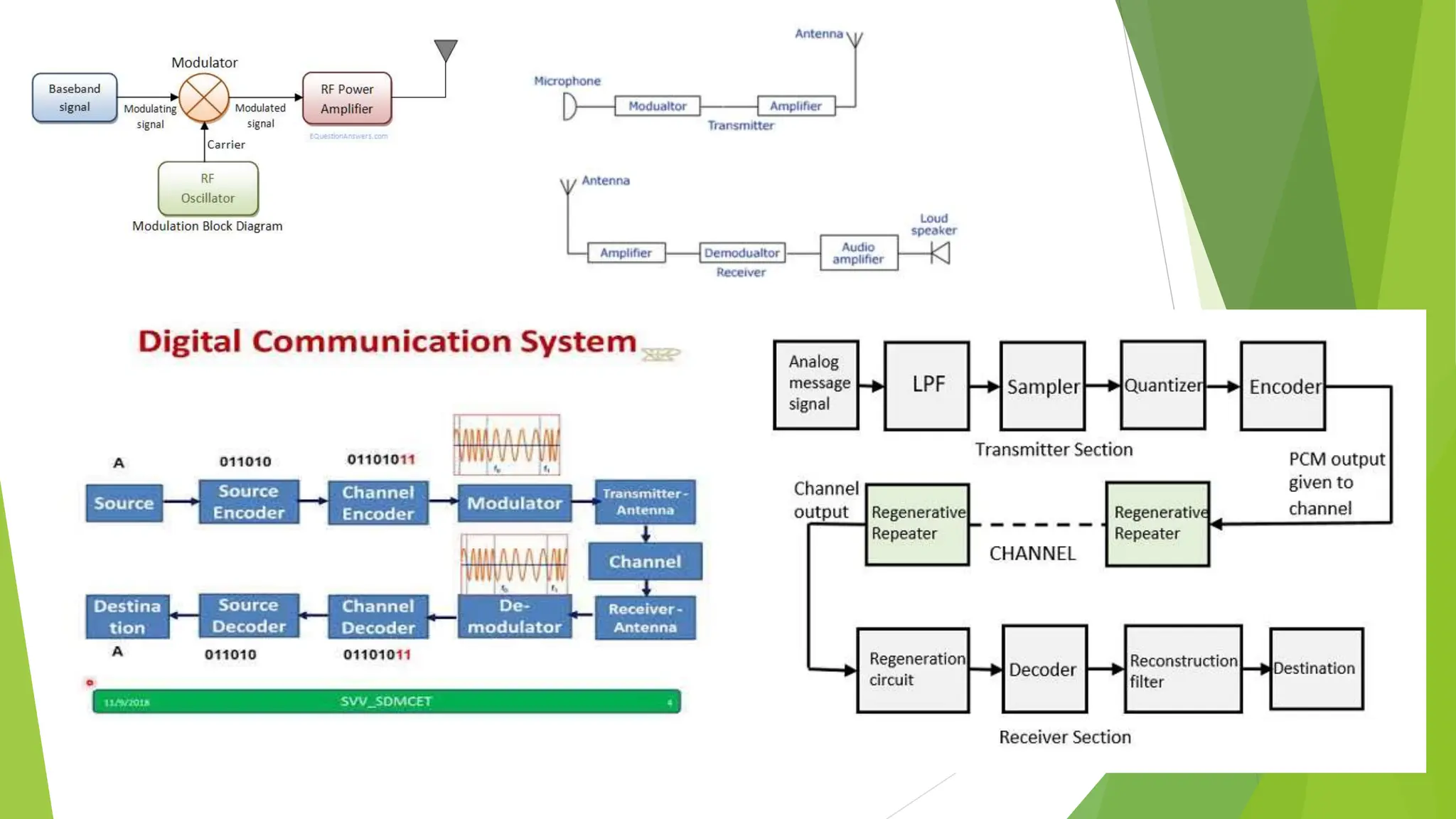
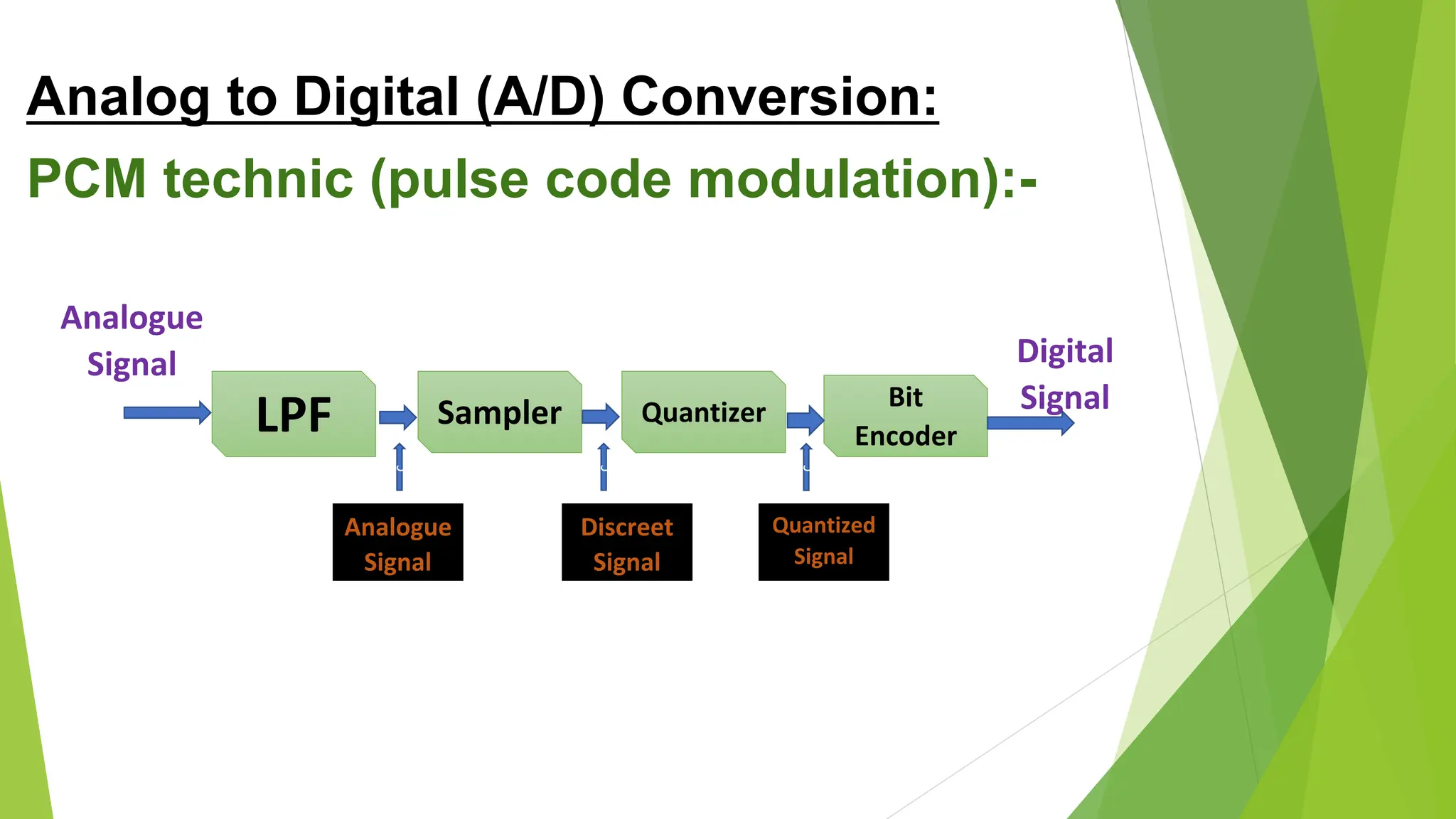
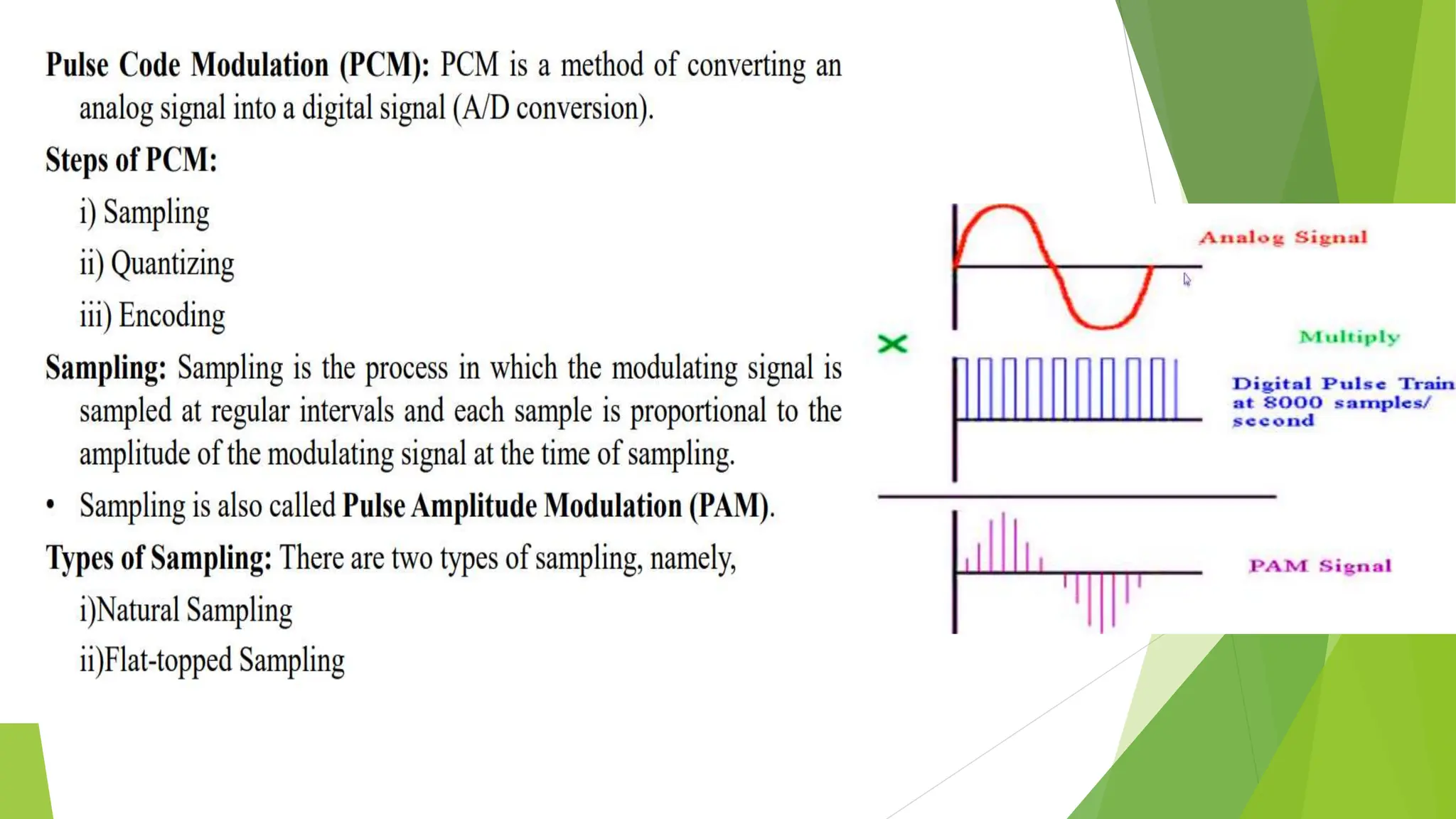
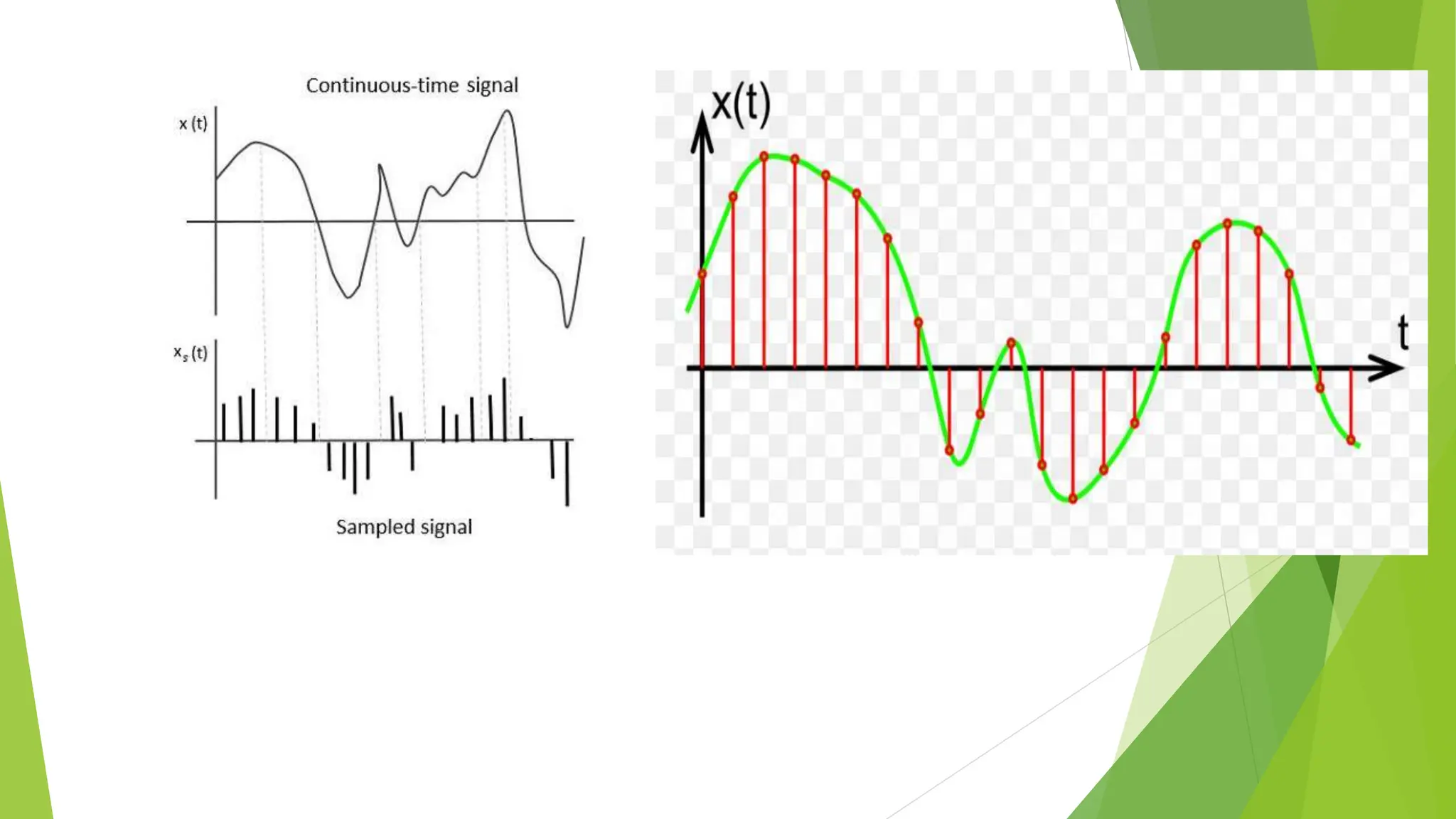
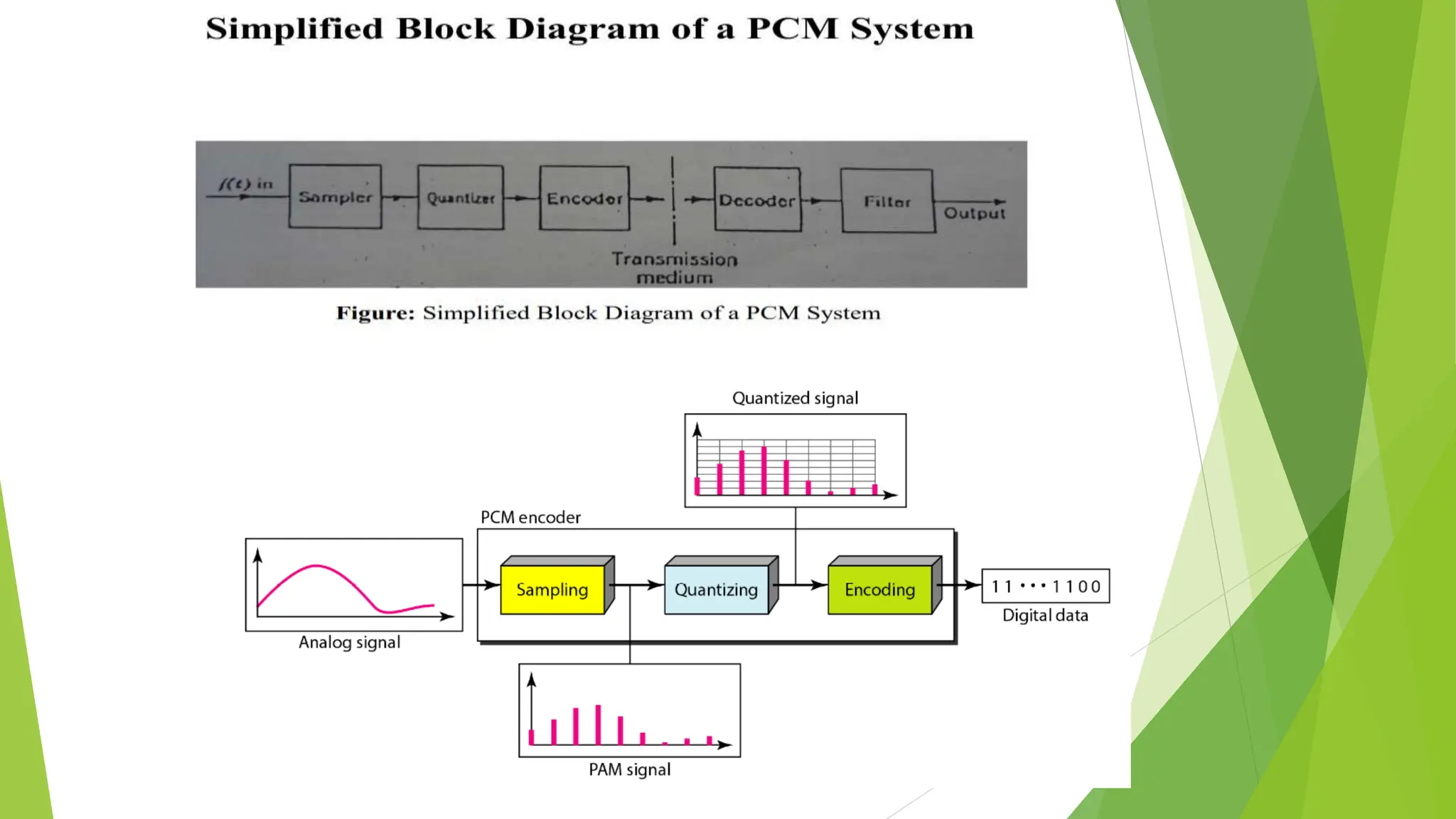
