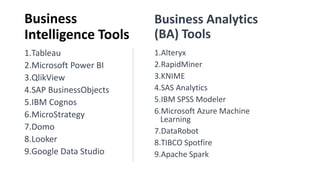
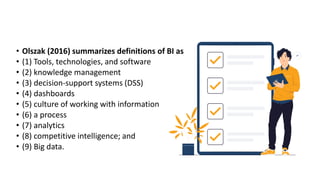
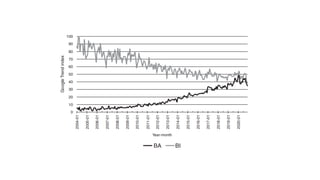
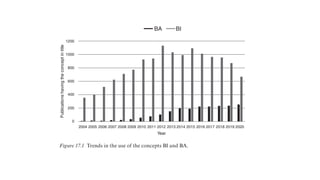
- Business analytics and business intelligence are concepts used for data-driven decision making but there are inconsistent definitions that create confusion.
- While business intelligence traditionally focused on descriptive reporting and operations, business analytics aims to provide strategic insights through predictive and prescriptive techniques.
- However, both terms are sometimes used interchangeably and it is unclear whether one is a subset of the other. Leading consultancies are shifting away from these terms towards advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and big data.
- To reduce conceptual confusion, the chapter proposes focusing solely on the term "analytics" which refers clearly to generating insights from data through a structured process to inform decision making.