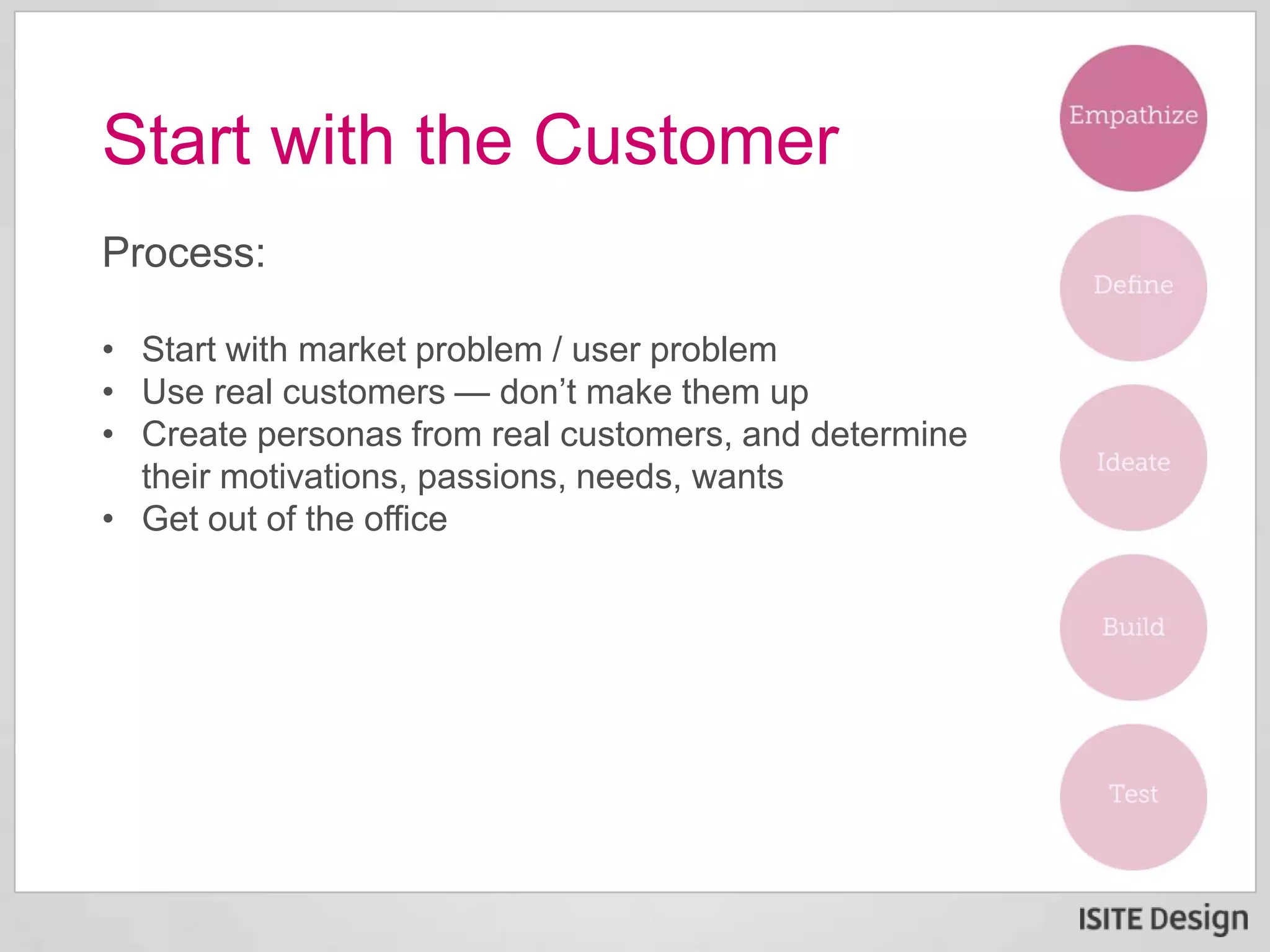
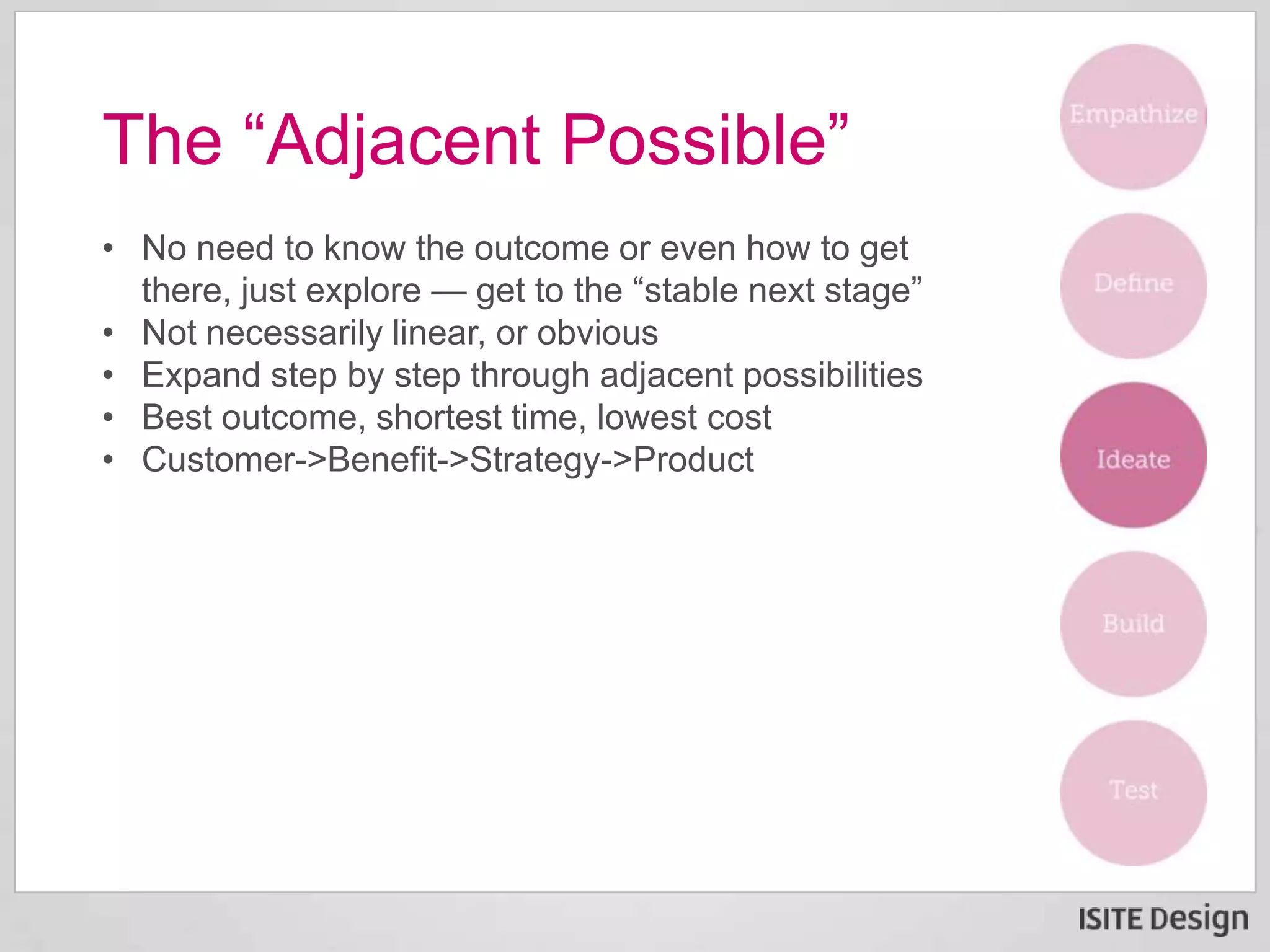
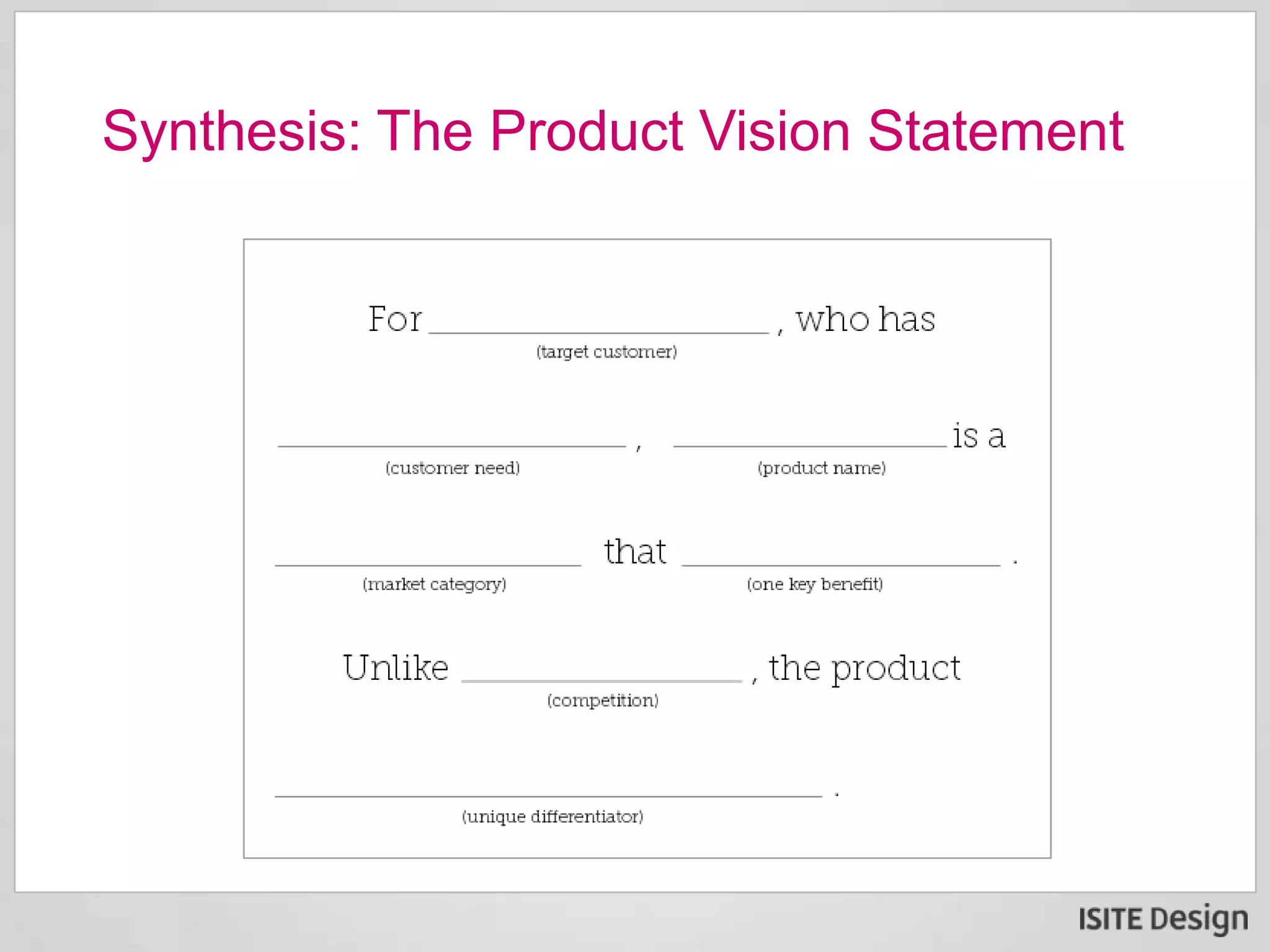
The document discusses a strategic briefing on digital disruption featuring Neel Banerjee and Gene Ehrbar, focusing on its definition, significance in customer-focused innovation, and methods for fostering collaborative teams. Key themes include the emergence of digital disruption due to affordable tools, rapid market engagement by startups, and the necessity for enterprises to adopt innovative practices to remain competitive. The briefing also presents actionable steps organizations can take to harness digital disruption effectively.