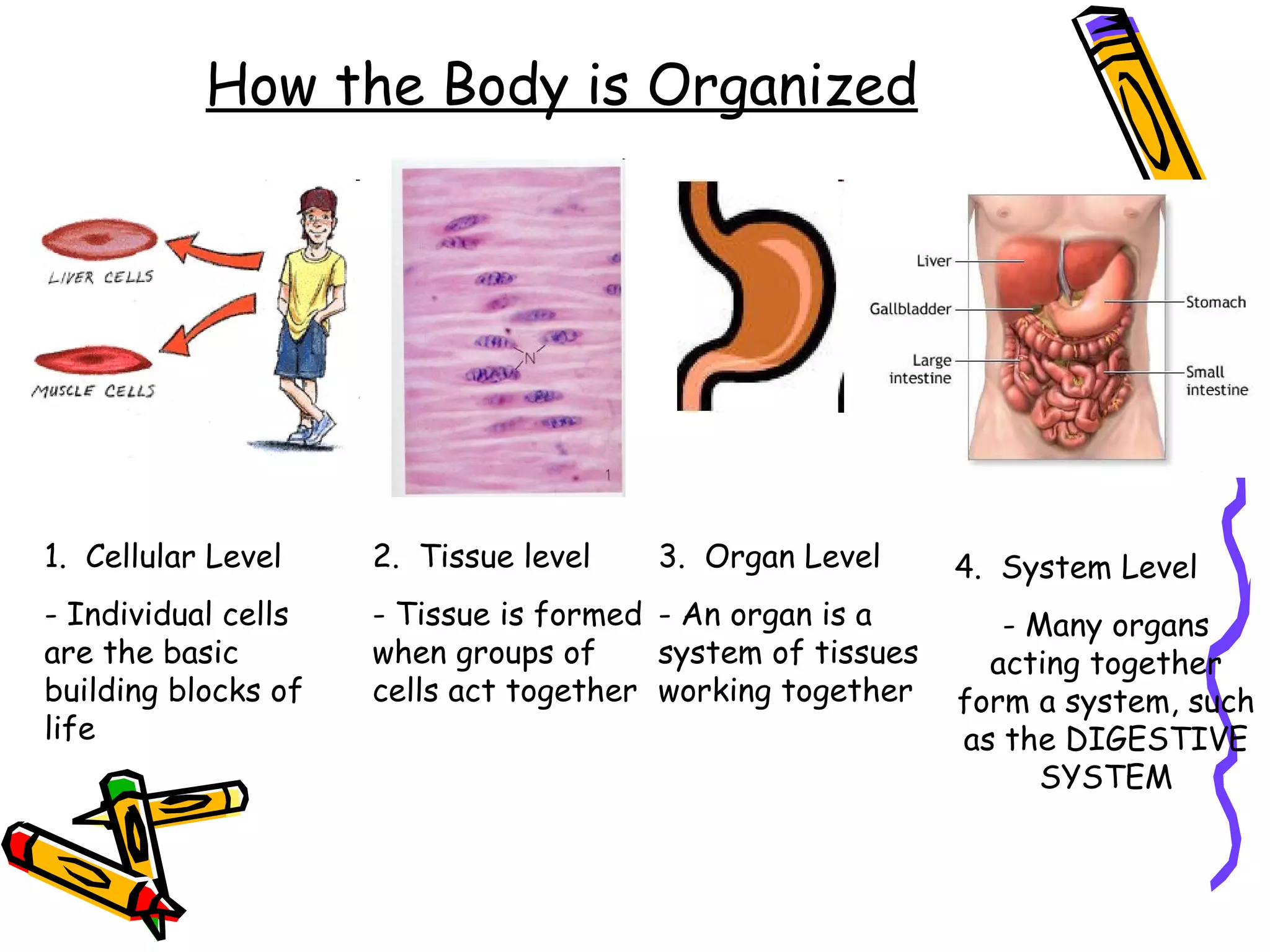
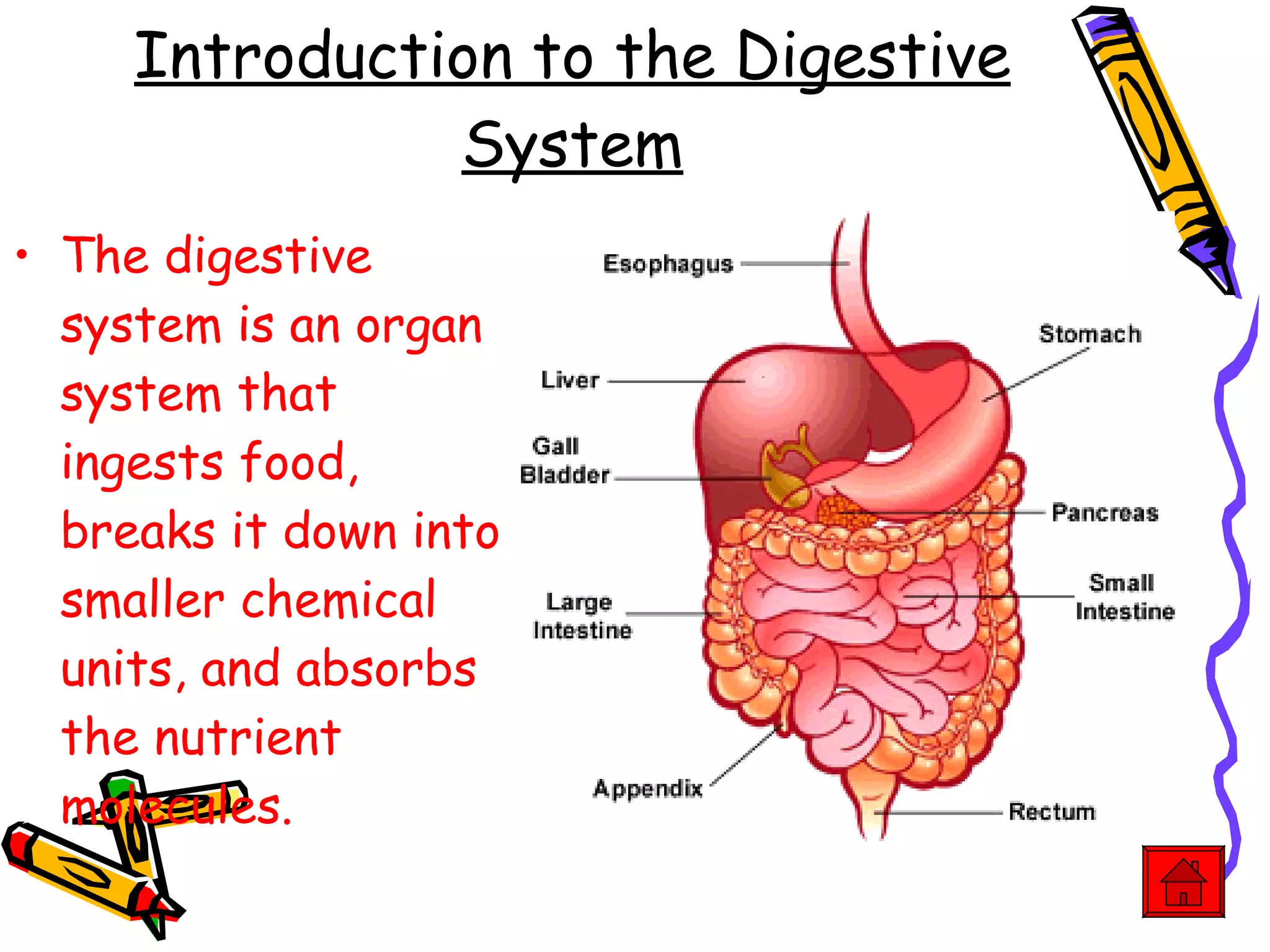
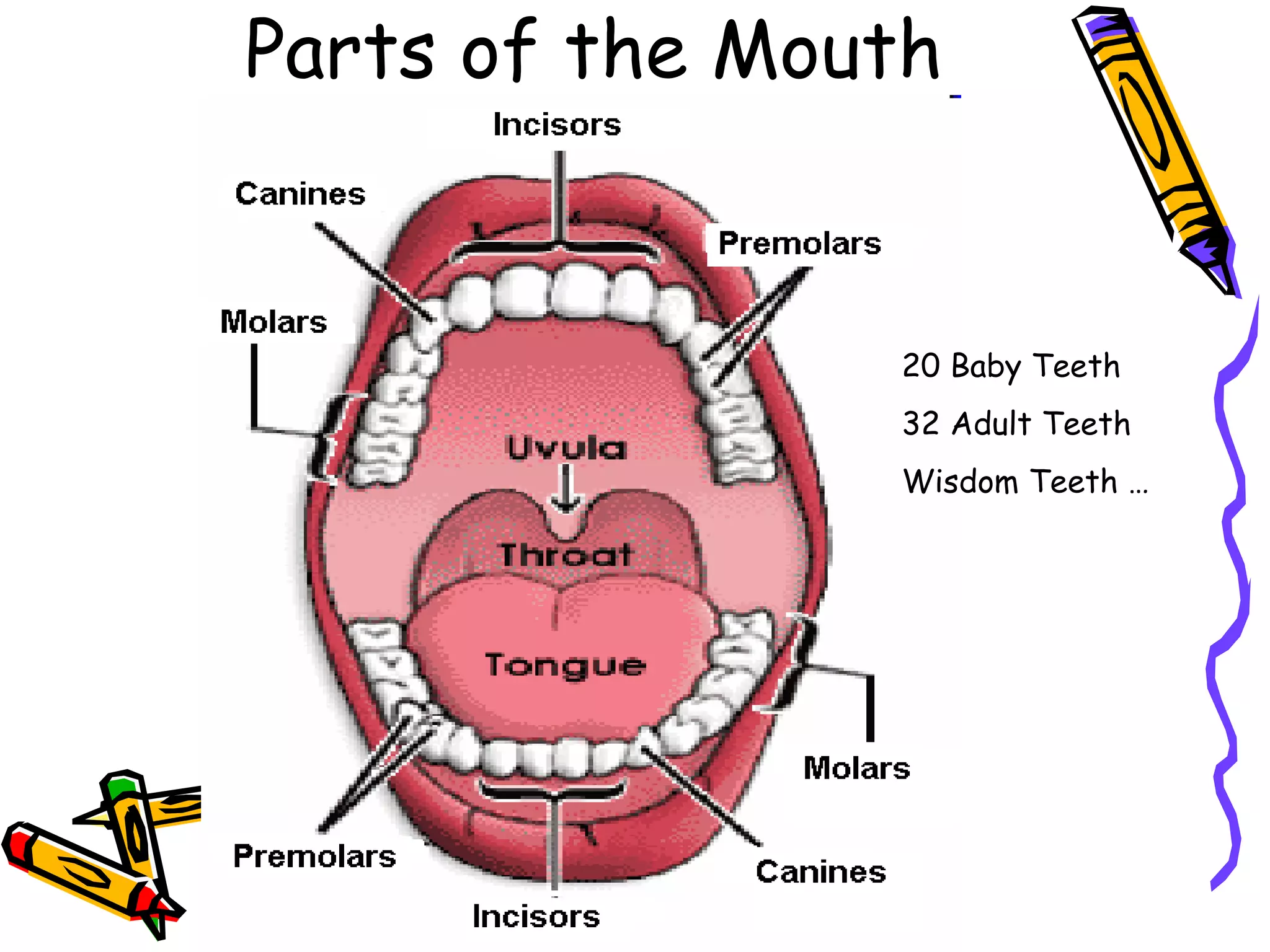
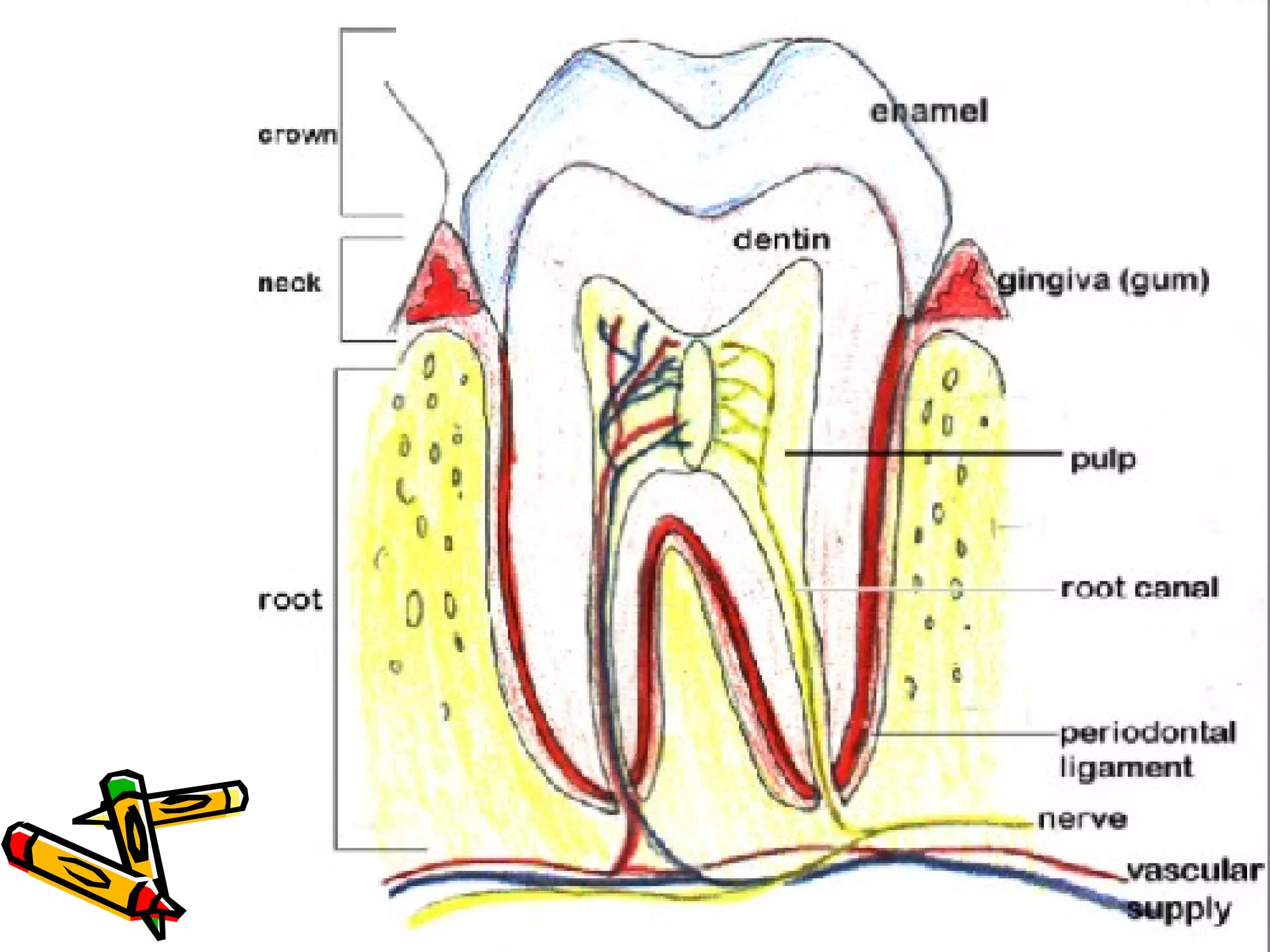
