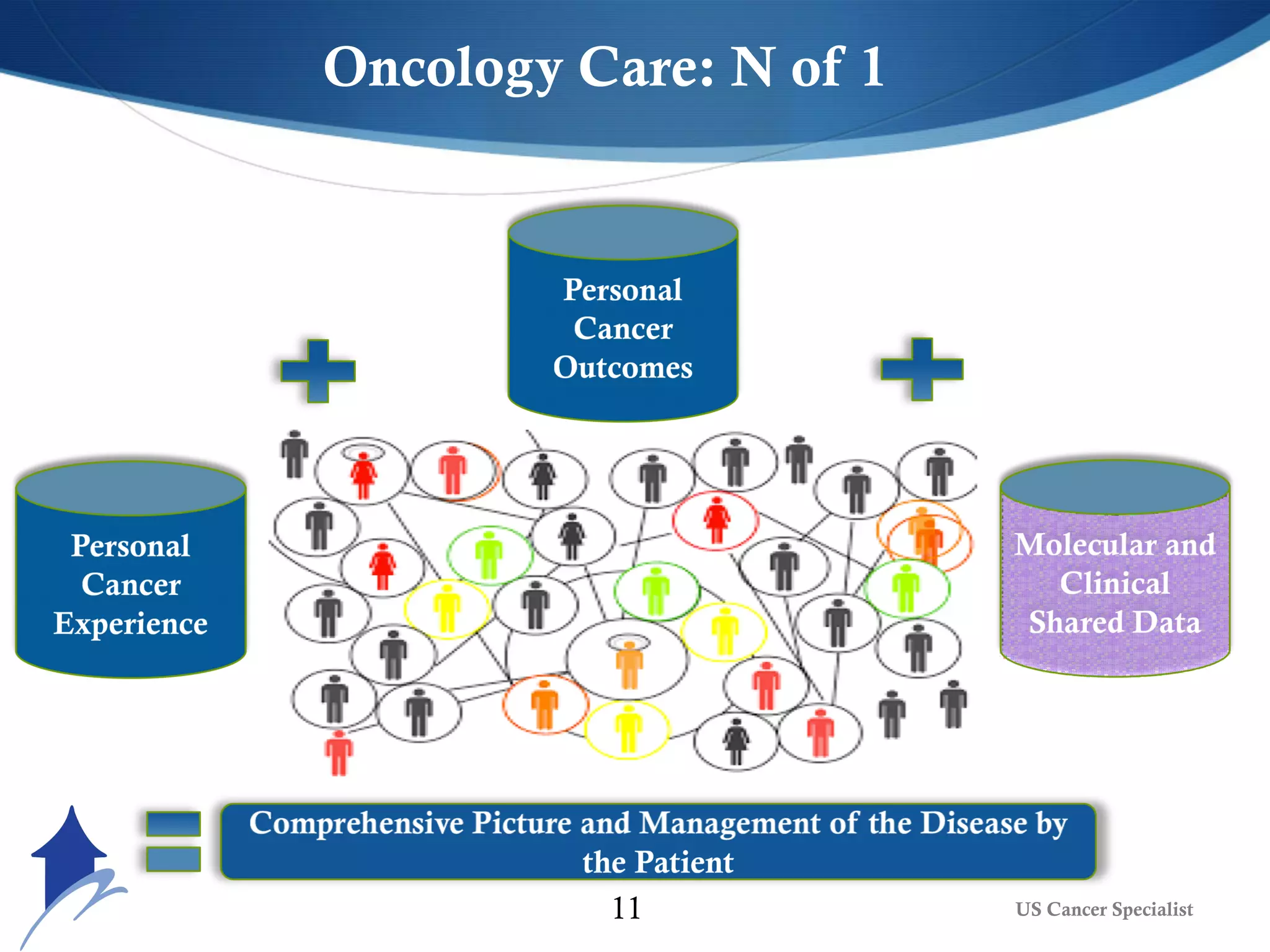
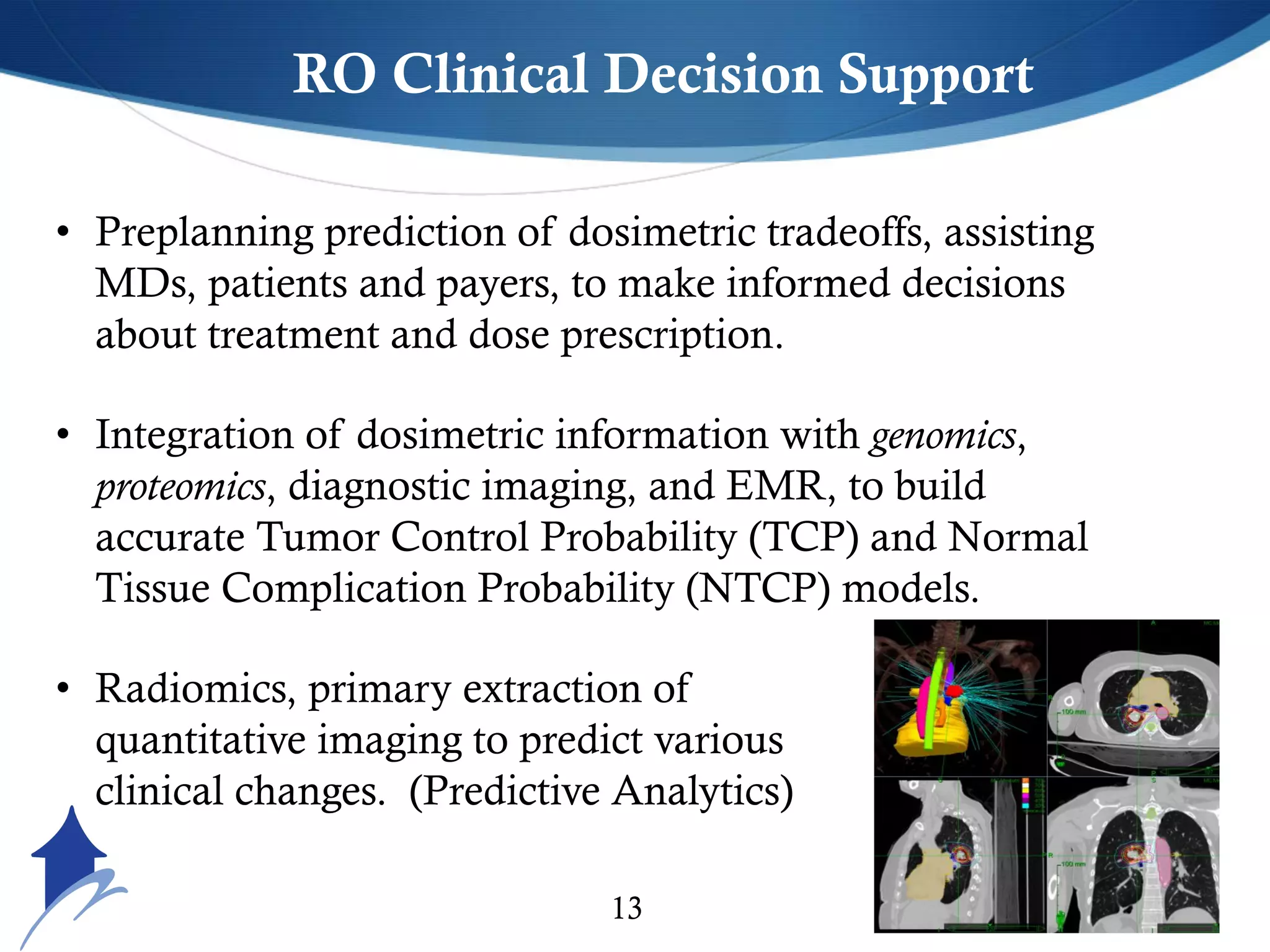
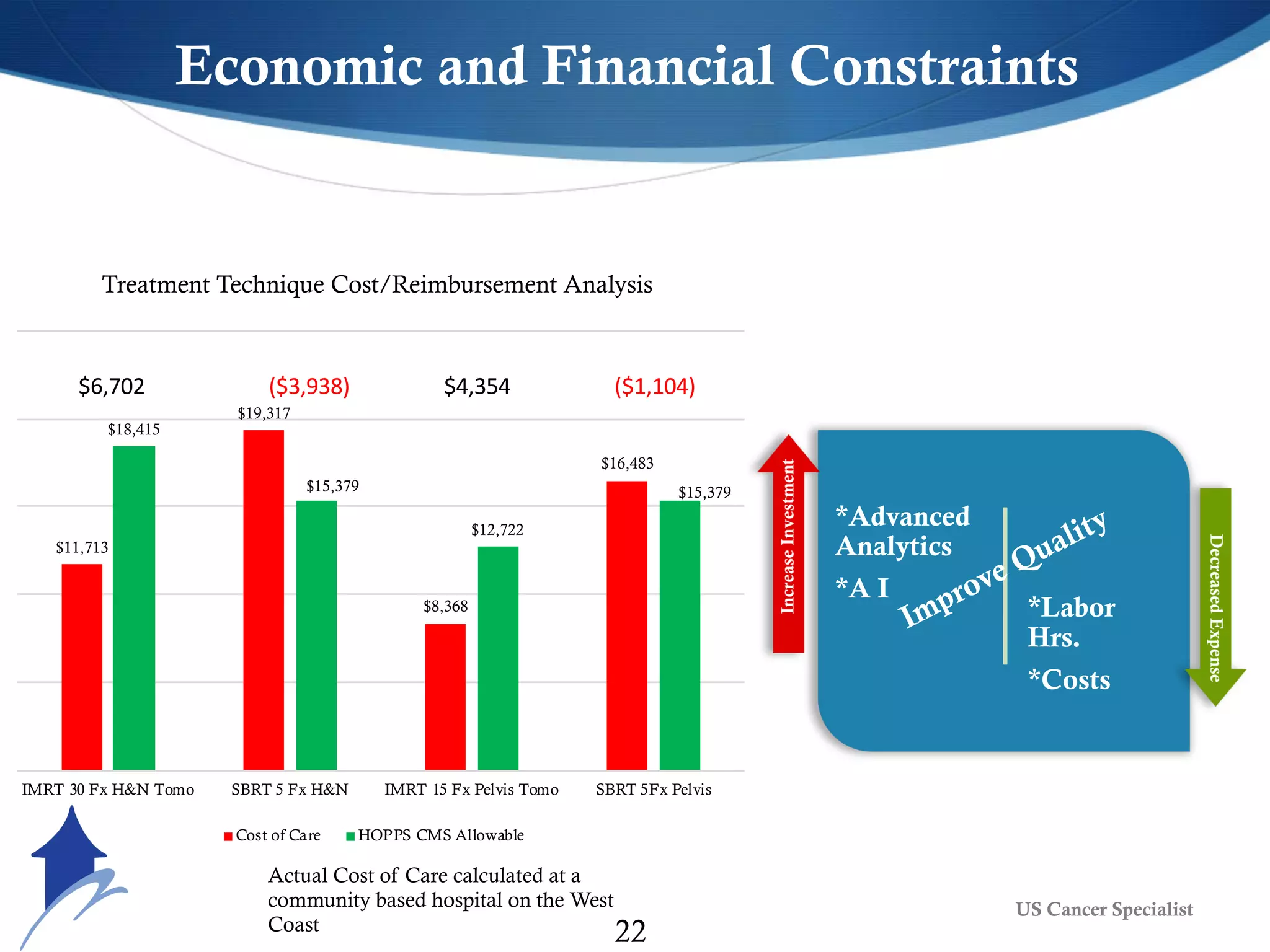
