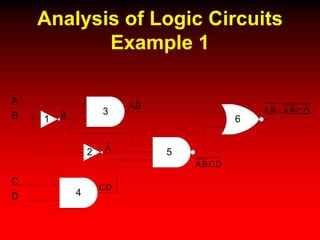
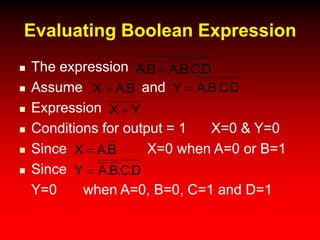
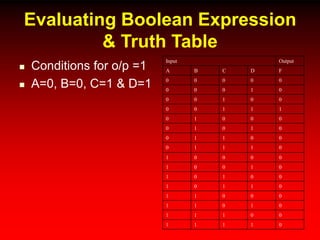
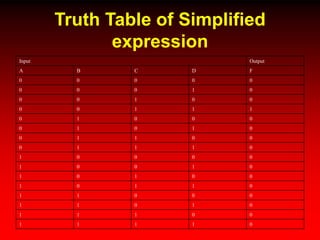
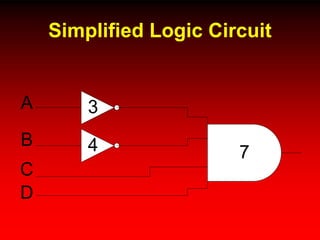
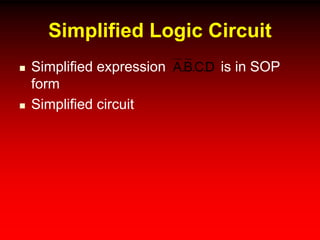
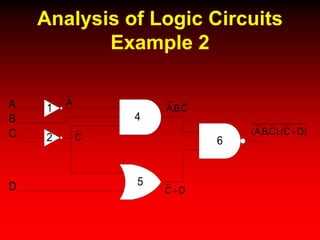
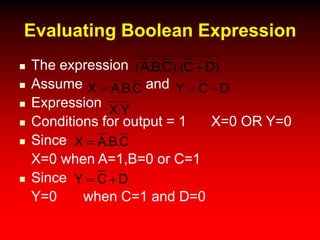
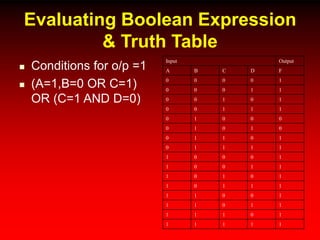
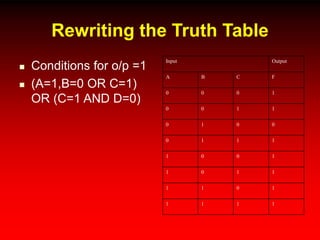
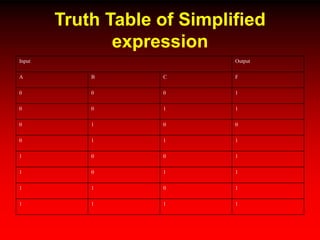
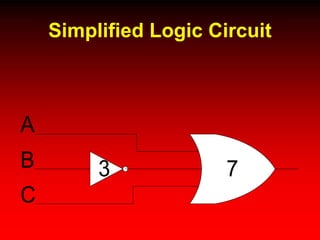
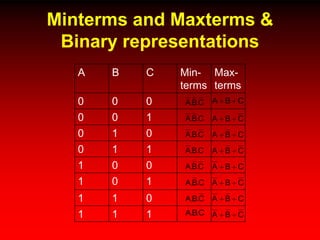
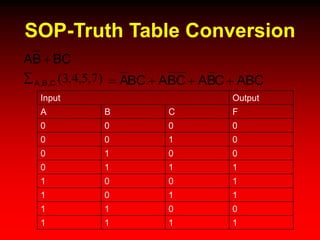
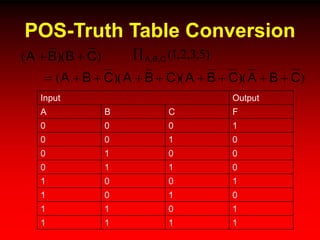
This document discusses digital logic design and analysis of logic circuits. It provides two examples of evaluating Boolean expressions, constructing truth tables, simplifying expressions, and deriving simplified logic circuits. Standard forms such as SOP and POS are discussed along with their relationship to minterms, maxterms, and truth tables. Conversion between different representations is also covered.