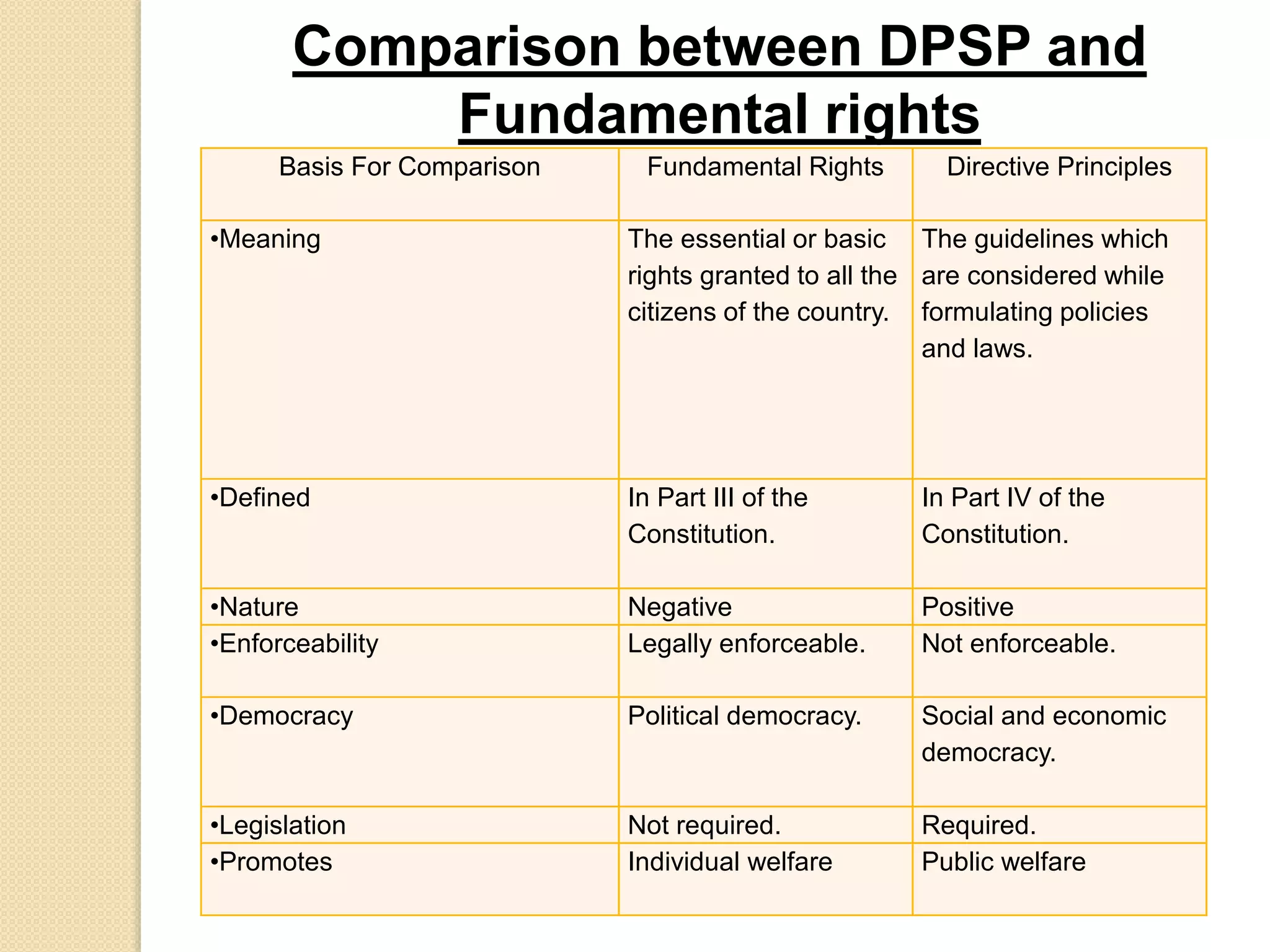
The document discusses the Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP) in the Indian Constitution. The DPSP were included to help establish a welfare state and provide guidelines for government policies on social, economic and political matters. Key points include that the DPSP are non-justiciable ideals that cover articles 36-51 and guide the government towards justice, liberty and equality. They establish India as a welfare state focused on public welfare rather than individual rights.