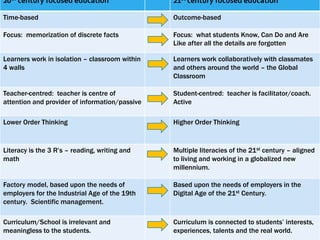
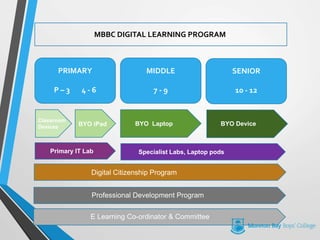
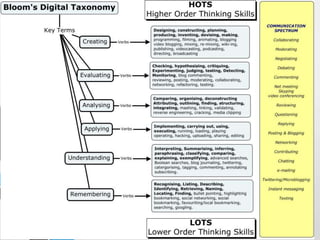
The document summarizes MBBC's digital learning program which introduces BYOD (bring your own device) for students. It will be implemented in stages between 2014-2018, starting with Year 4 students. The program aims to prepare students for 21st century skills by teaching with and through technology across the curriculum. Professional development for teachers and a digital citizenship program will support the initiative.