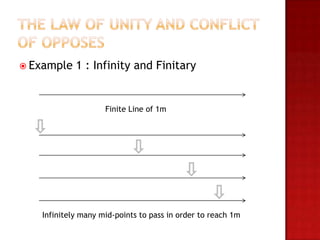
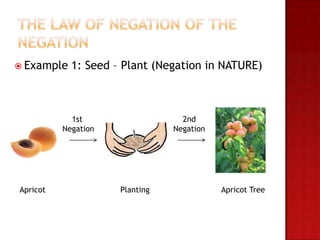
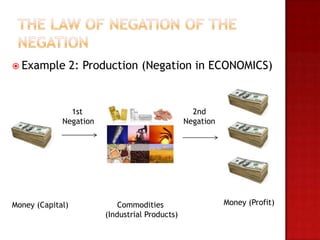
This document outlines the key concepts of dialectical materialism including dialectics, materialism, and Engels' three laws of dialectics. It defines dialectical materialism as the view that ideas and thoughts change due to the movement and existence of matter. Materialism holds that the world is material and phenomena consist of matter in motion according to natural laws. Engels' three laws of dialectics are described as the law of unity and conflict of opposes, the law of passage of quantitative to qualitative changes, and the law of negation of the negation. Examples are provided for each law.





![ Materialism is a realist philosophy of
science, which holds that the world is
material; all phenomena in the universe
consist of “matter in motion” according to
natural laws.
Materialism asserts the primacy of the
material world: matter precedes thought.
Thought is a reflection of material world.
“The ideal is nothing else than the material world reflected by the
human mind, and translated into forms of thought.” [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diyalektikmateryalizmsunus-130306054125-phpapp01/85/Dialectical-Materialism-6-320.jpg)





![ Wikipedia. Dialectical Materialism
Diyalektik
Materyalizme Giriş. August
Thalheimer.
On the Negation of the Negation. Dave Muller
[1] – K. MARX . Das Kapital, vol. 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diyalektikmateryalizmsunus-130306054125-phpapp01/85/Dialectical-Materialism-15-320.jpg)