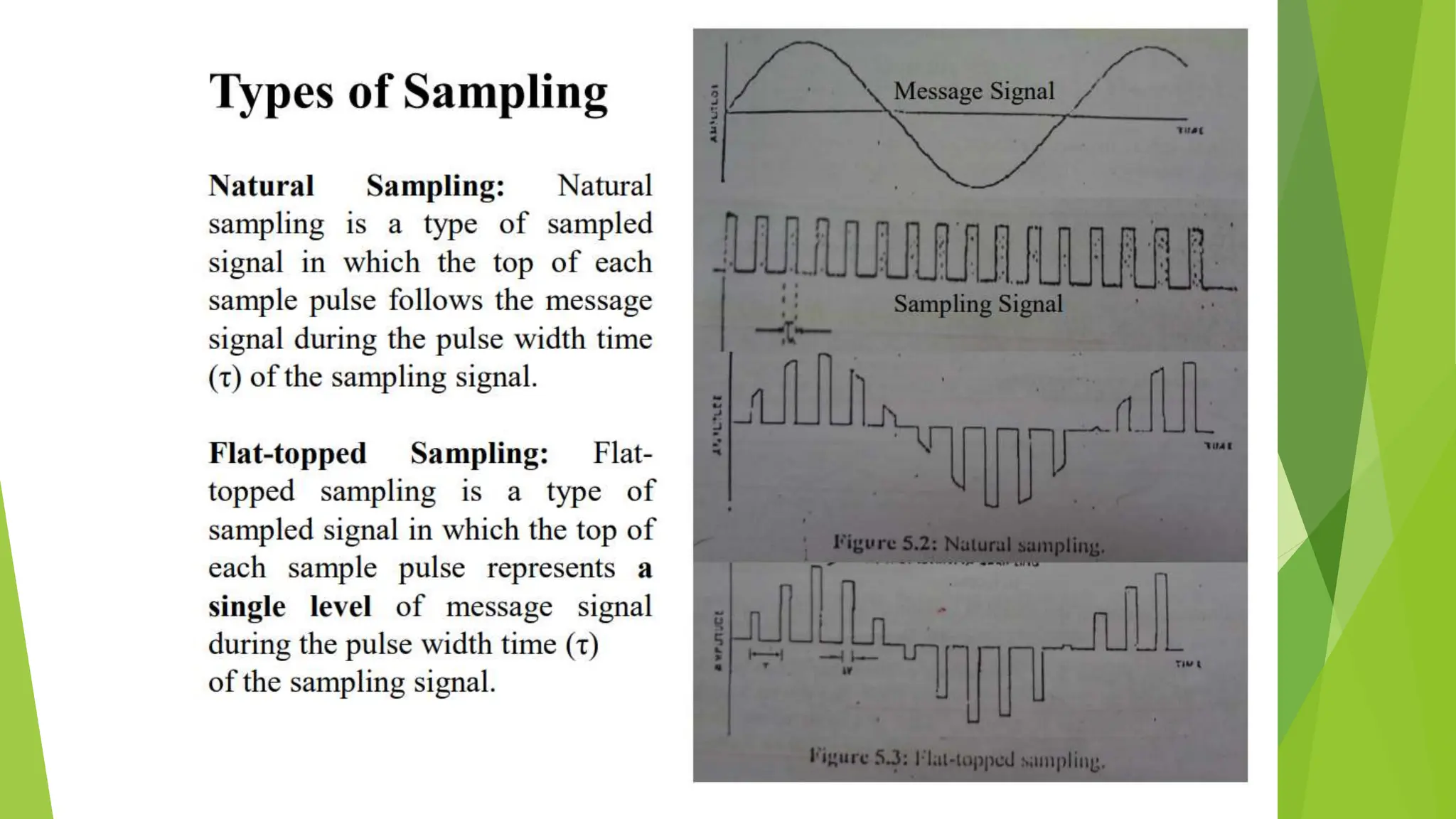
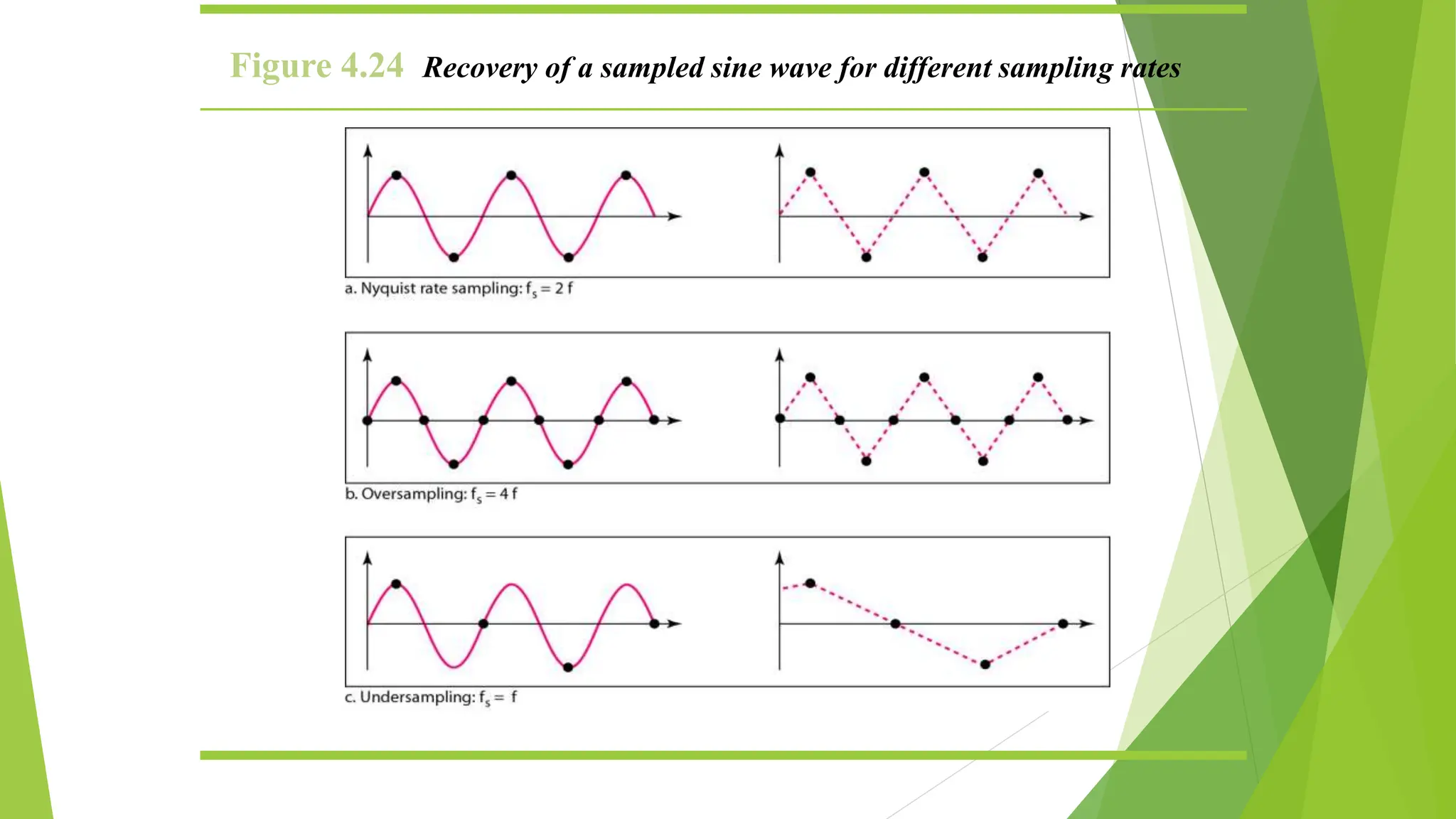
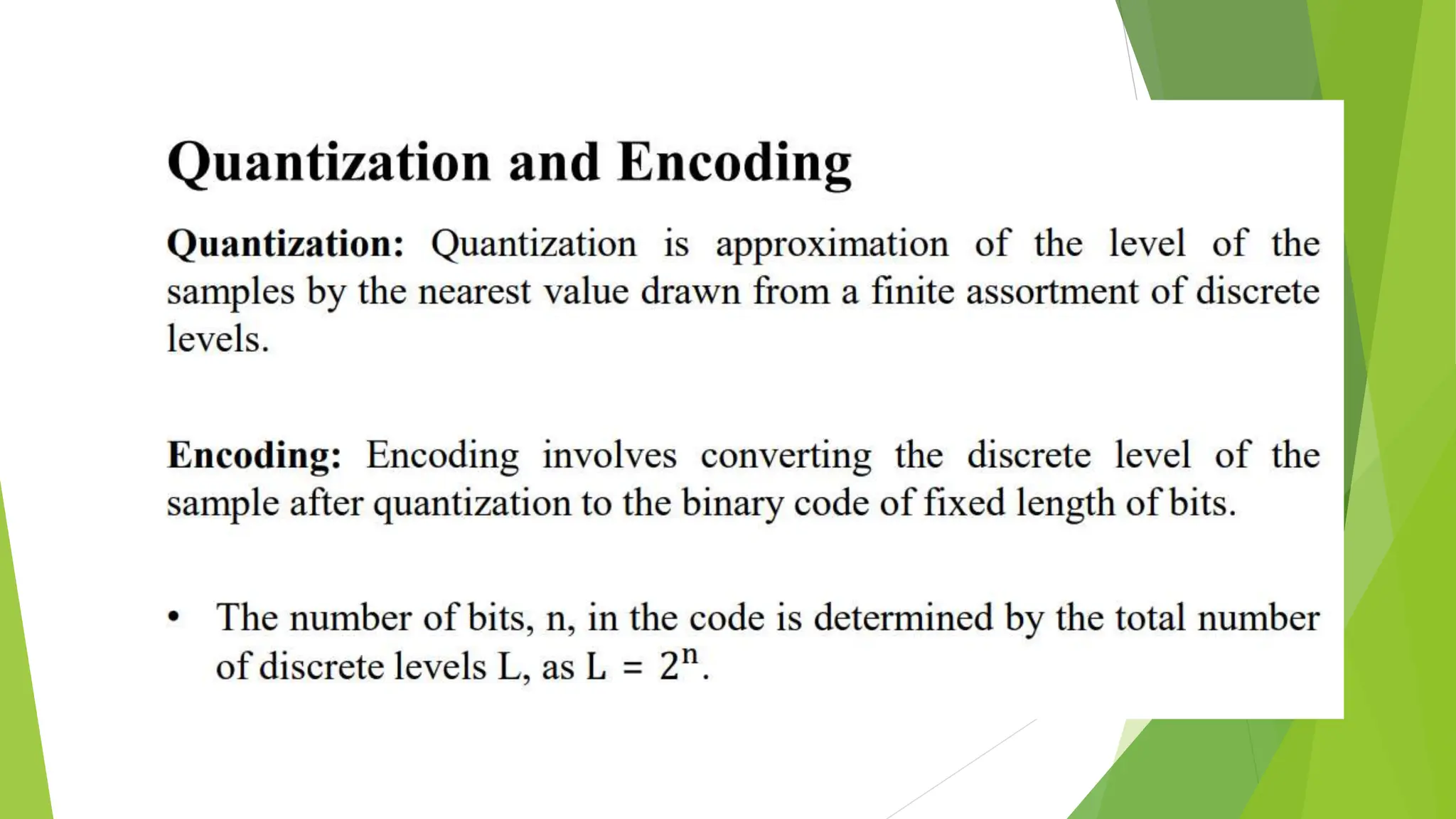
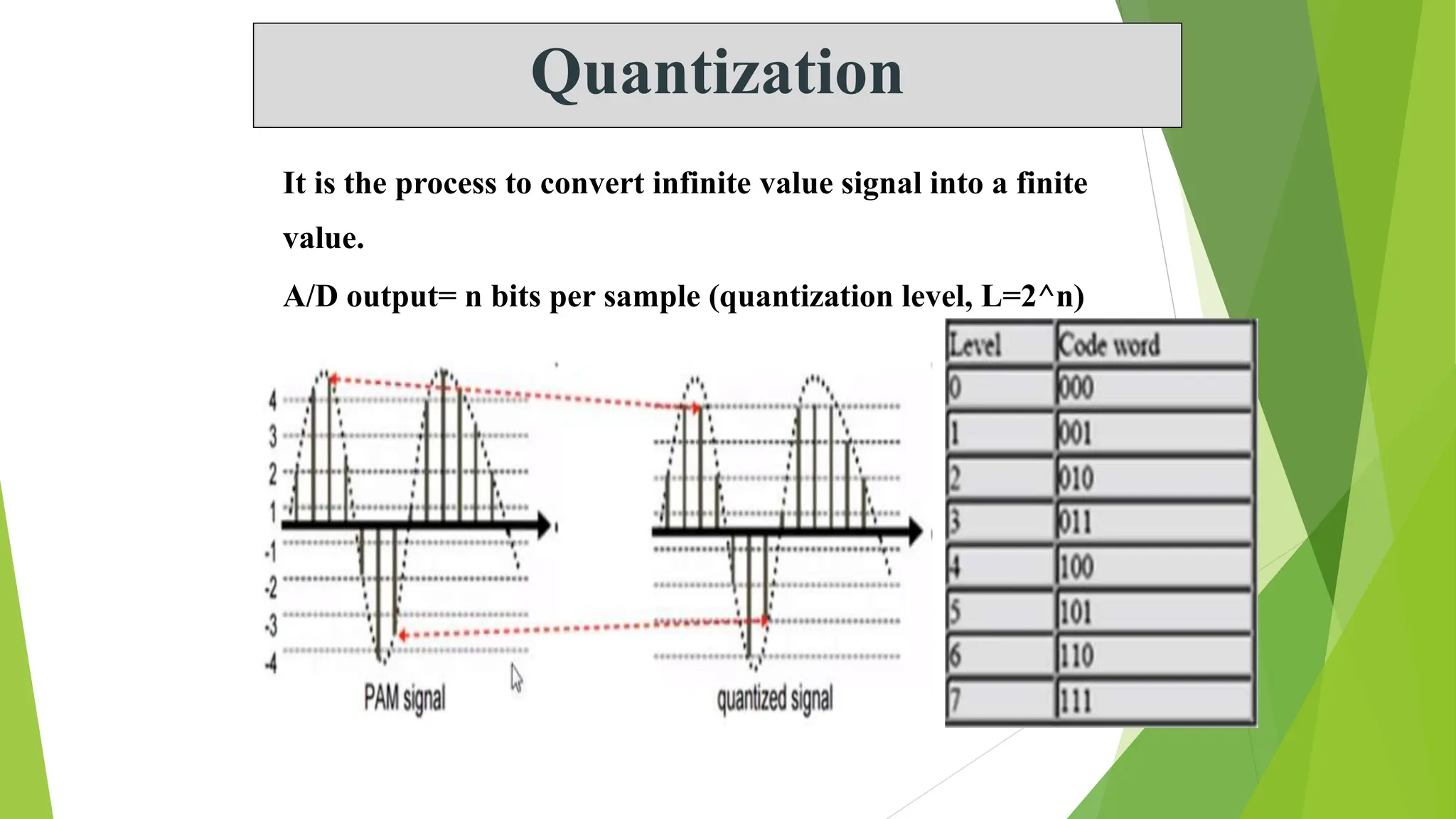
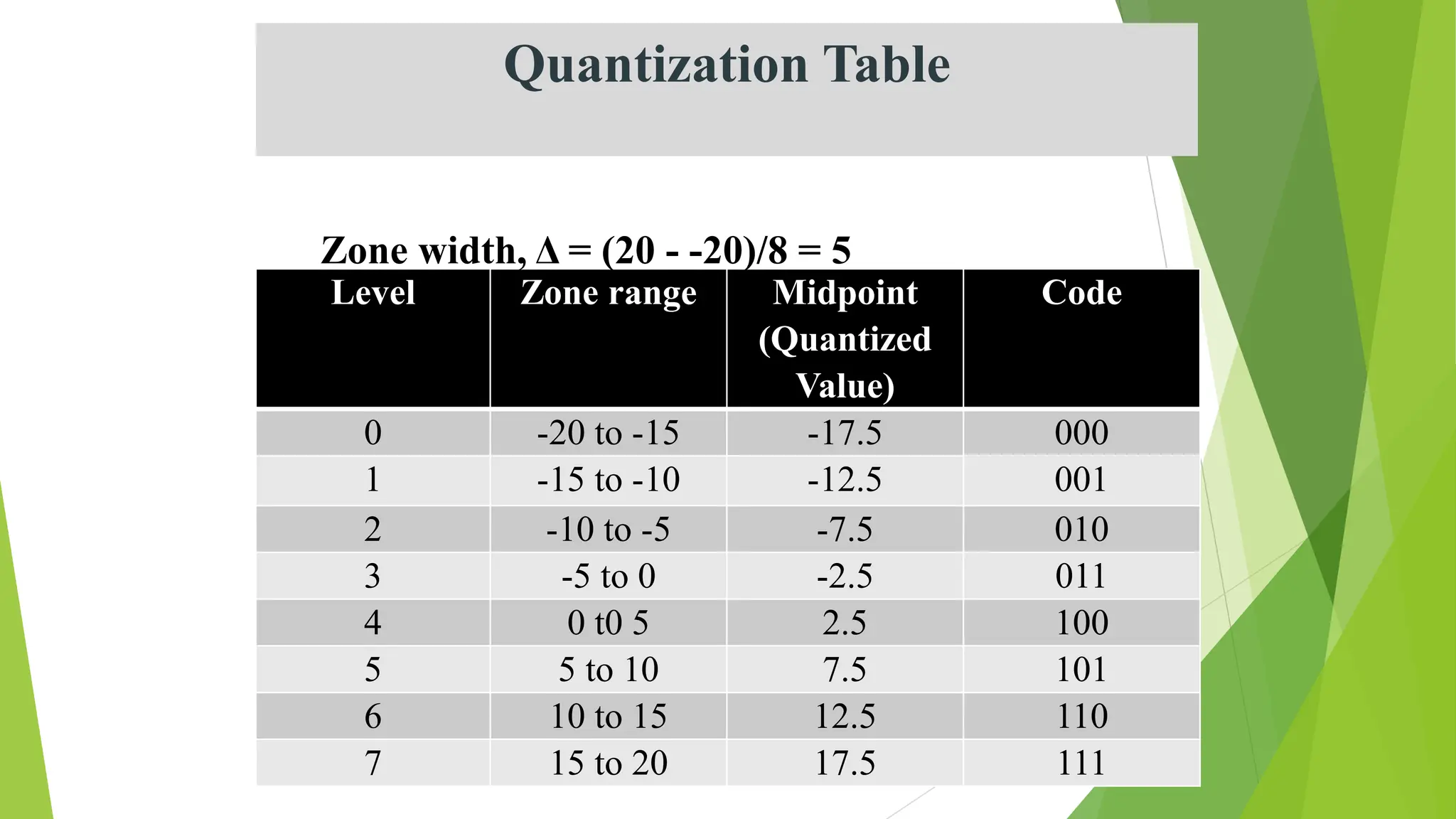
