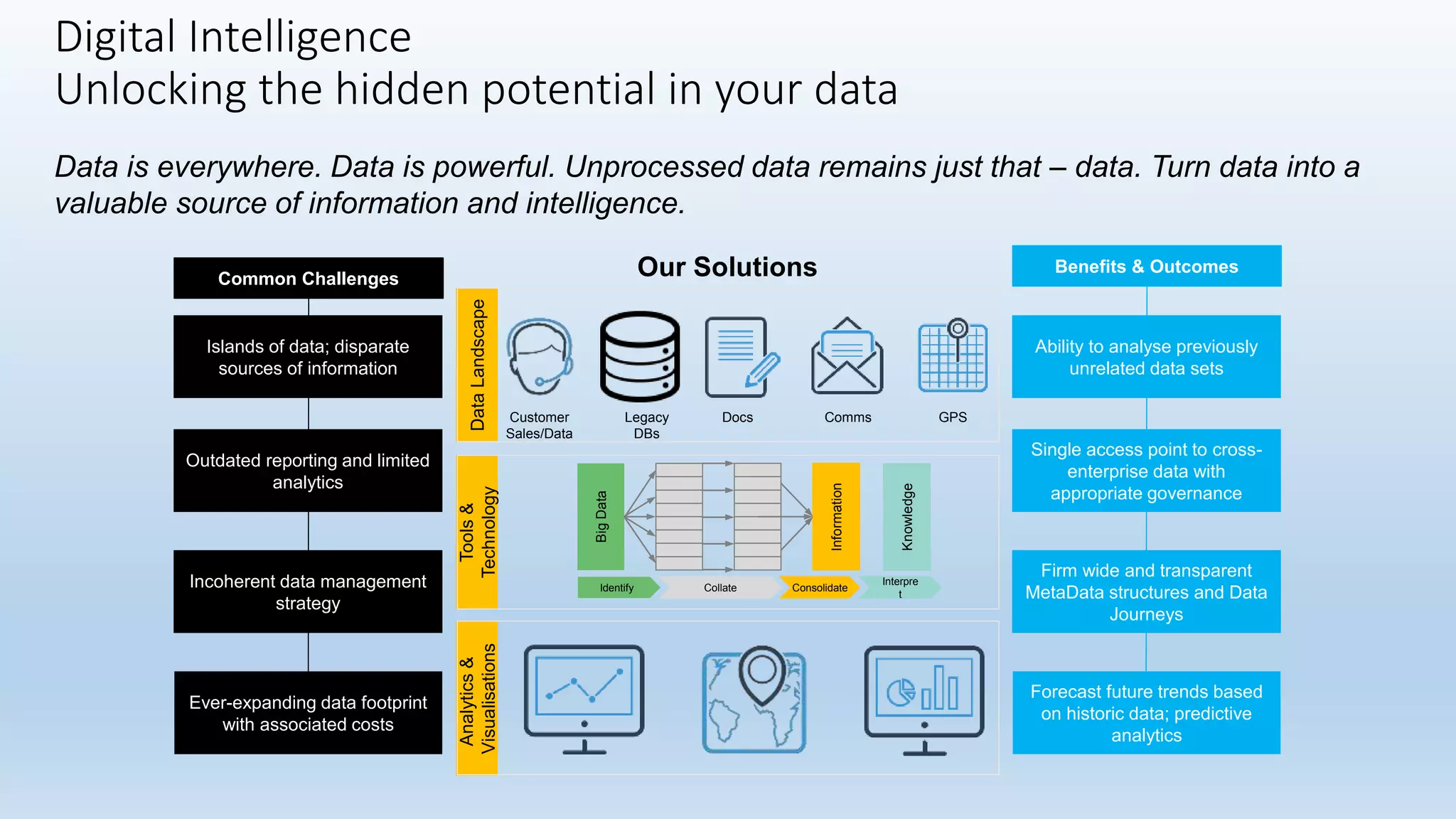
The document outlines the challenges of managing disparate data sources and emphasizes the importance of quality data for effective analysis and decision-making. It discusses key attributes of good data, necessary processes, and project considerations to enhance data access and governance across organizations. The document promotes leveraging predictive analytics and visualization tools to unlock the potential of data, highlighting the importance of a structured approach to data management.








![• Reduce risk of data errors
• Reduce systems workload through not moving data around
• Increase speed of access to data on a real-time basis
• Significantly reduce development and support time
• Increase governance and reduce risk through the use of policies[5]
• Reduce data storage required
Virtualization benefits](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalintelligencesatishbhatia-200125133721/85/Digital-intelligence-satish-bhatia-10-320.jpg)
