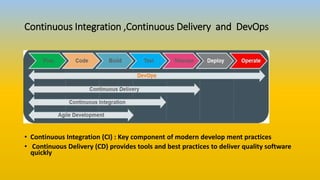
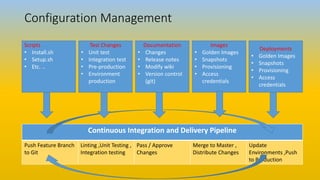
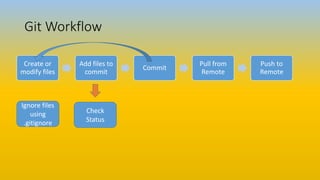
This document provides an overview of DevOps, Git basics, and their relationship. It discusses how DevOps aims to improve collaboration between development and operations teams through practices like continuous integration, continuous delivery, and infrastructure automation. It also introduces some key DevOps terminology. Additionally, it covers the basics of using Git for version control, including tracking files, staging changes, committing, ignoring files, and pushing/pulling from remote repositories.