A campaign launched by the Indian government
Launched by: Prime minister Narendra Modi
Date of launch: 1 July 2015
Its main objective: It was launched with the vision to transform India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy.
With following motives:
Enhancing online infrastructure.
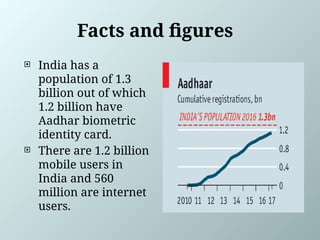
Increasing the internet connectivity.
Making country digitally empowered in the field of technology.
The motto of this mission is “Power to empower”.