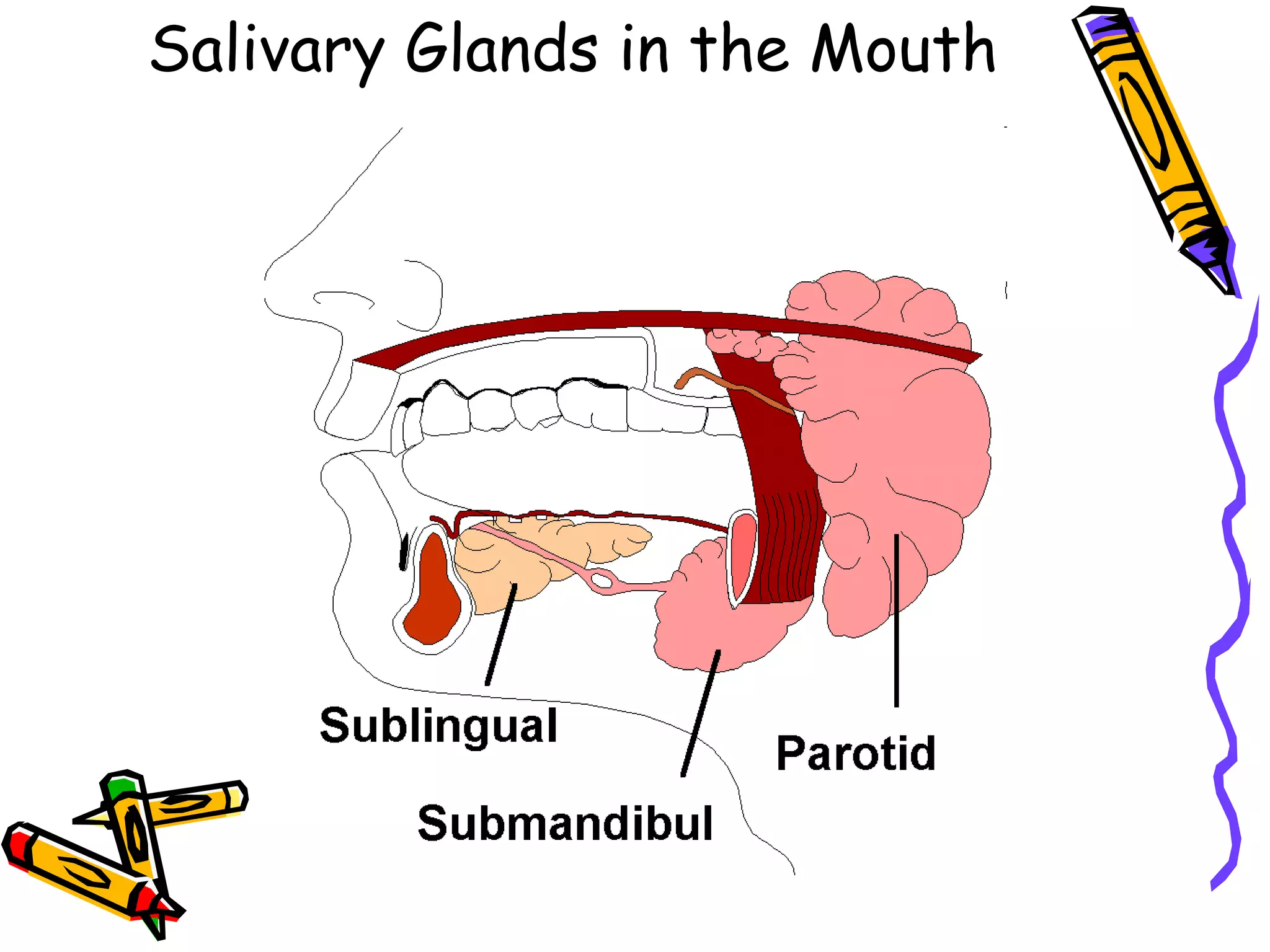
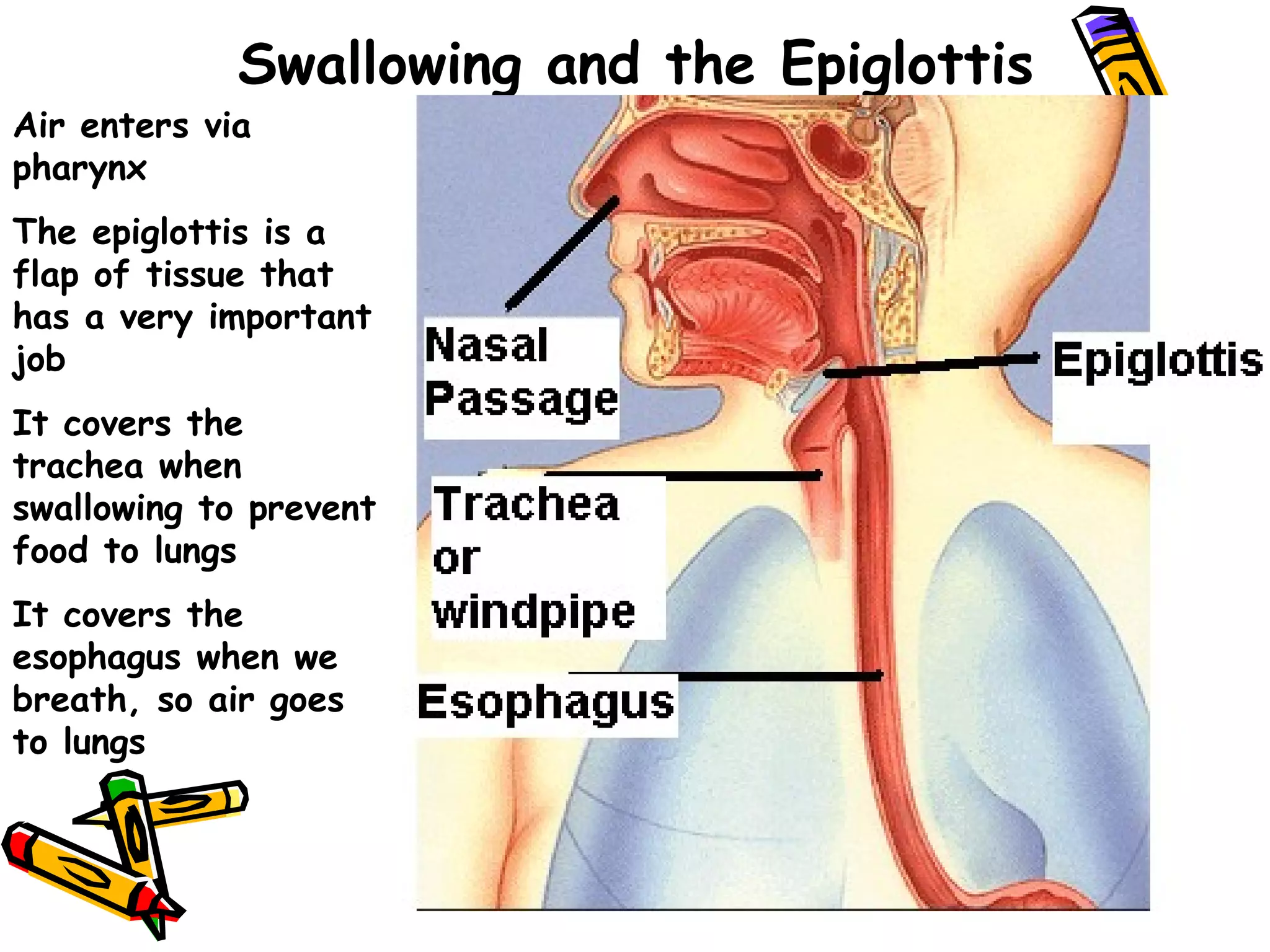
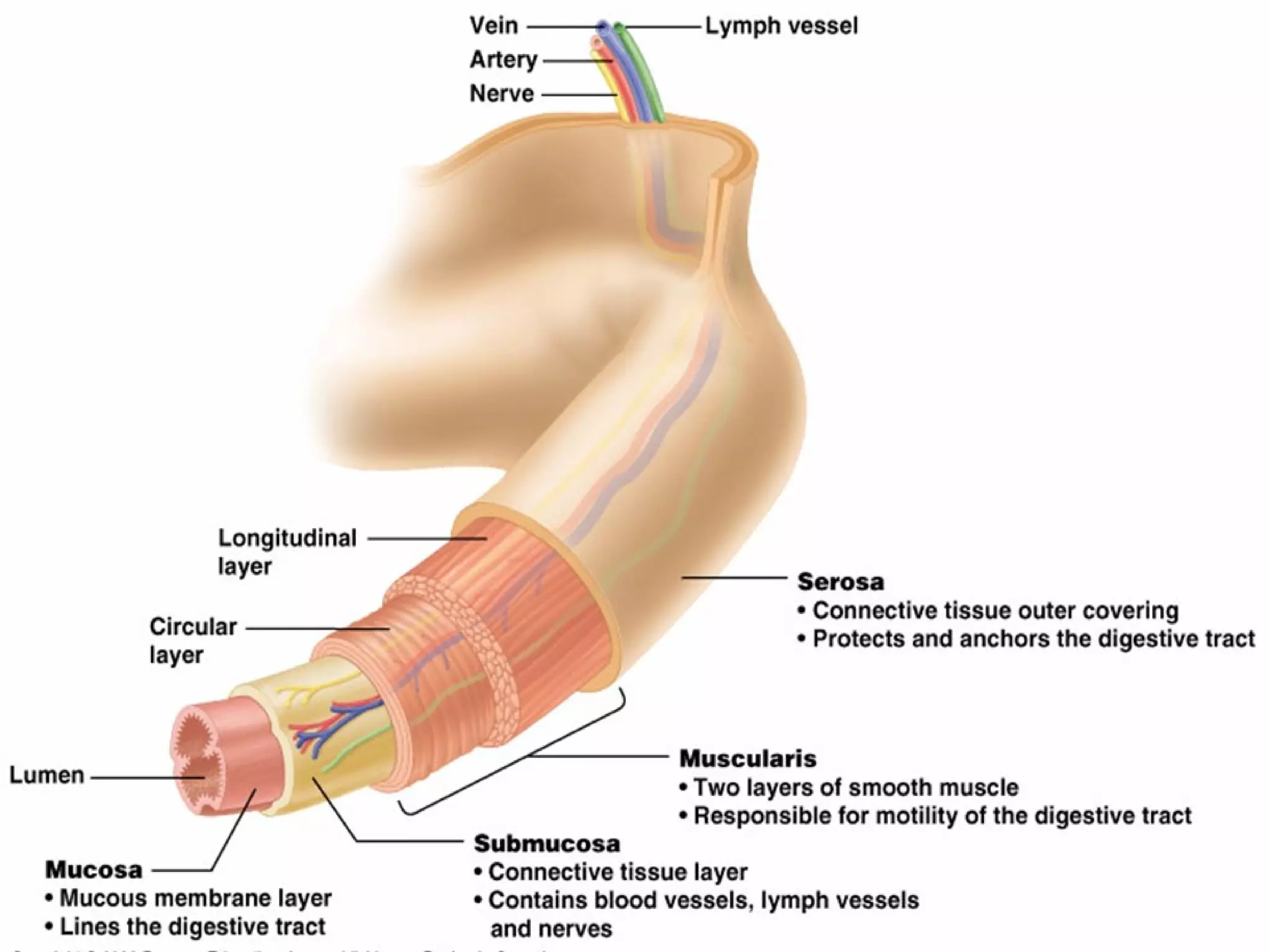
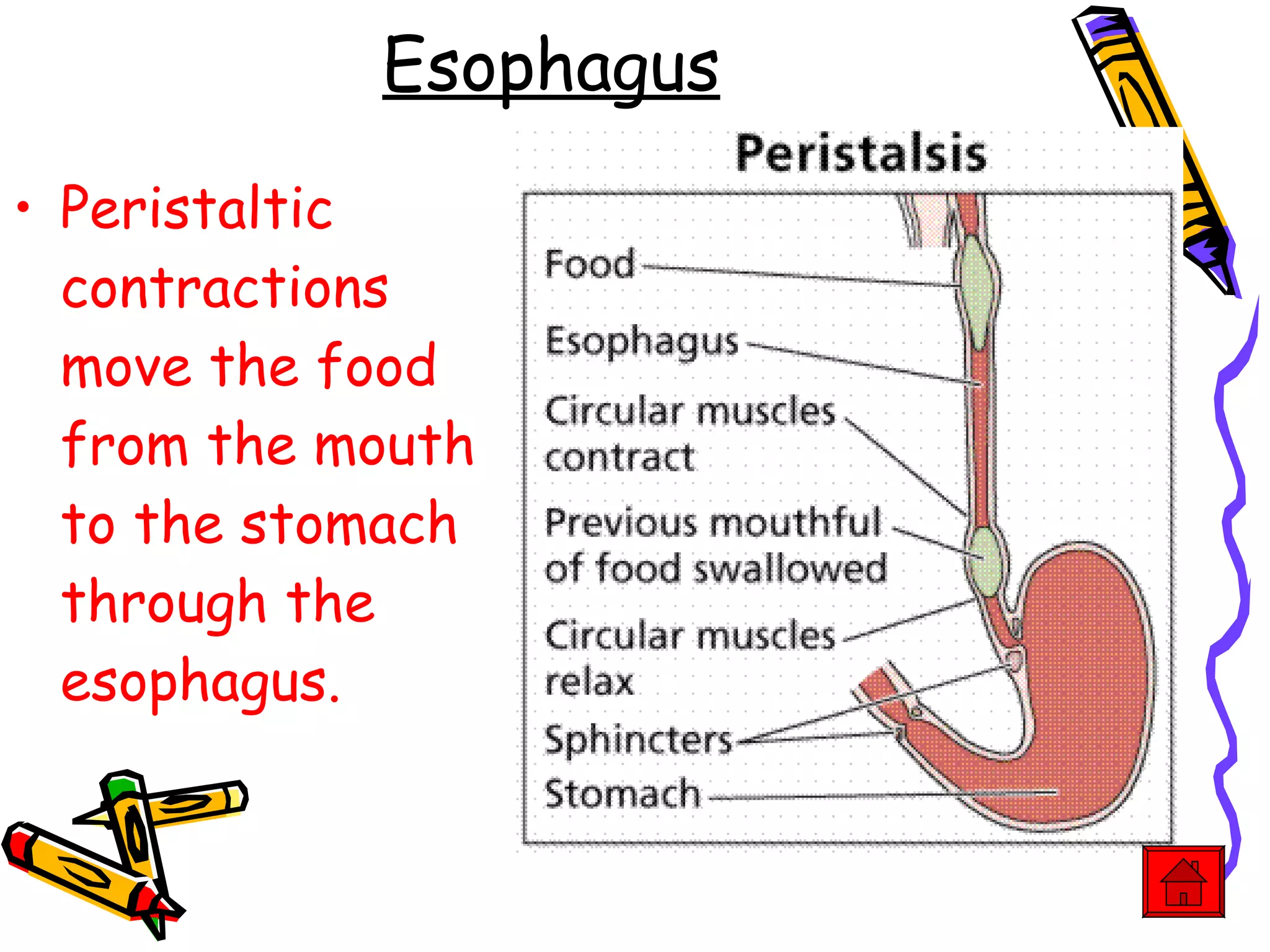
