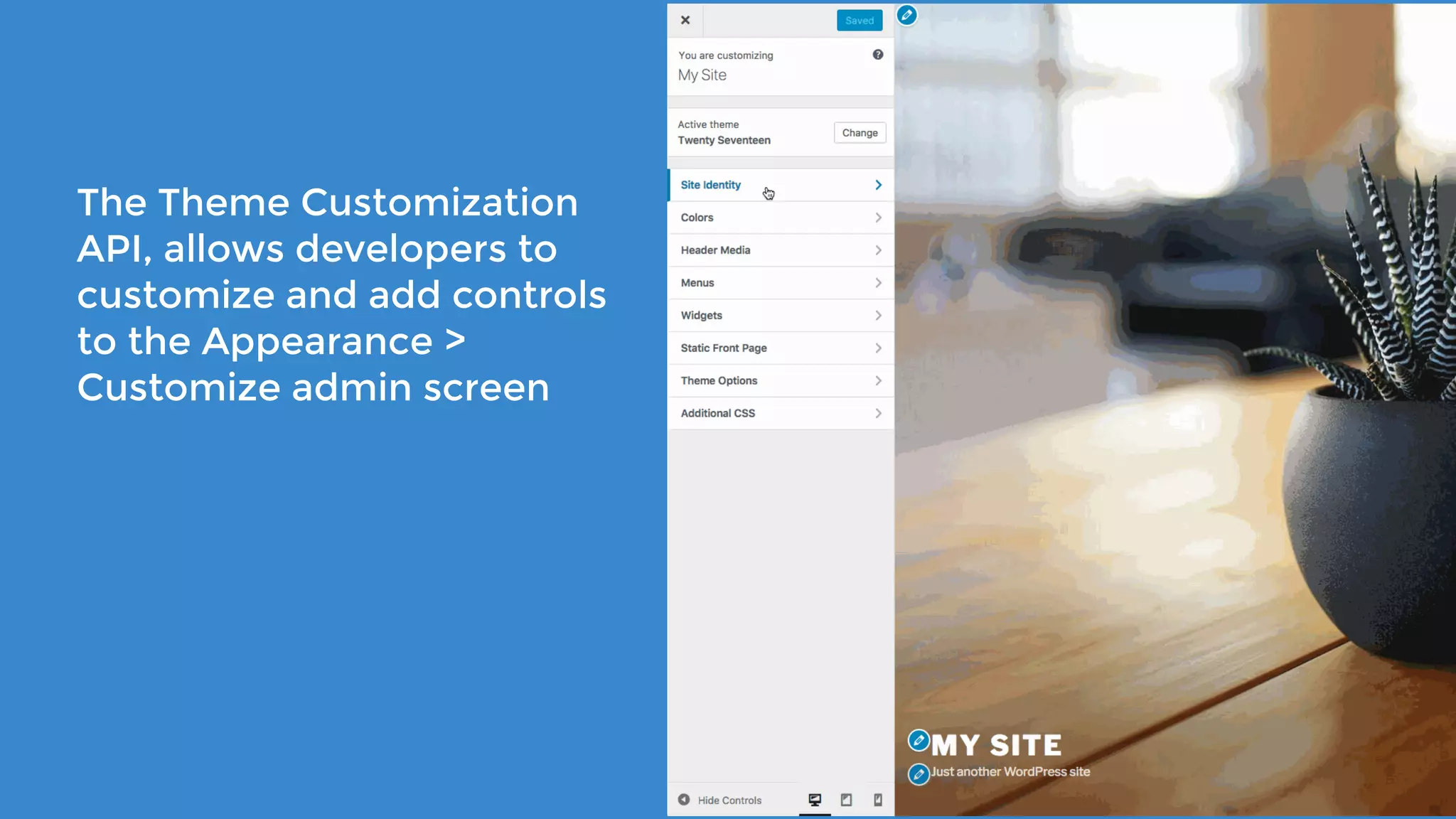