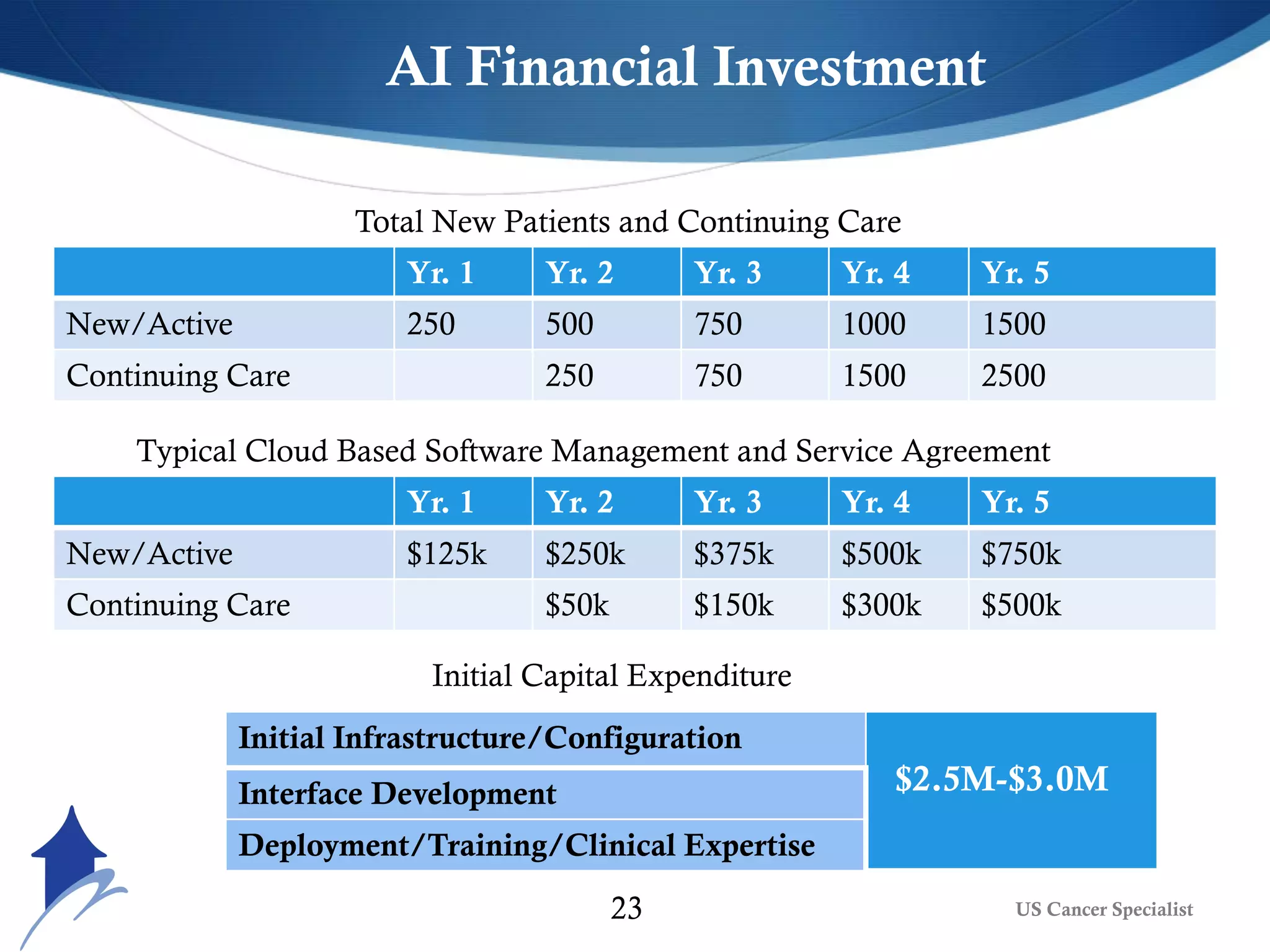
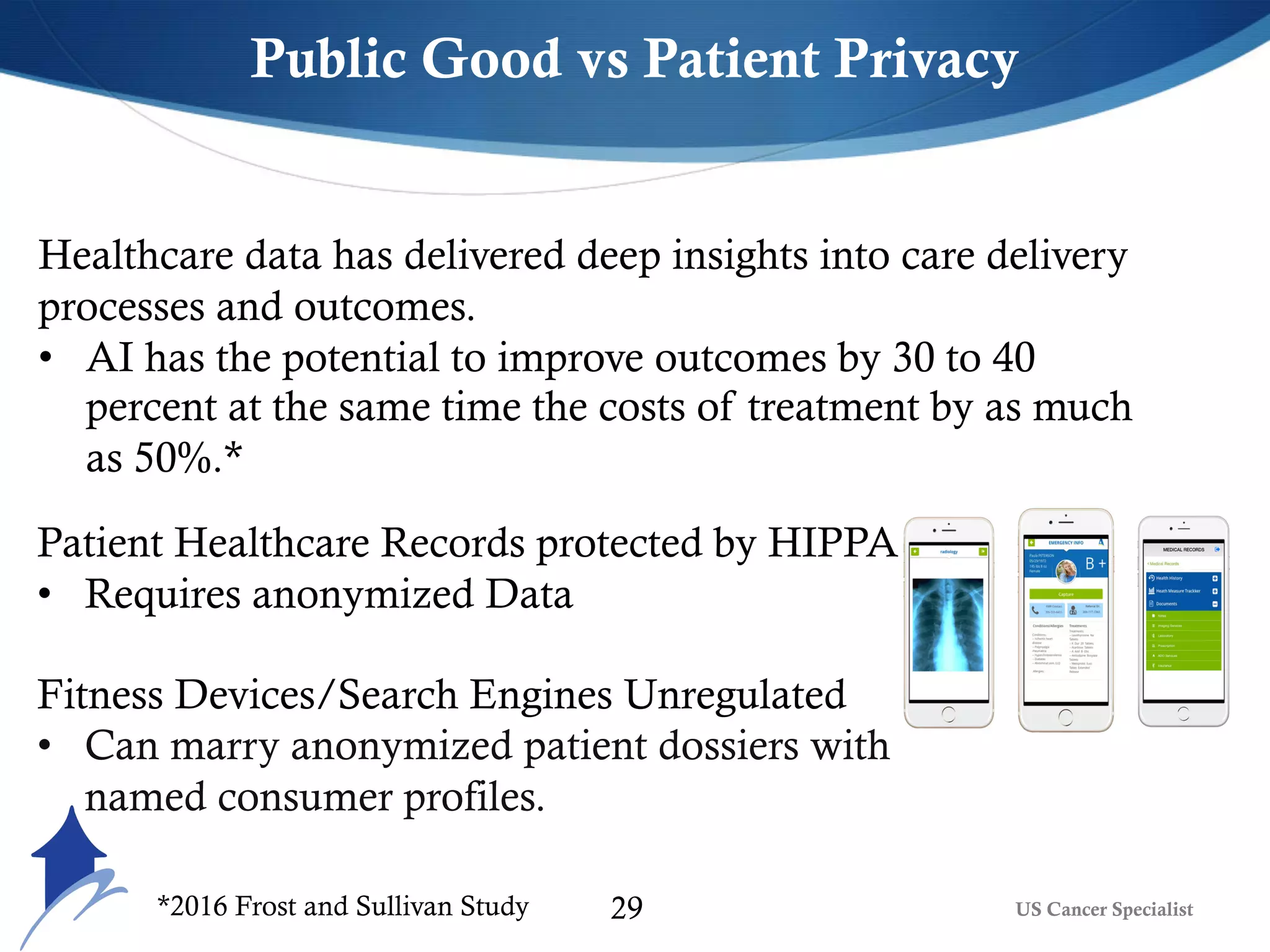
The document discusses the transformative role of AI and advanced analytics in oncology care, emphasizing their potential to enhance clinical decision-making and patient outcomes while addressing financial and ethical implications. Key topics include the integration of big data, personalized treatment approaches, and the shift toward value-based care. It also highlights challenges such as technology resistance, ethical considerations, and the importance of data management in optimizing healthcare delivery.