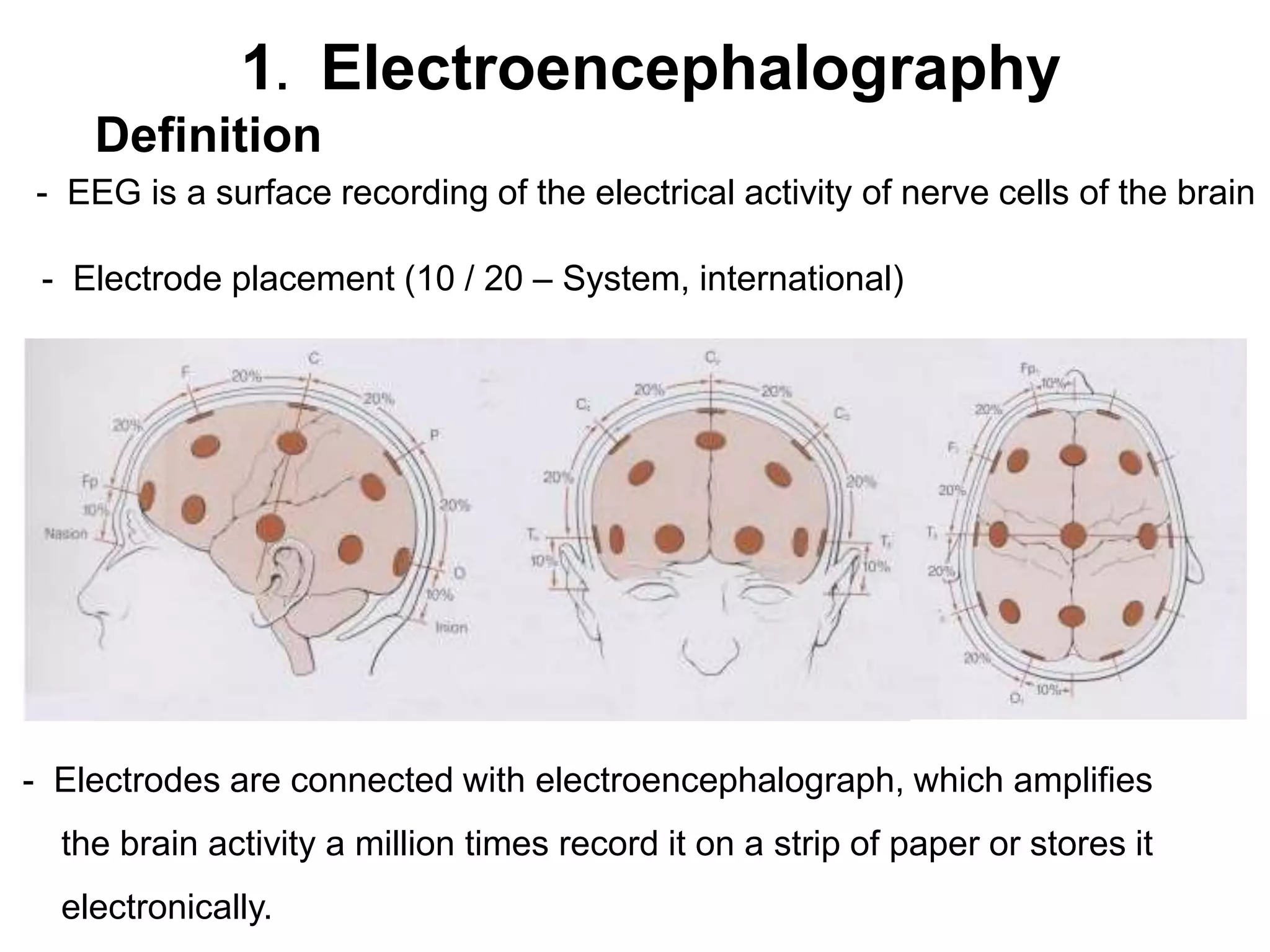
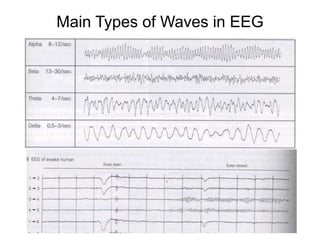
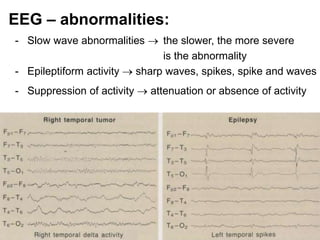
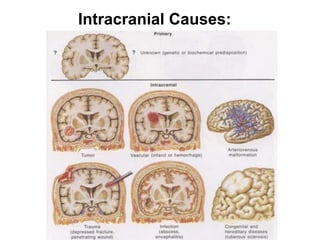
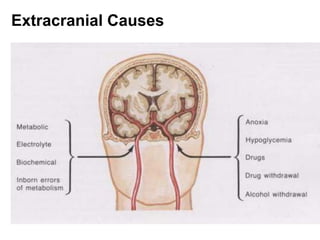
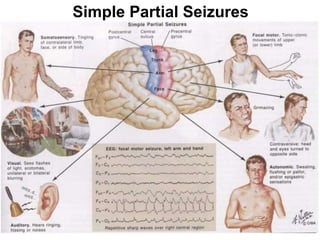
EEG is a recording of the electrical activity of the brain using electrodes placed on the scalp. It amplifies brain activity millions of times to detect normal wave patterns like alpha and beta activity in awake patients, and spindle activity during sleep. Abnormalities include slow wave activity indicating severity, epileptiform sharp waves or spikes, and signal suppression. EEG is used to diagnose seizure disorders, evaluate transient spells, detect intracranial diseases like tumors, and assess diffuse brain issues including comas and brain death.