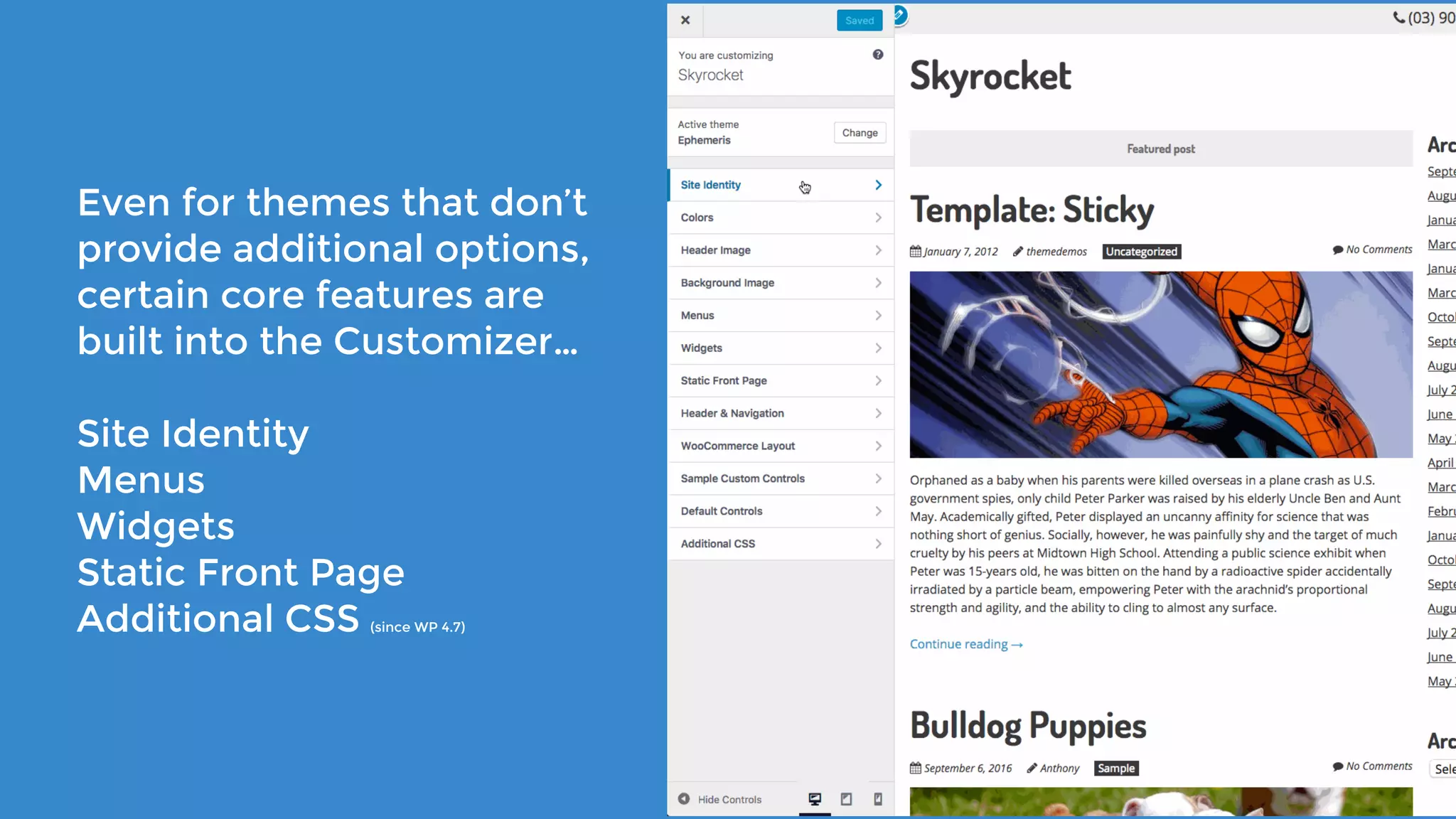