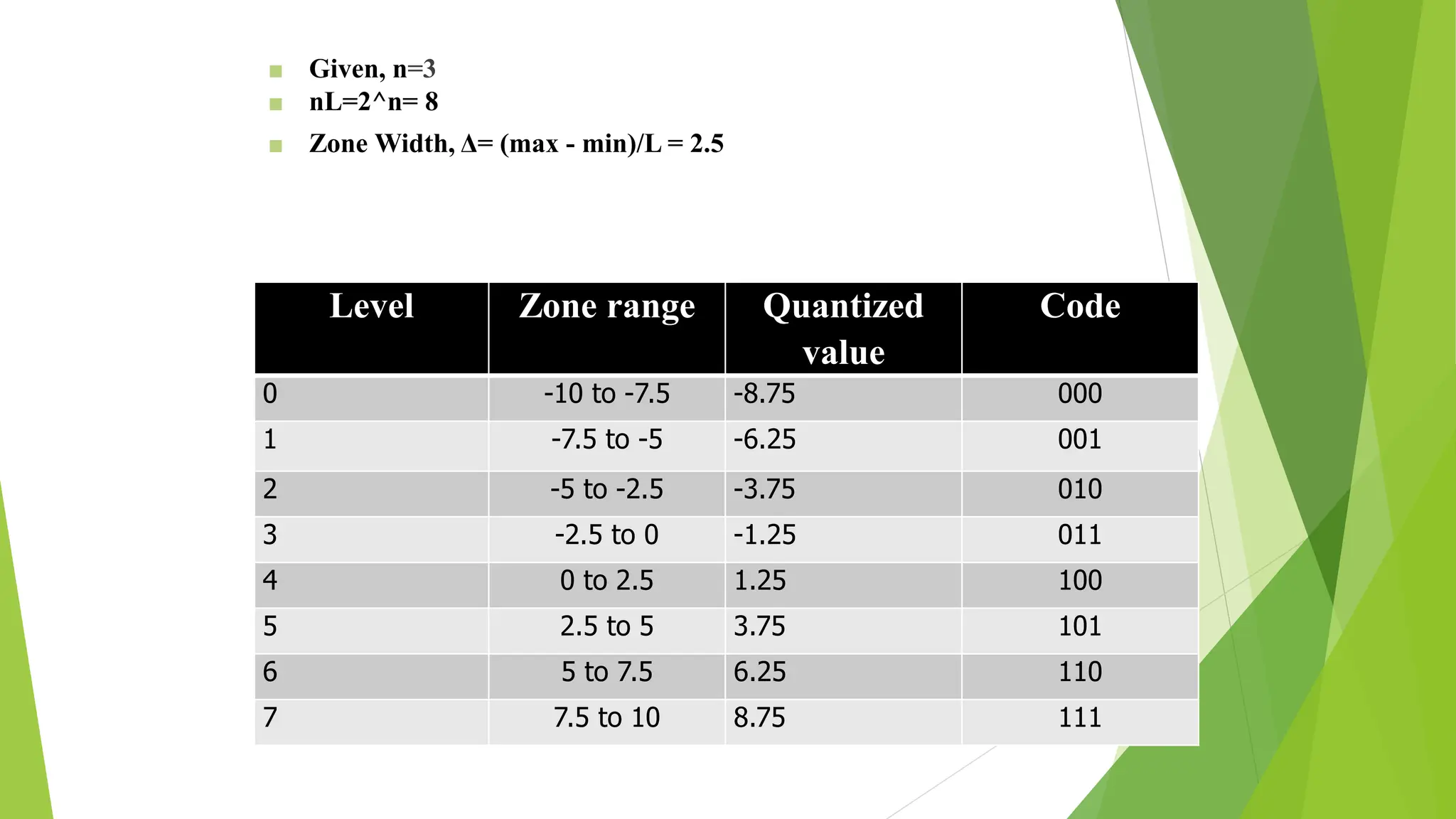
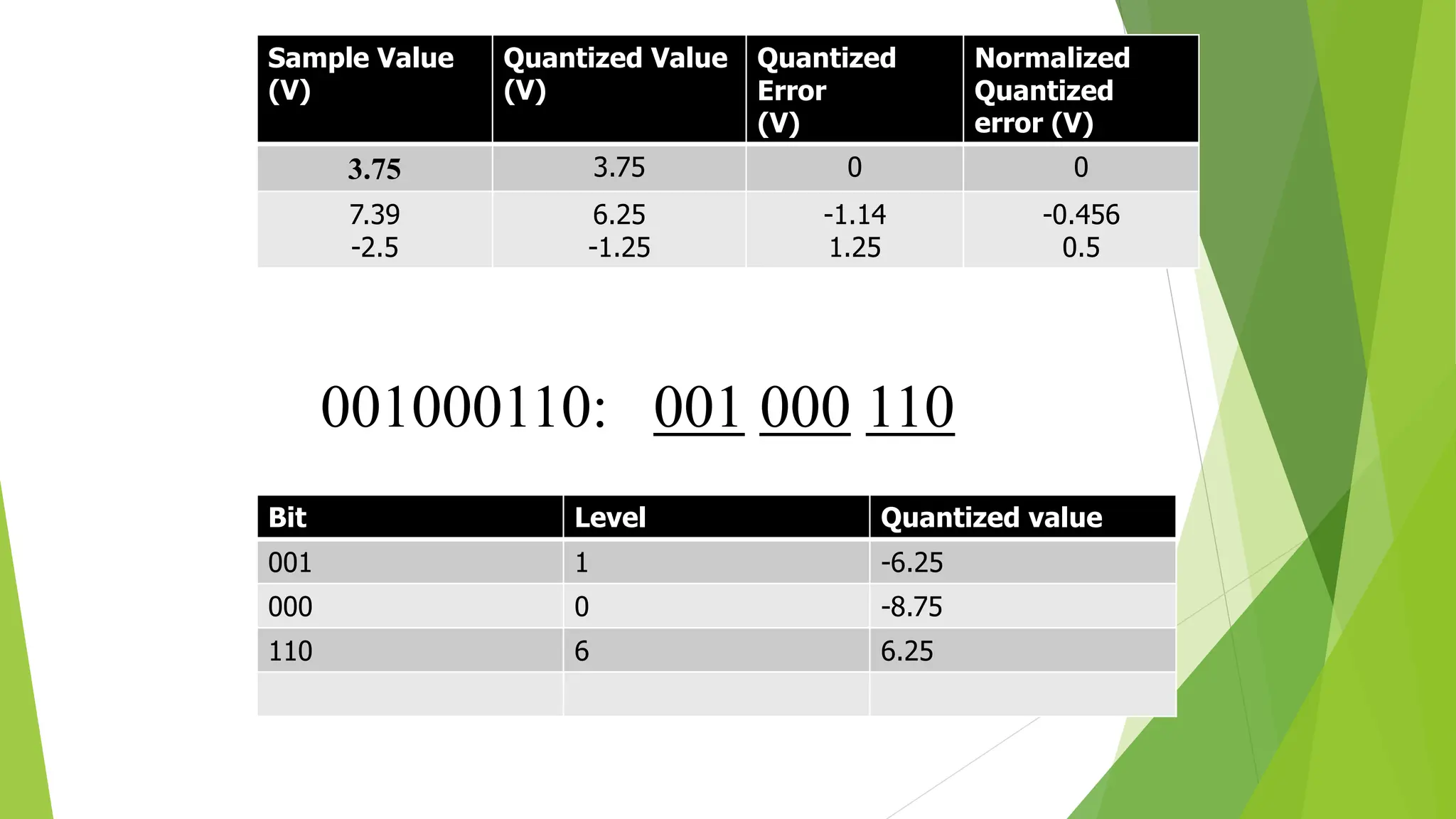
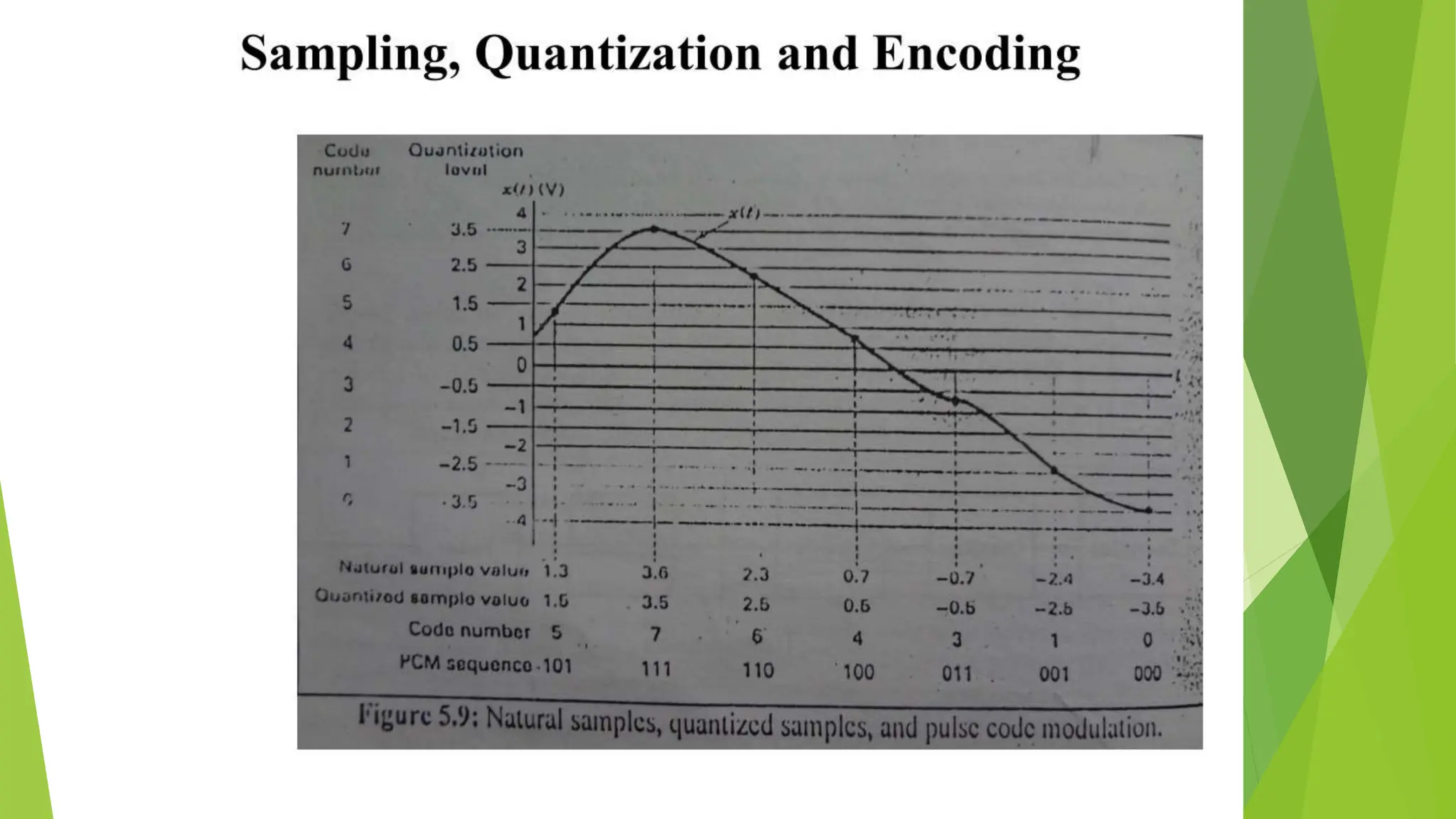
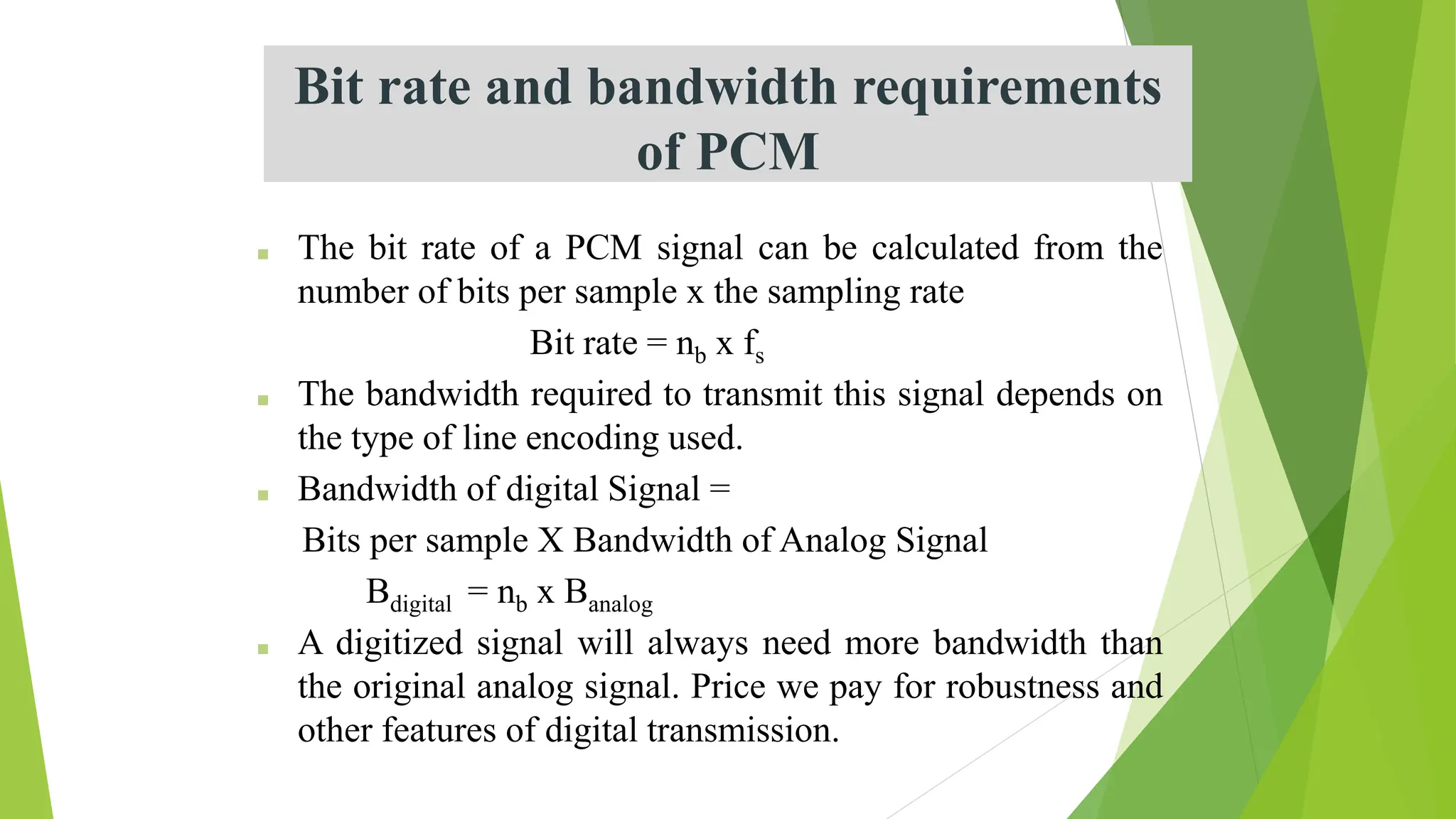
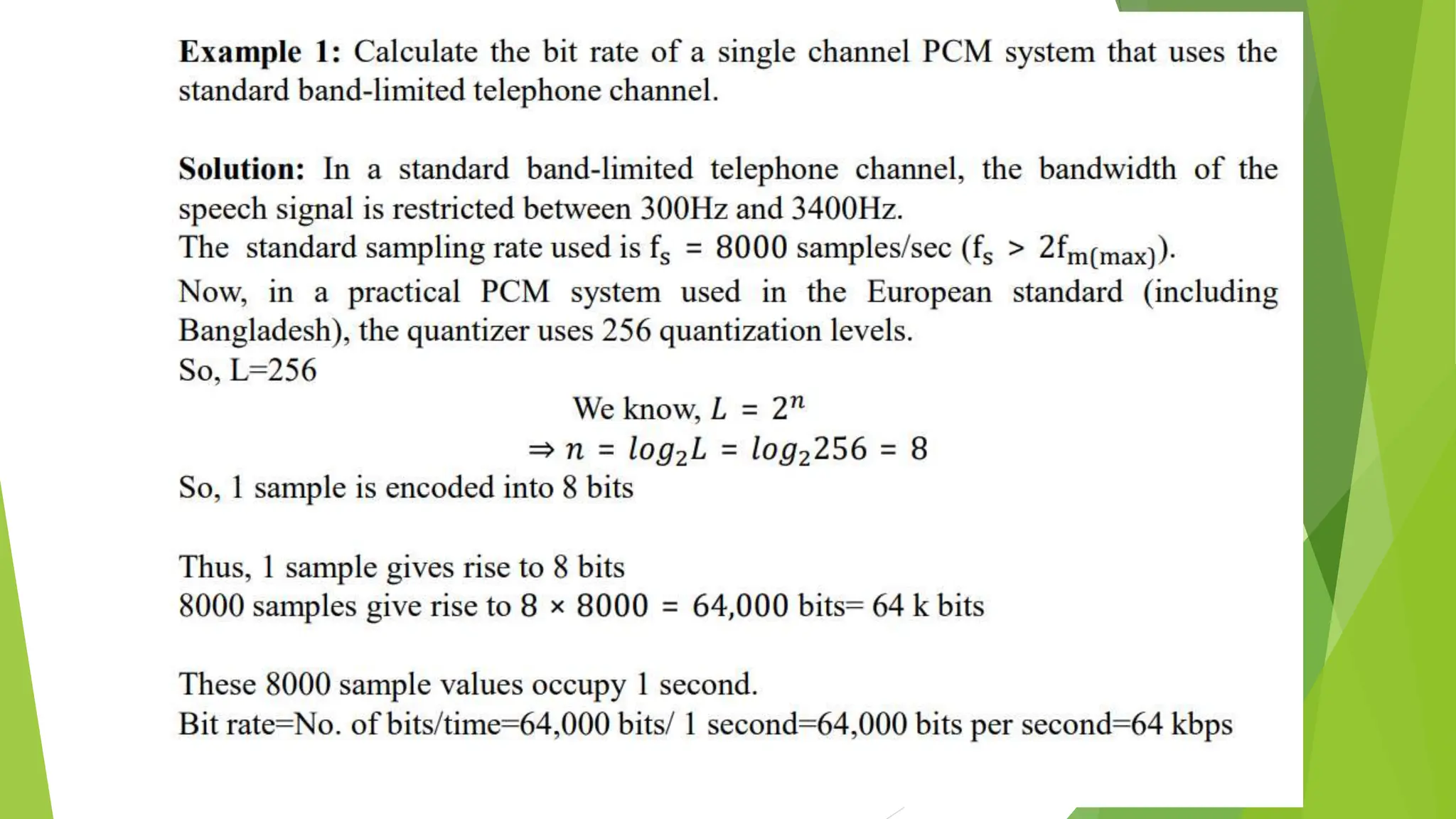