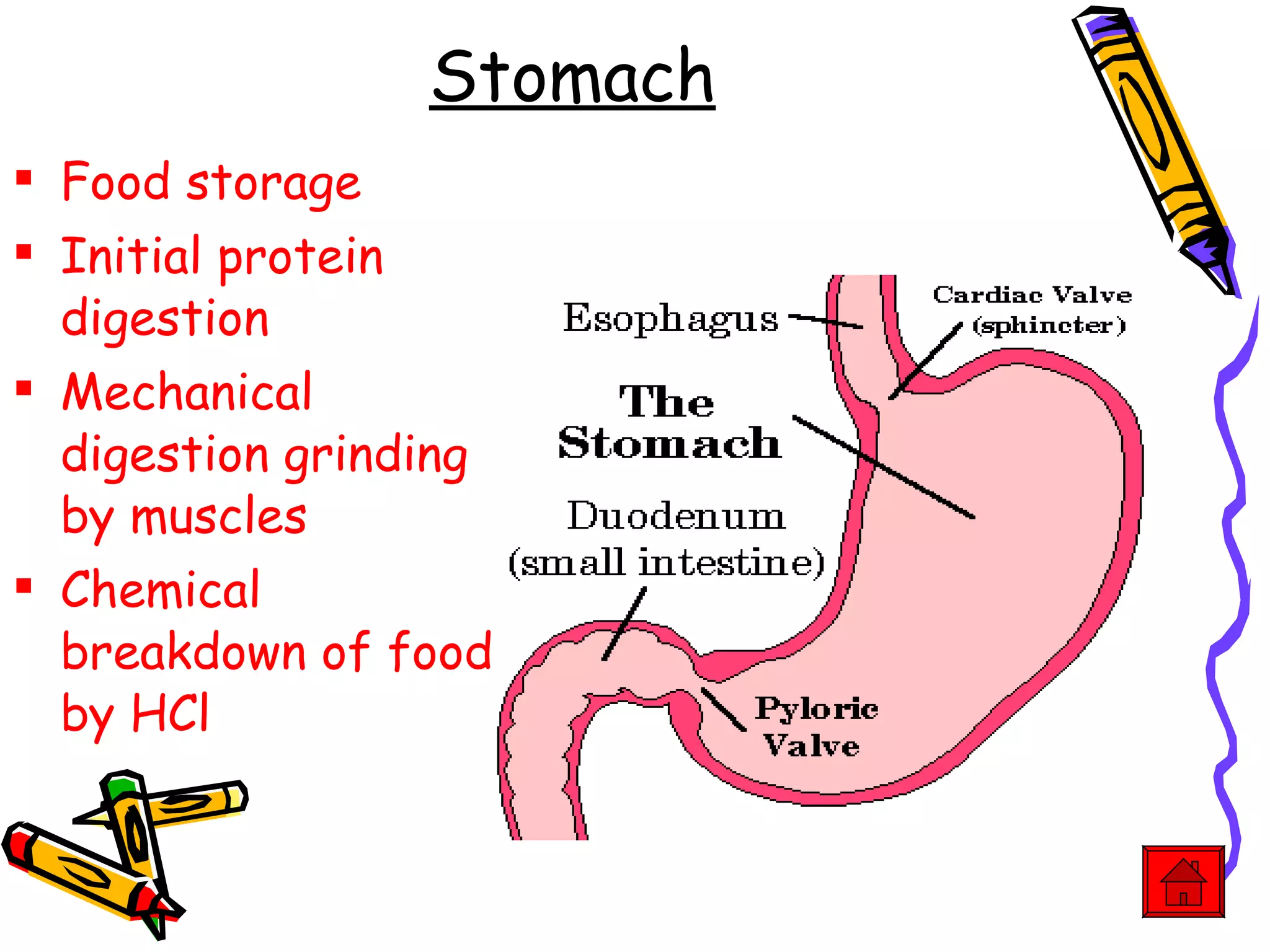
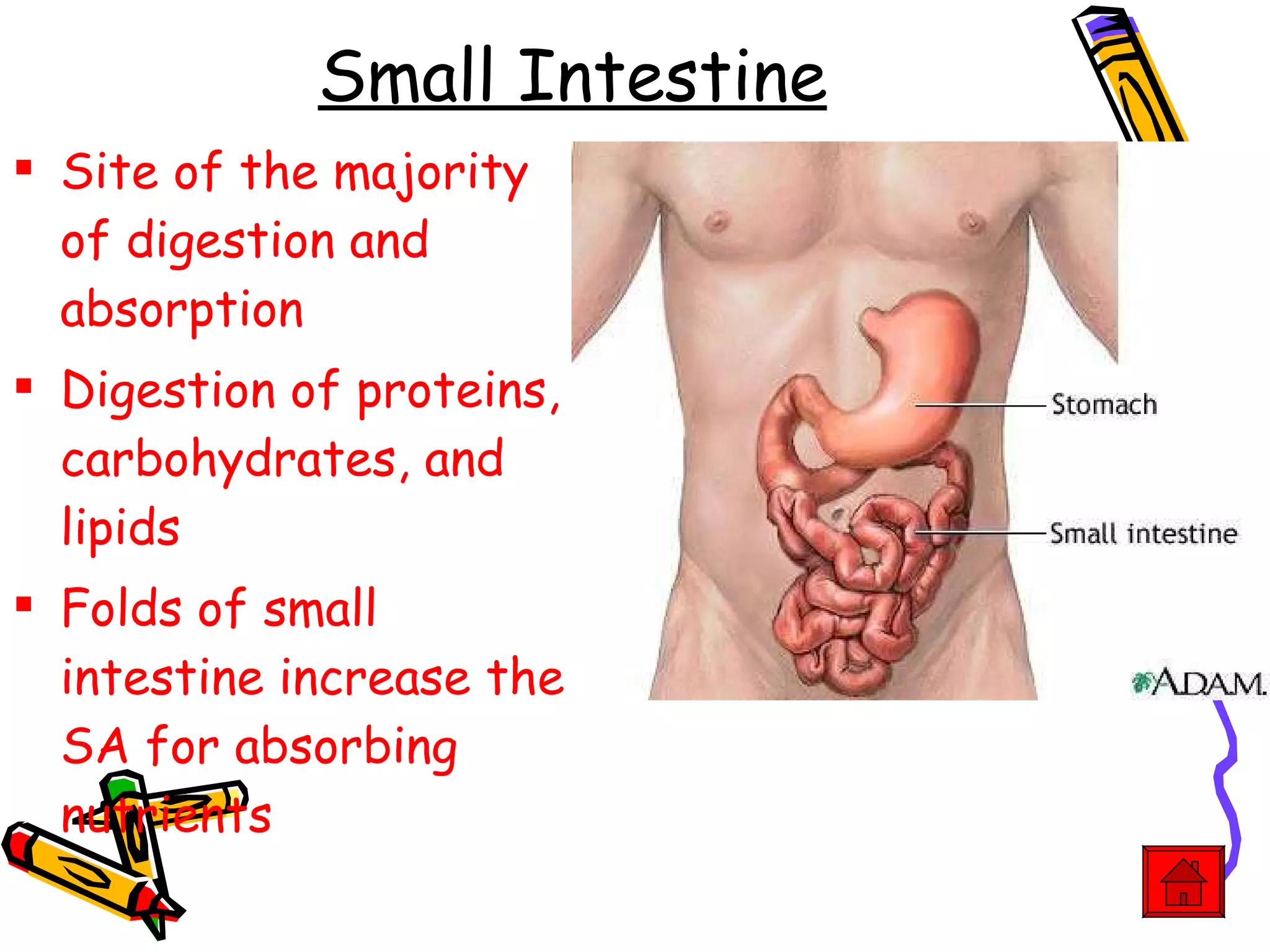
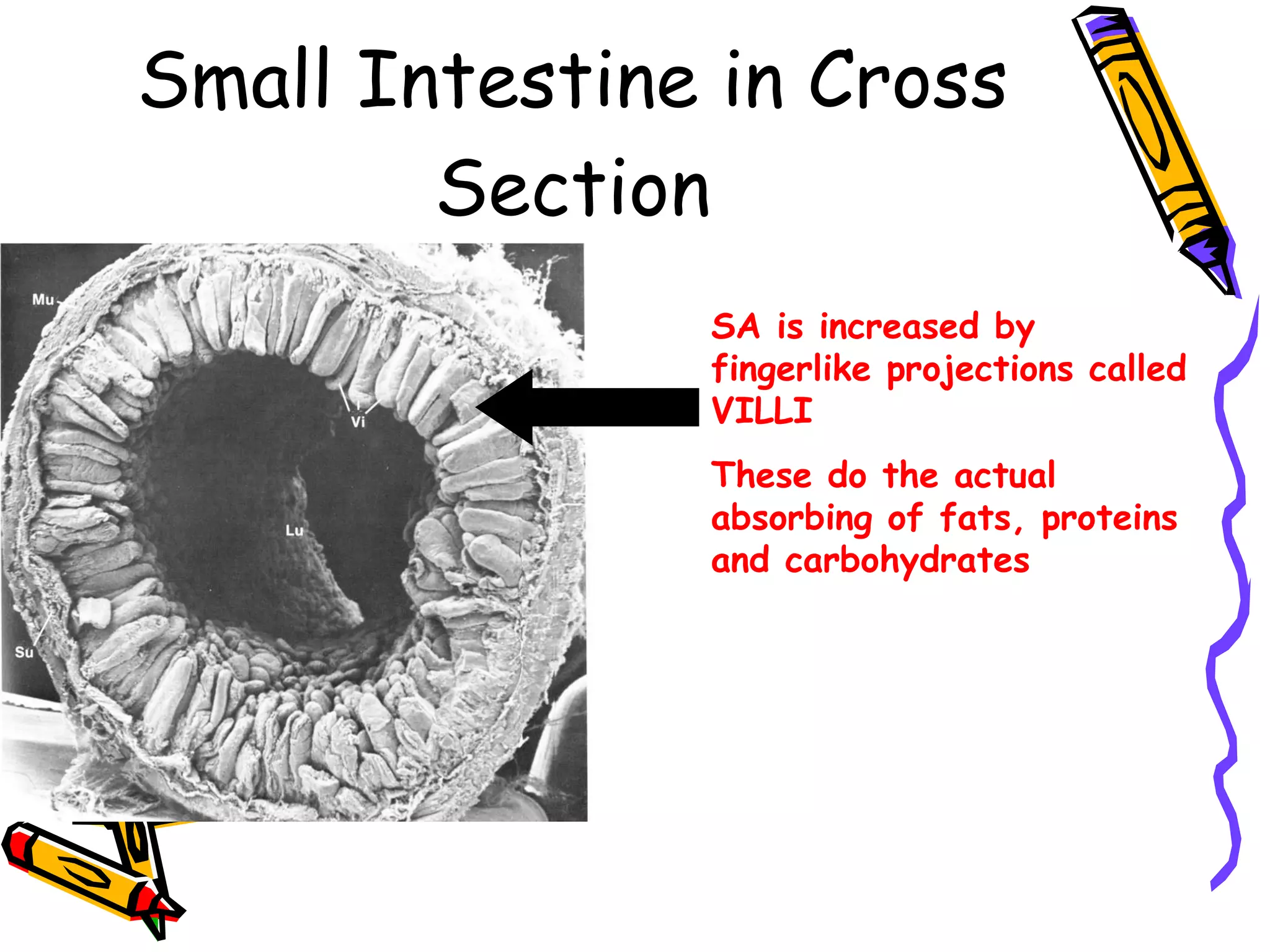
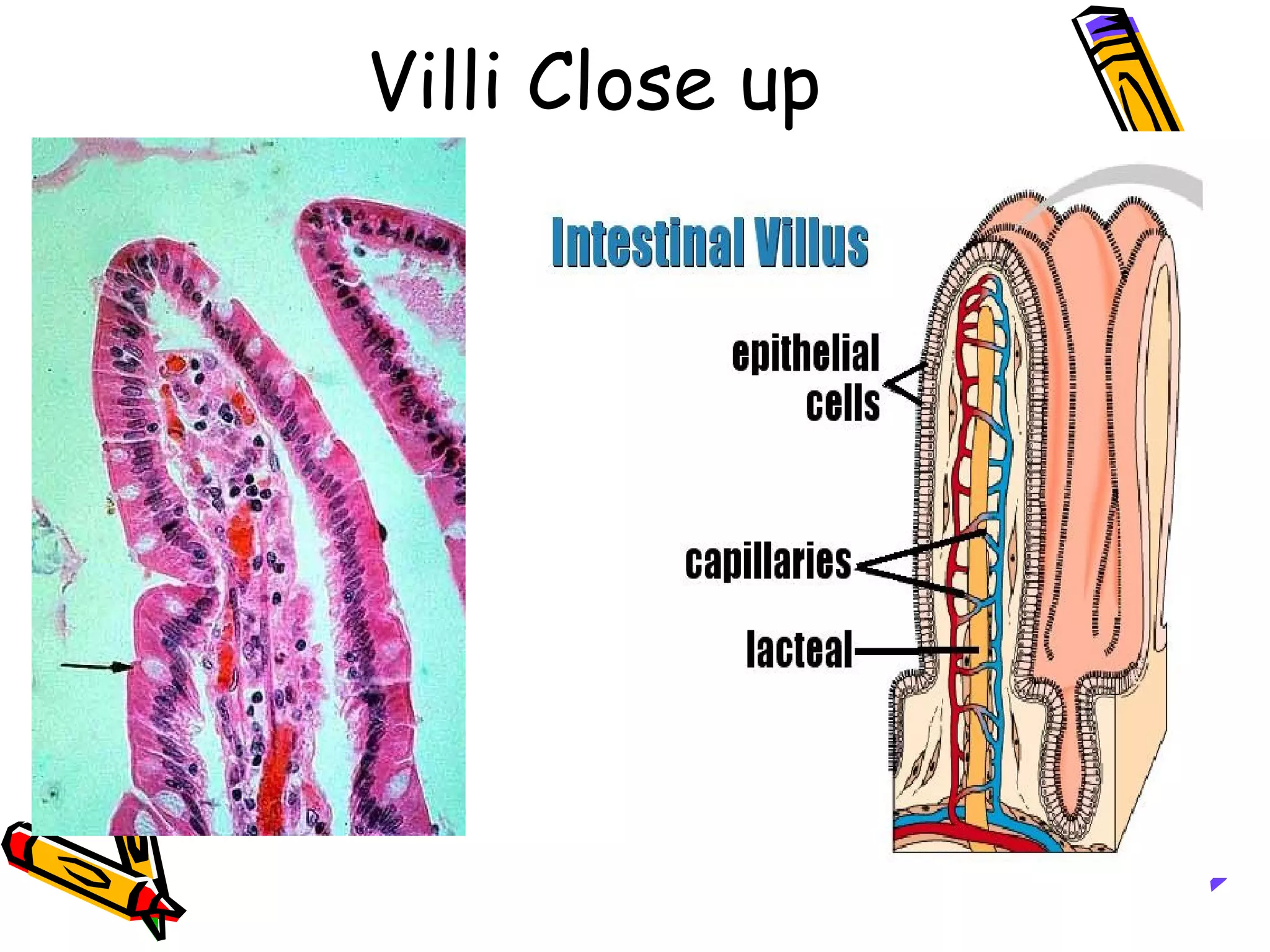
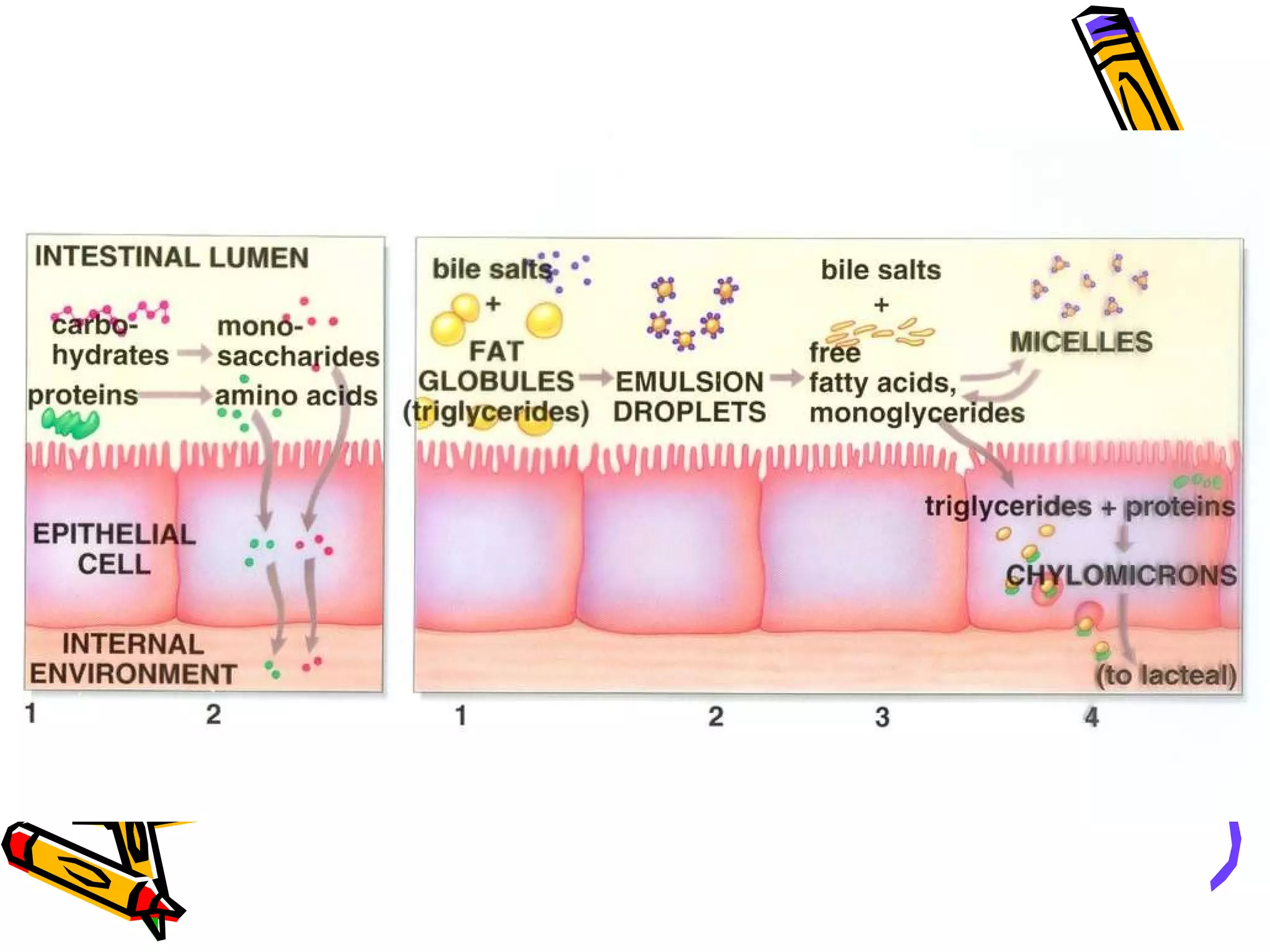