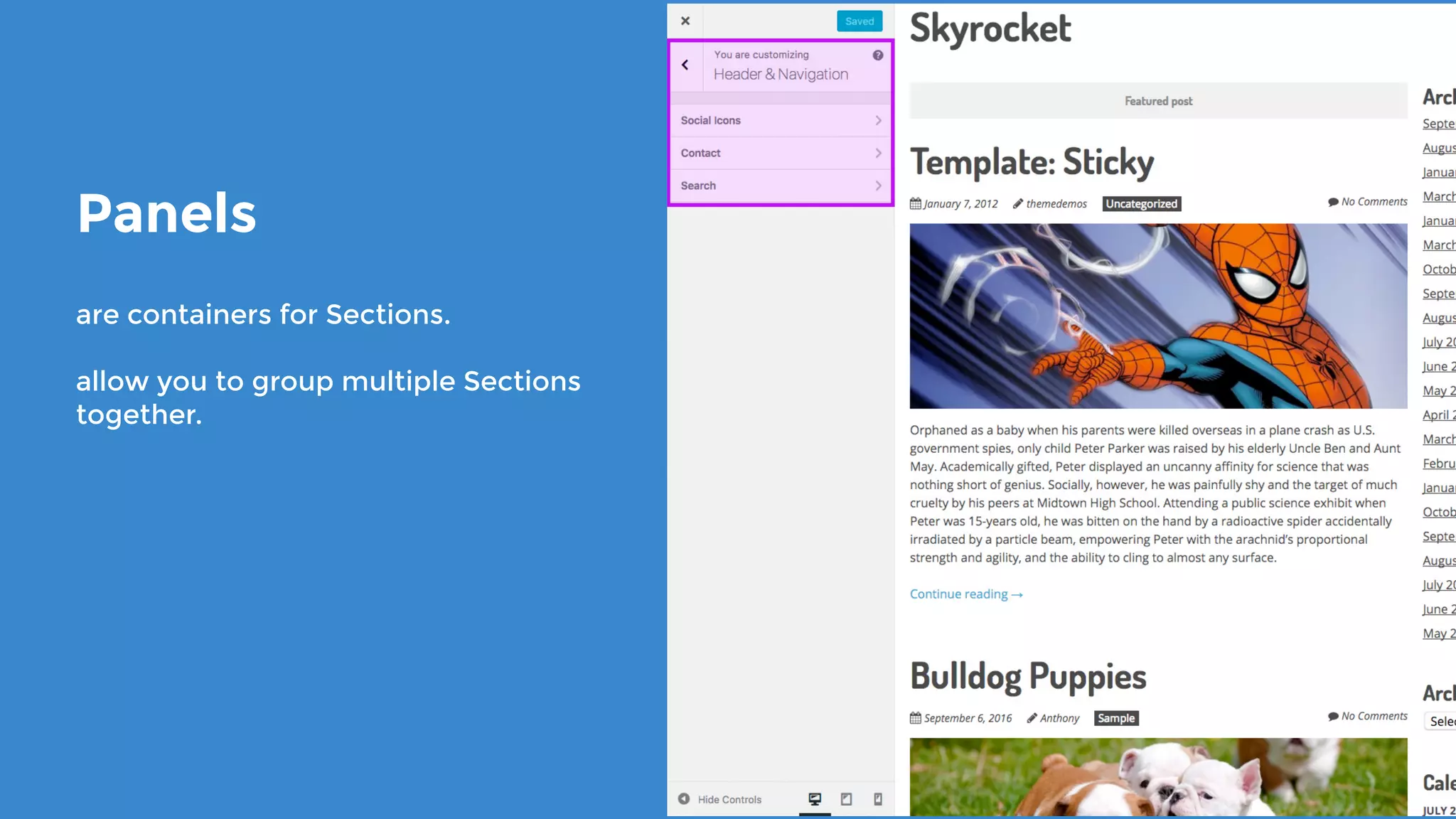
