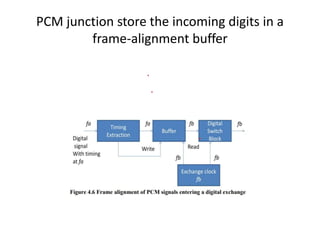
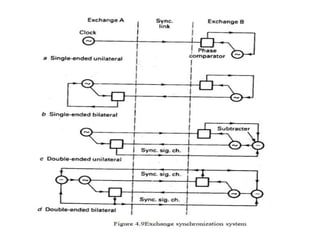
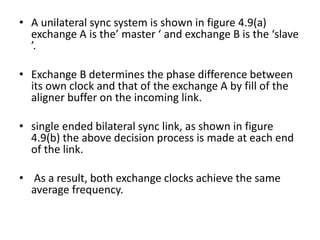
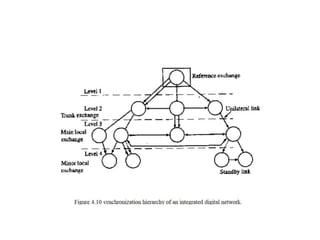
Frame alignment ensures that PCM frames from different sources entering a digital exchange are synchronized. A frame alignment buffer stores incoming digits and reads them out at the exchange clock rate to align frames. Synchronization networks use reference clocks to control exchange clocks and ensure frames are aligned across the entire network. Unilateral and bilateral synchronization links can control clock frequencies between two exchanges, while double-ended systems can distinguish between frequency drift and propagation delays better than single-ended systems. An integrated digital network uses a synchronizing auxiliary network to link all exchanges.