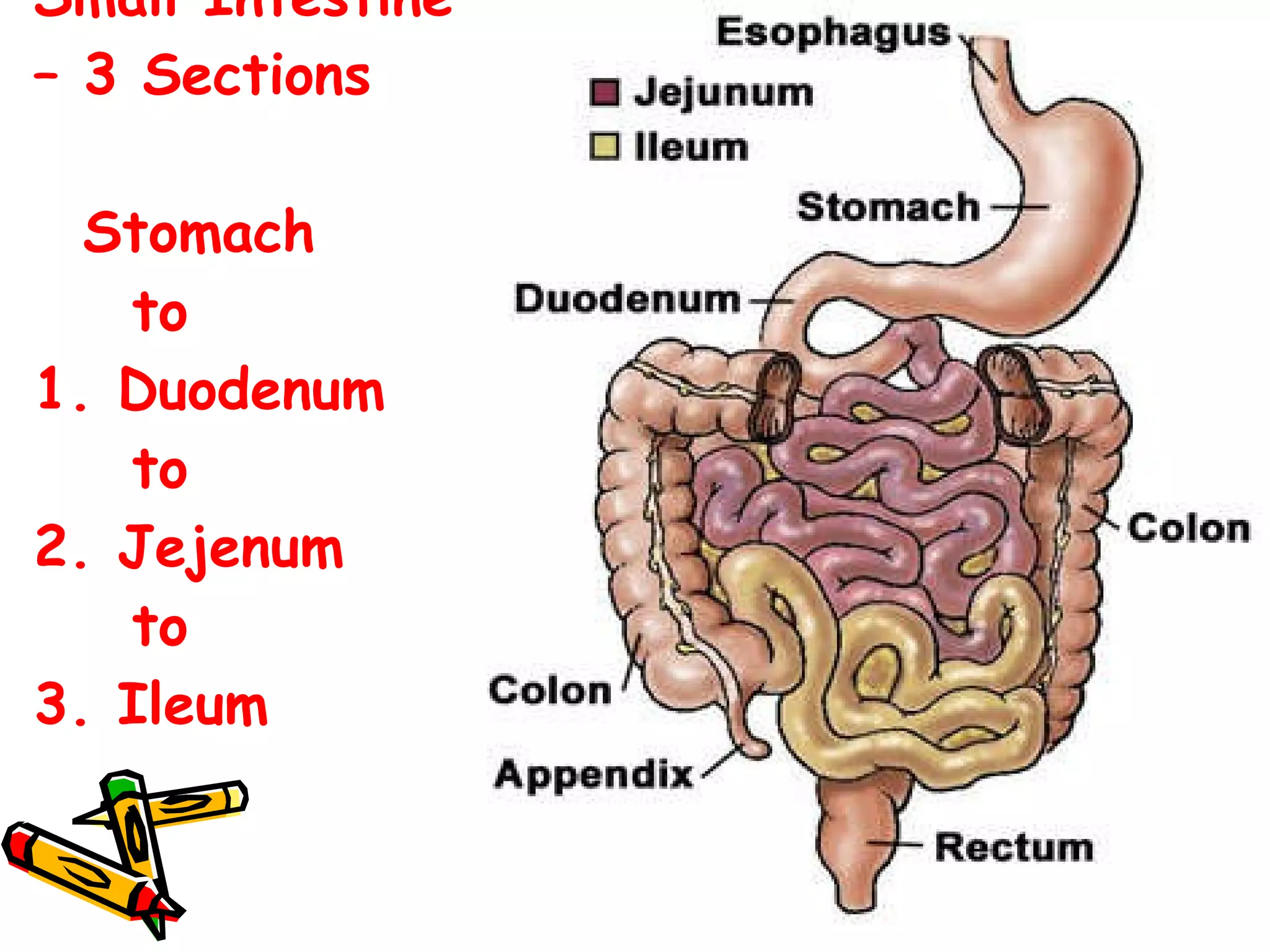
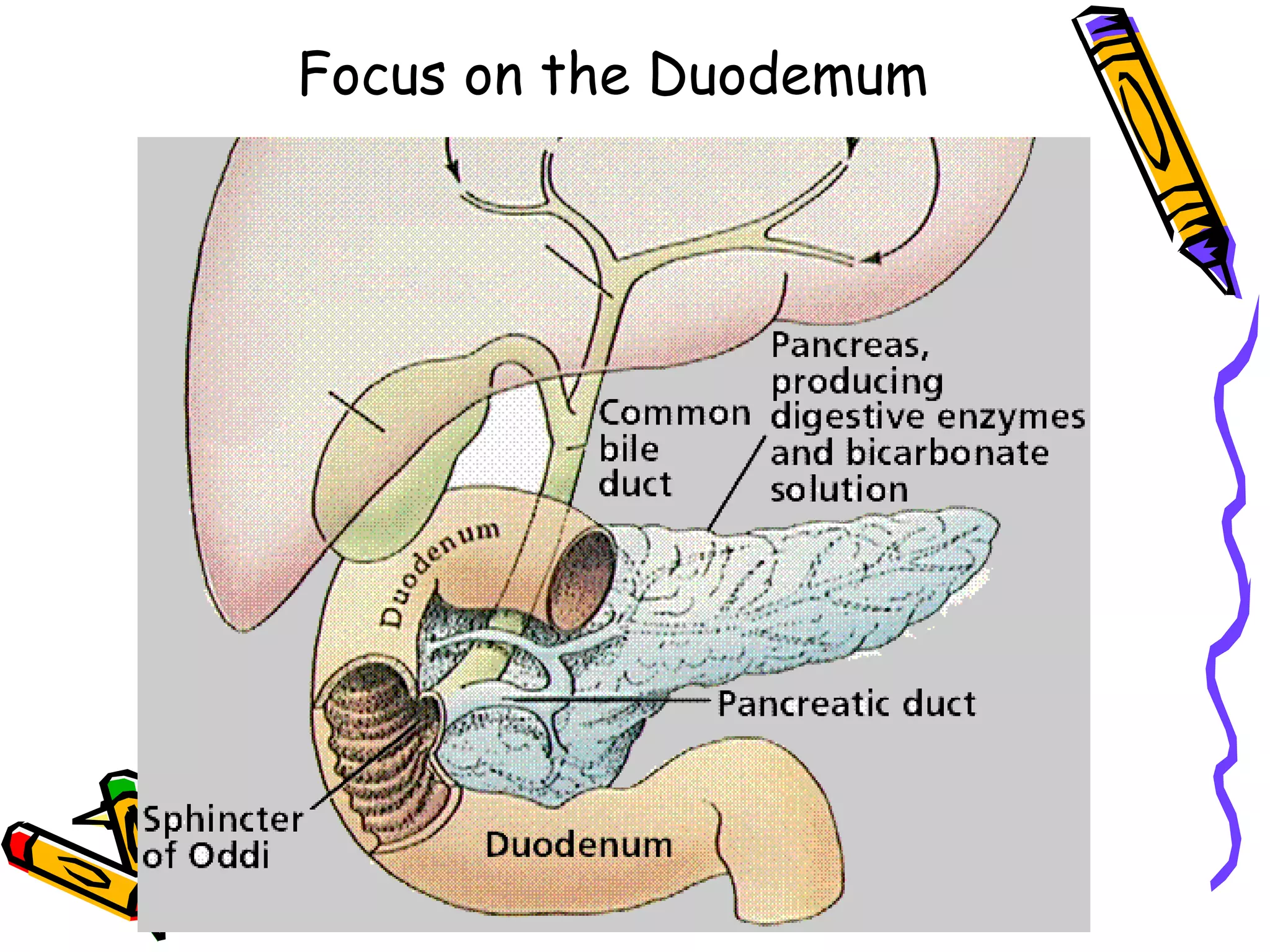
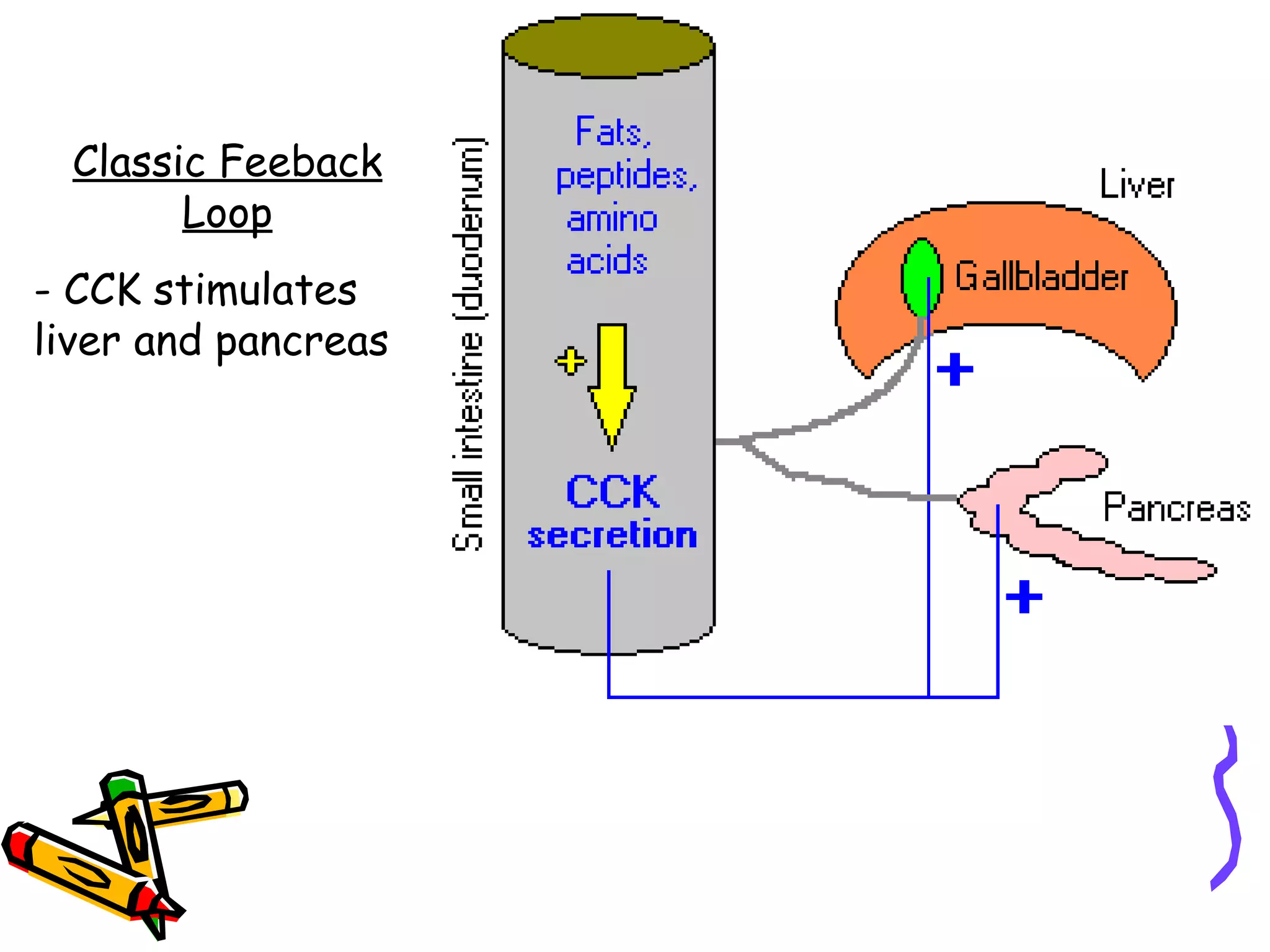
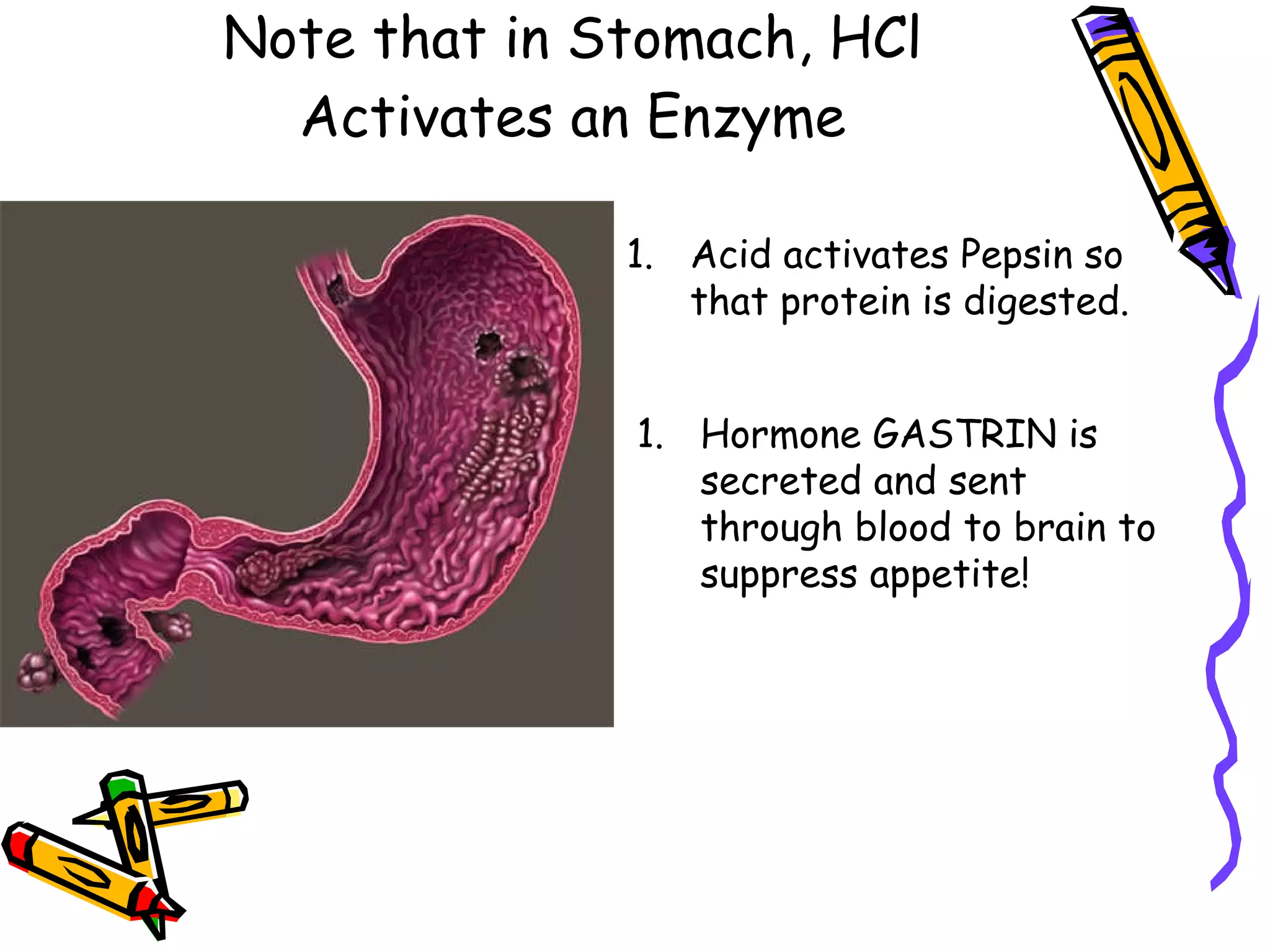