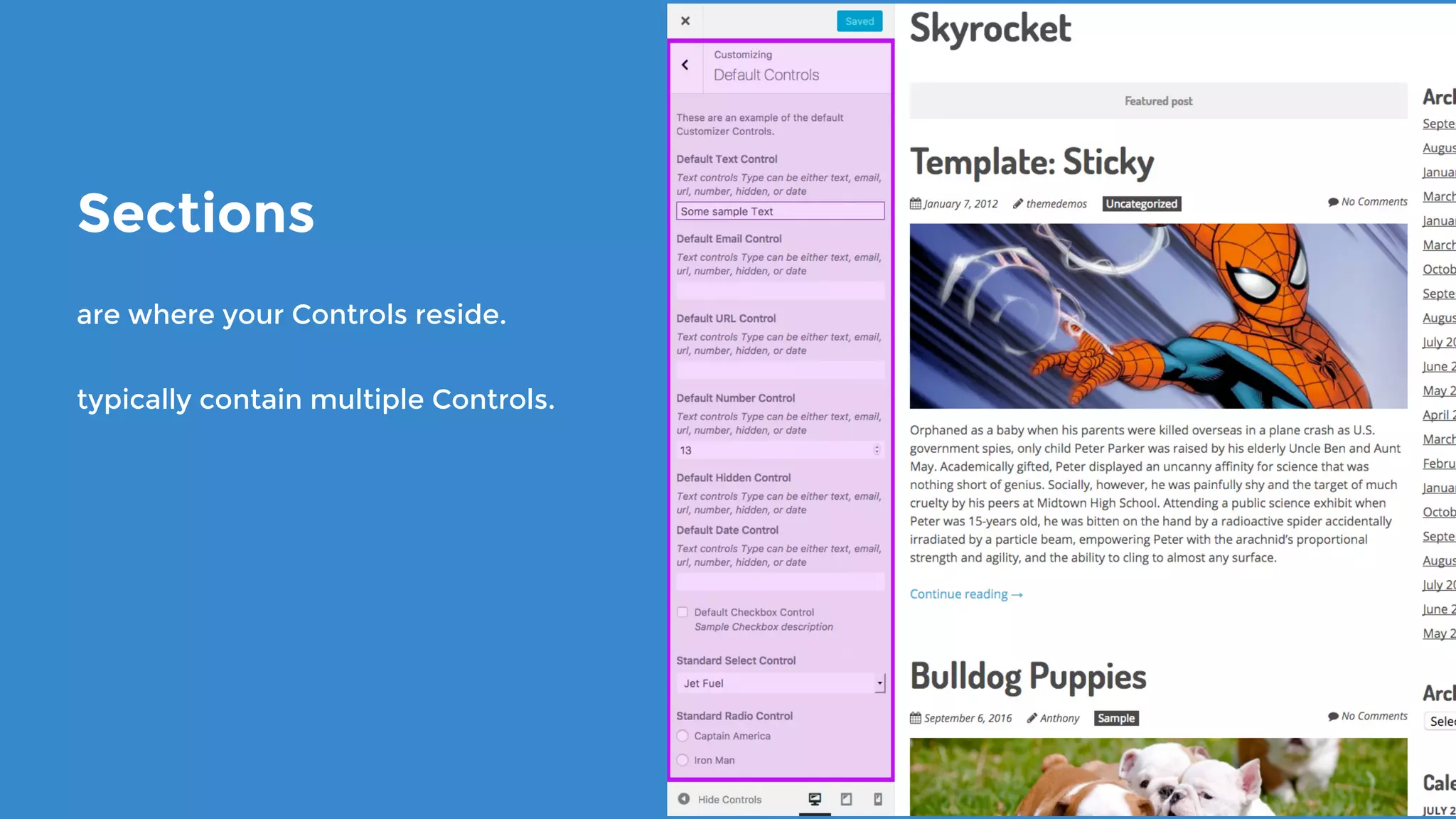