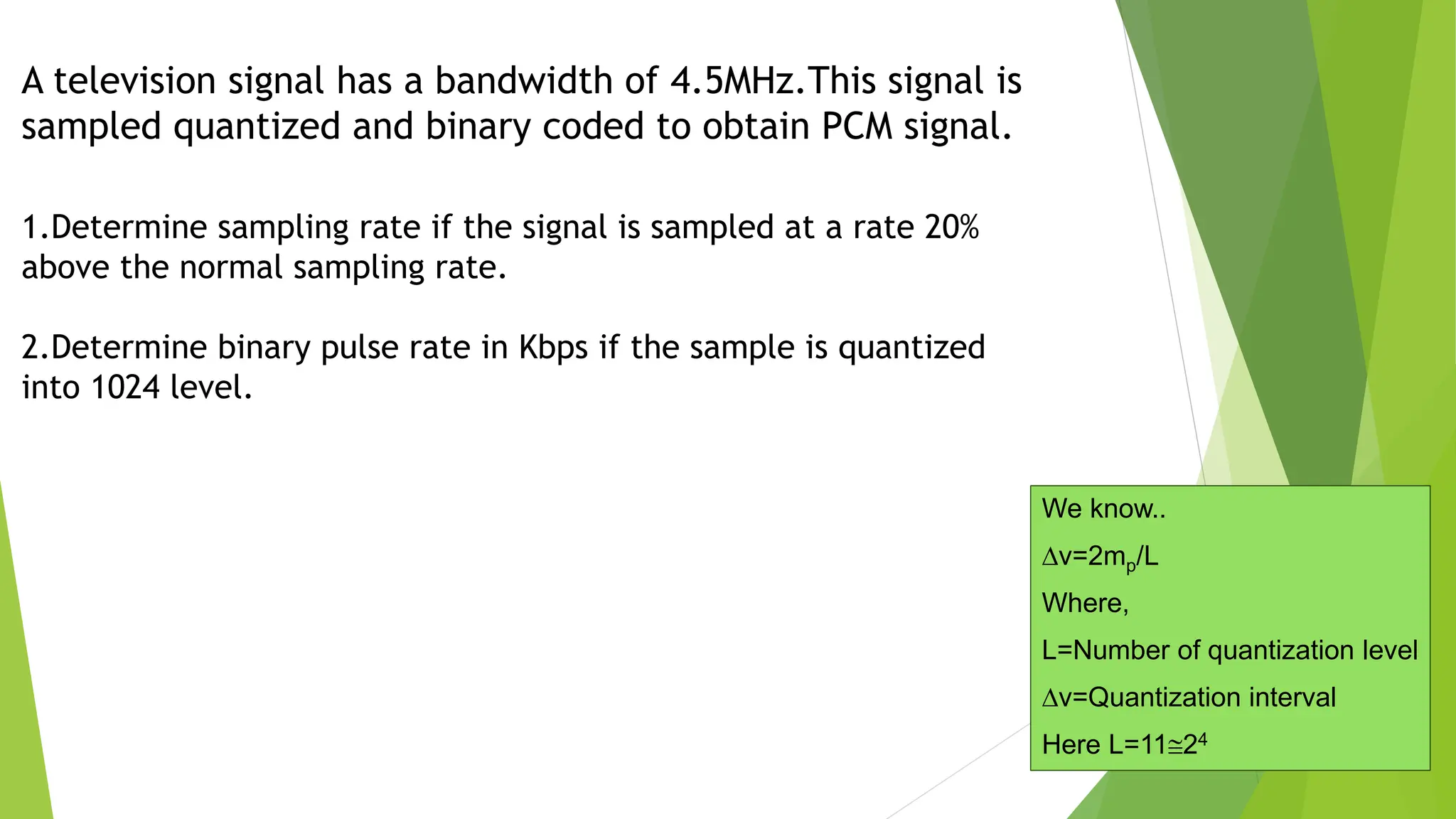
The document provides an overview of digital communication, comparing it with analog communication, and explaining the concepts of digital and analog signals, digital modulation techniques, and A/D conversion. It also discusses quantization, sampling, and the processes involved in converting and recovering signals, including examples and calculations pertaining to bit rates, sampling rates, and quantization errors. Finally, it addresses problems related to signal bandwidth and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) for various scenarios.



![A/D
Converter
Channel
Encoder Modulator
[Input signal]
Analog or continuous
signal
Digital Bit
Digital signal pulse
Digital Modulated
signal
Digital Message signal
and
Carrier signal
Digital Communication (Digital Transmitter)
A/D Converter: Analog To Digital Converter](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalcomlec01seu-240626053021-9bc0c1ec/75/digital-comMUNICATION-ENGINEERING-LECTURES-4-2048.jpg)