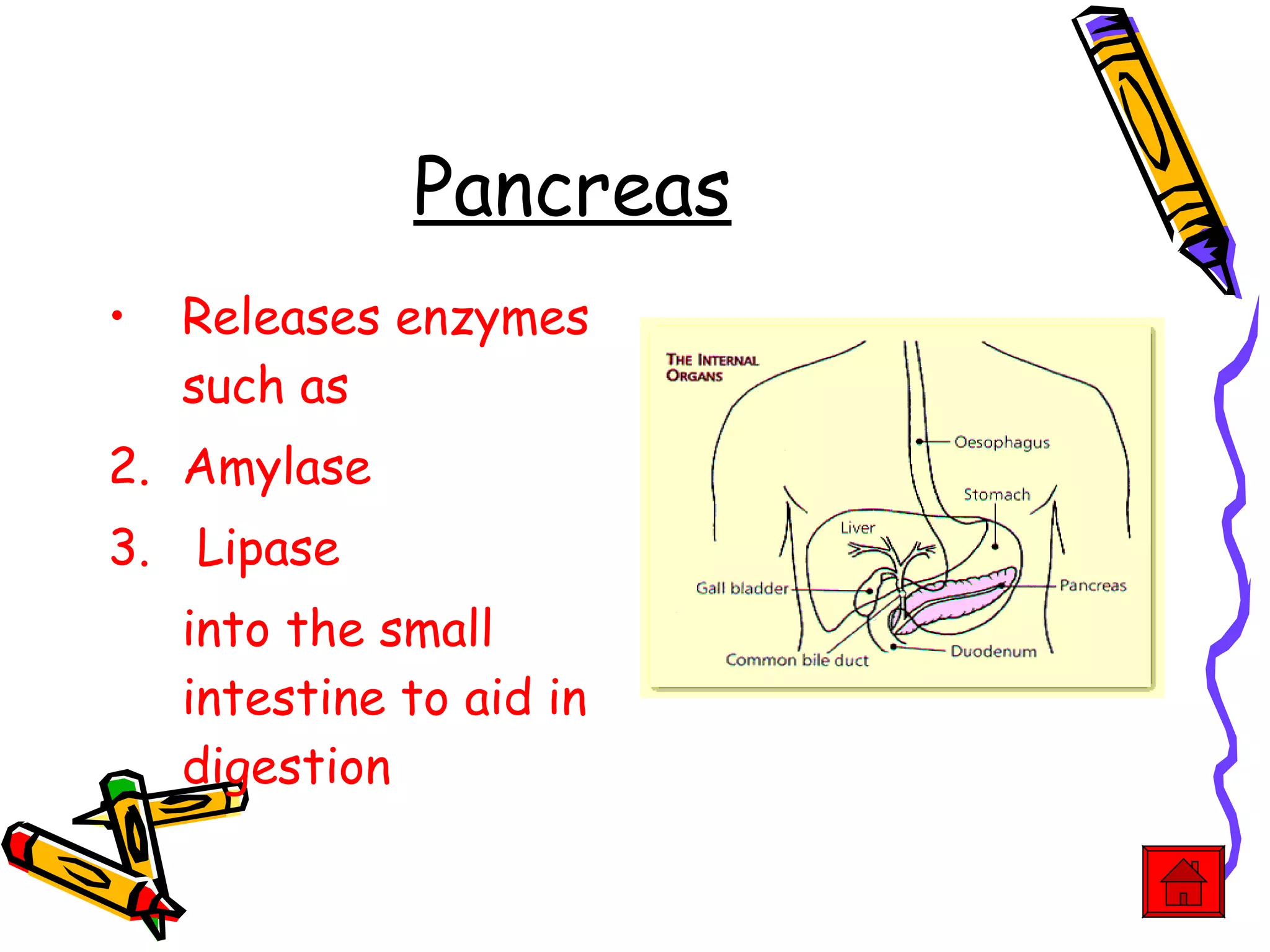
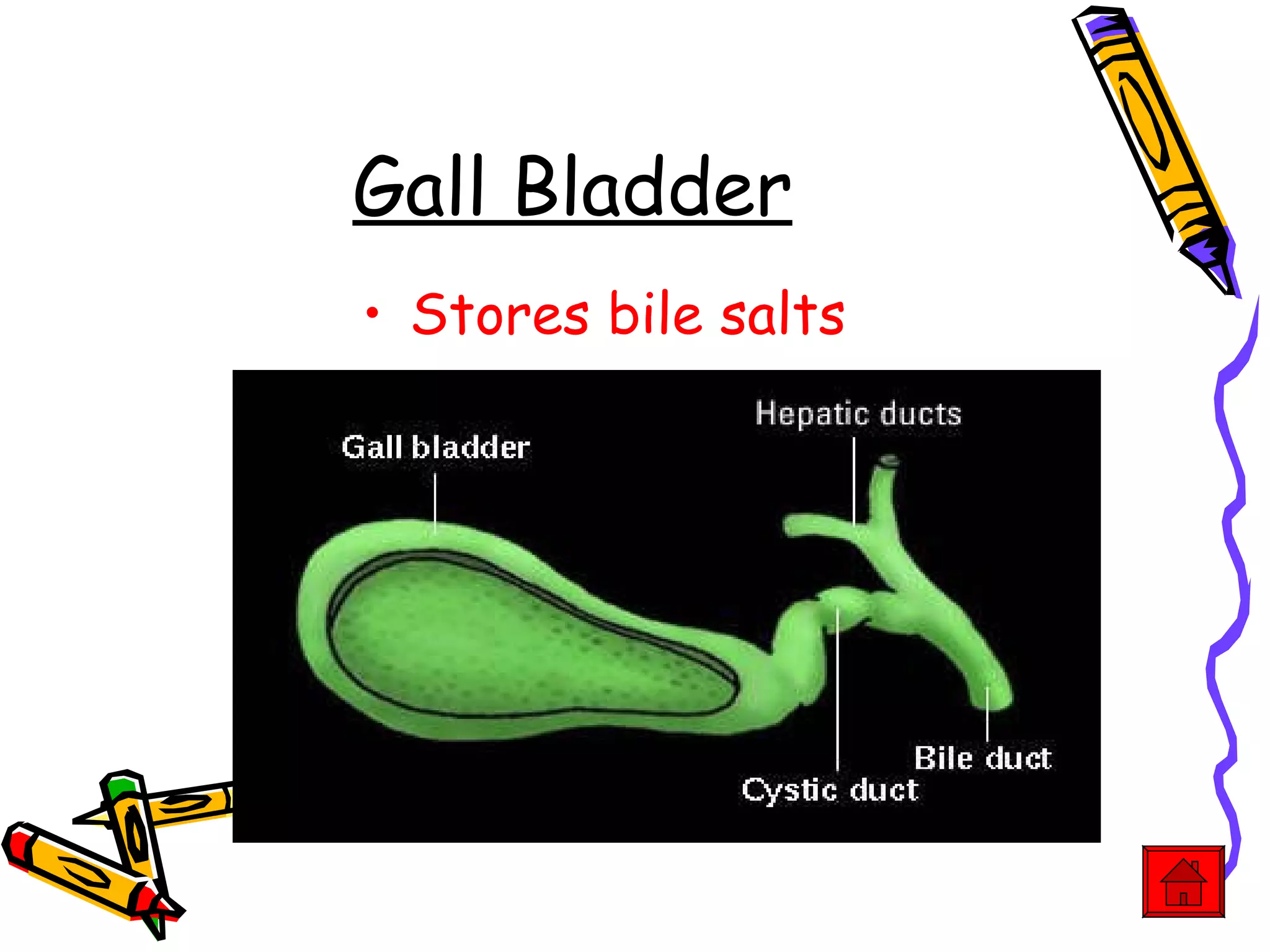
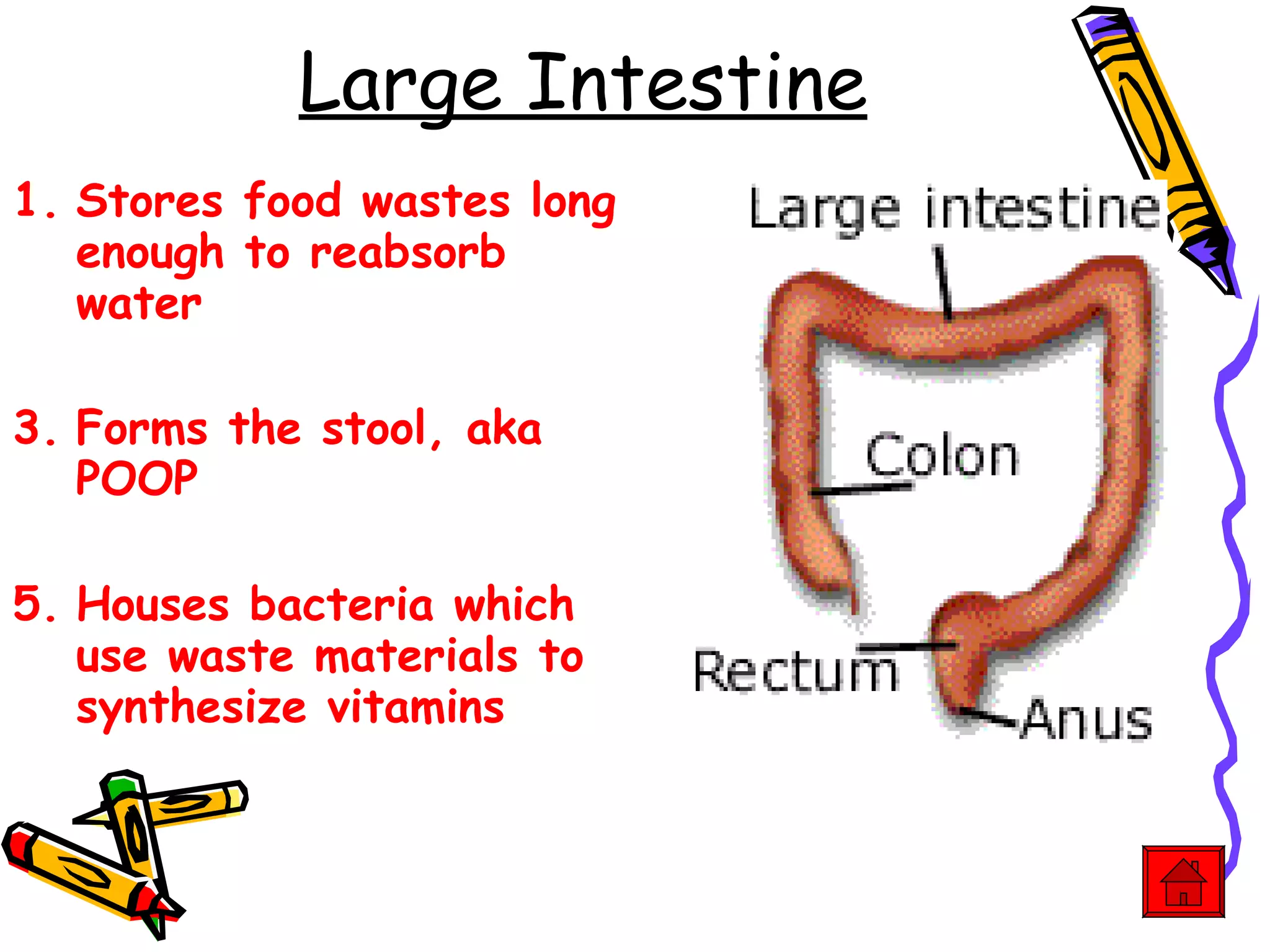
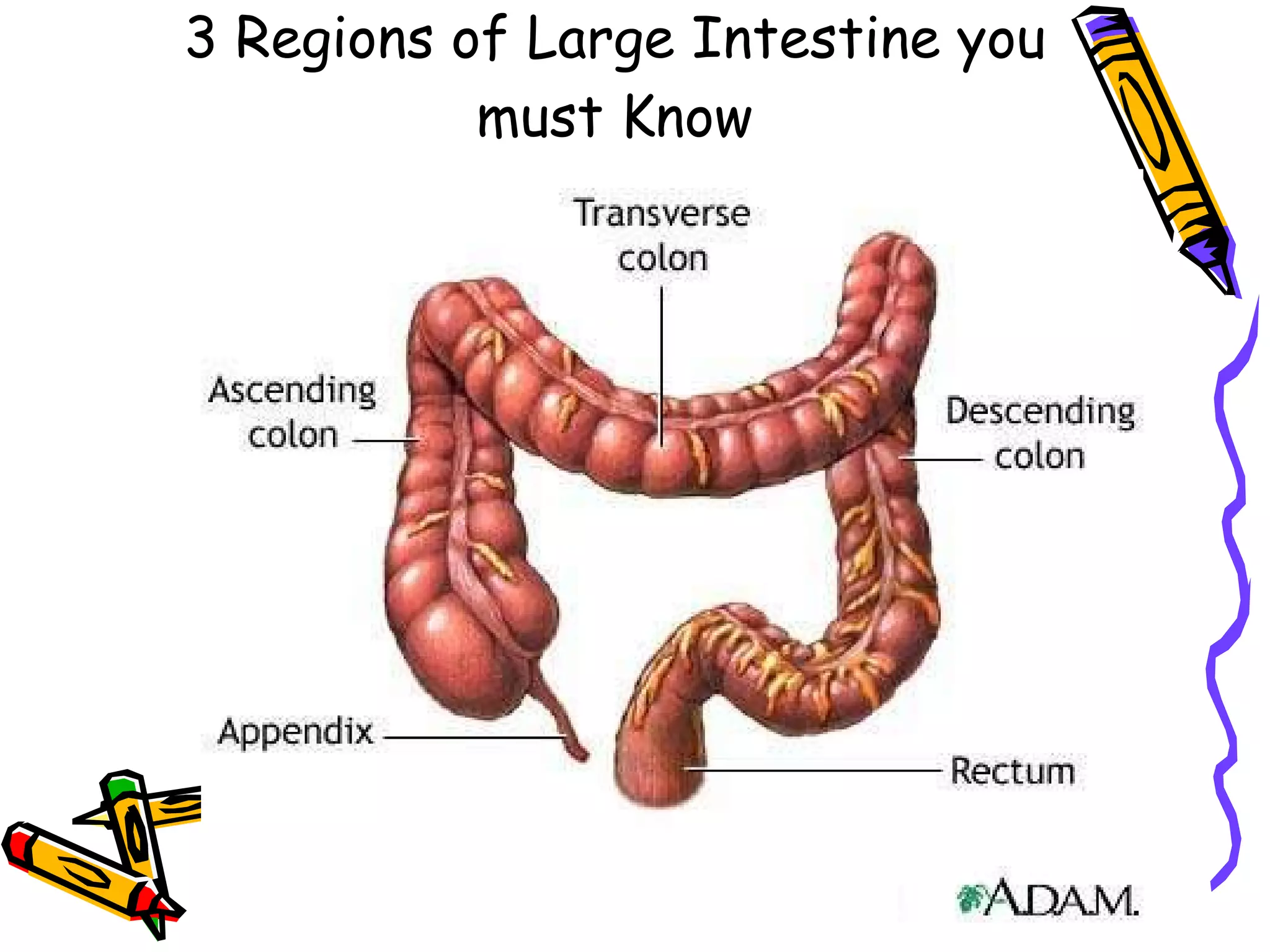
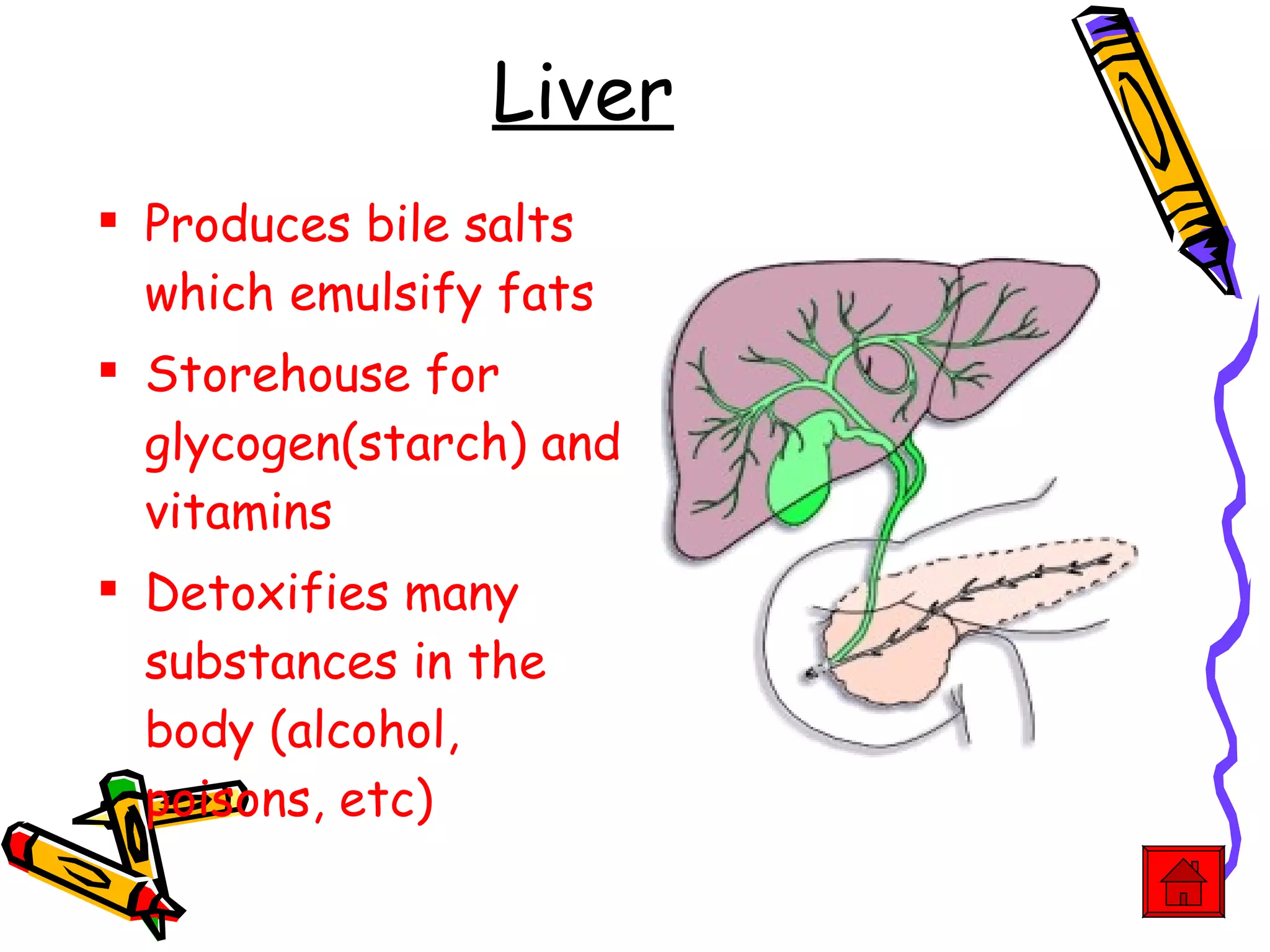The document provides an overview of the human digestive system, including its main components and functions. It describes the four main stages of digestion: ingestion, digestion, absorption, and egestion. It then outlines each major organ of the digestive system, including the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, gallbladder and pancreas. It explains the roles and processes that occur in each organ to break down food and absorb nutrients into the bloodstream.