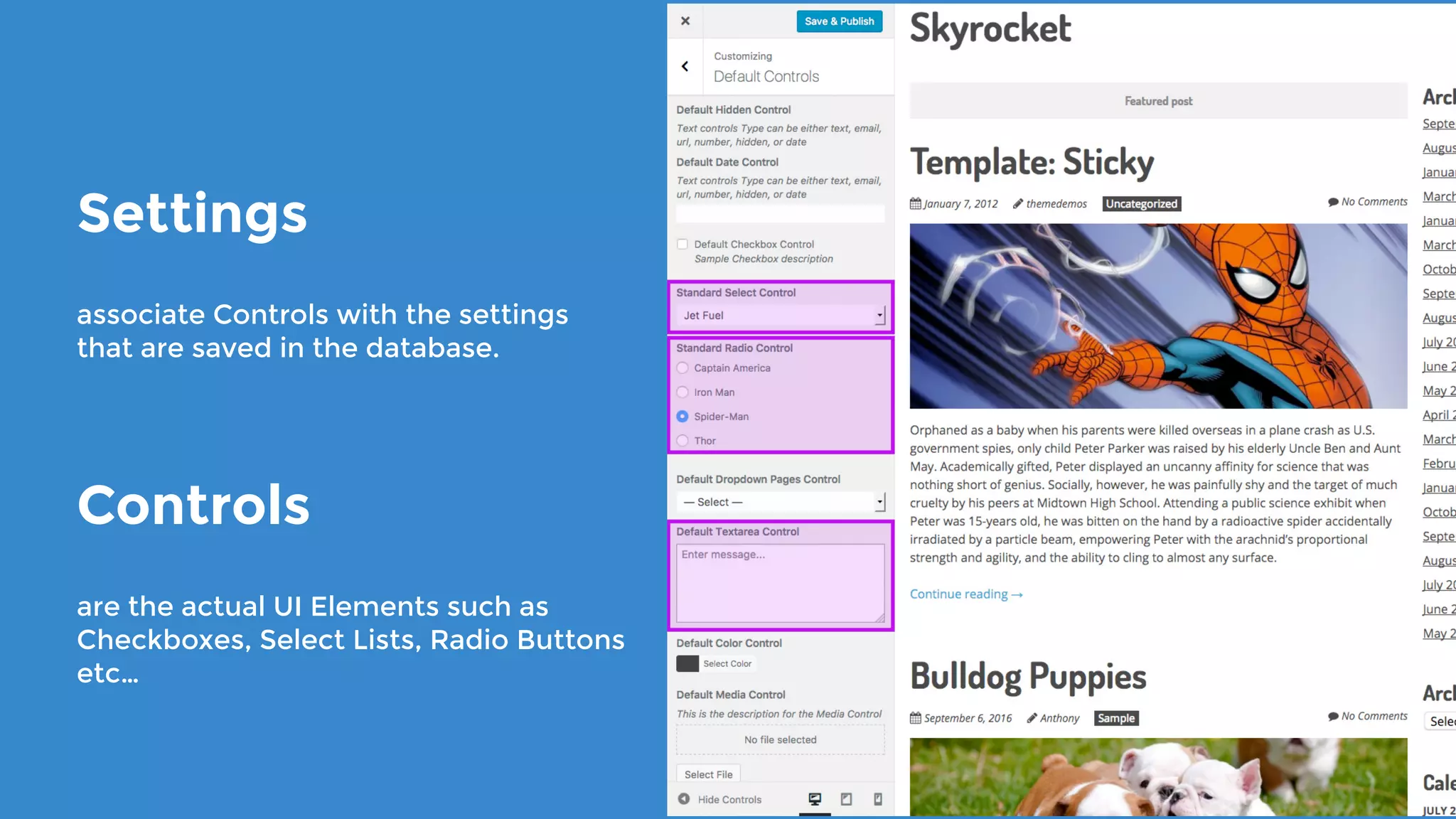
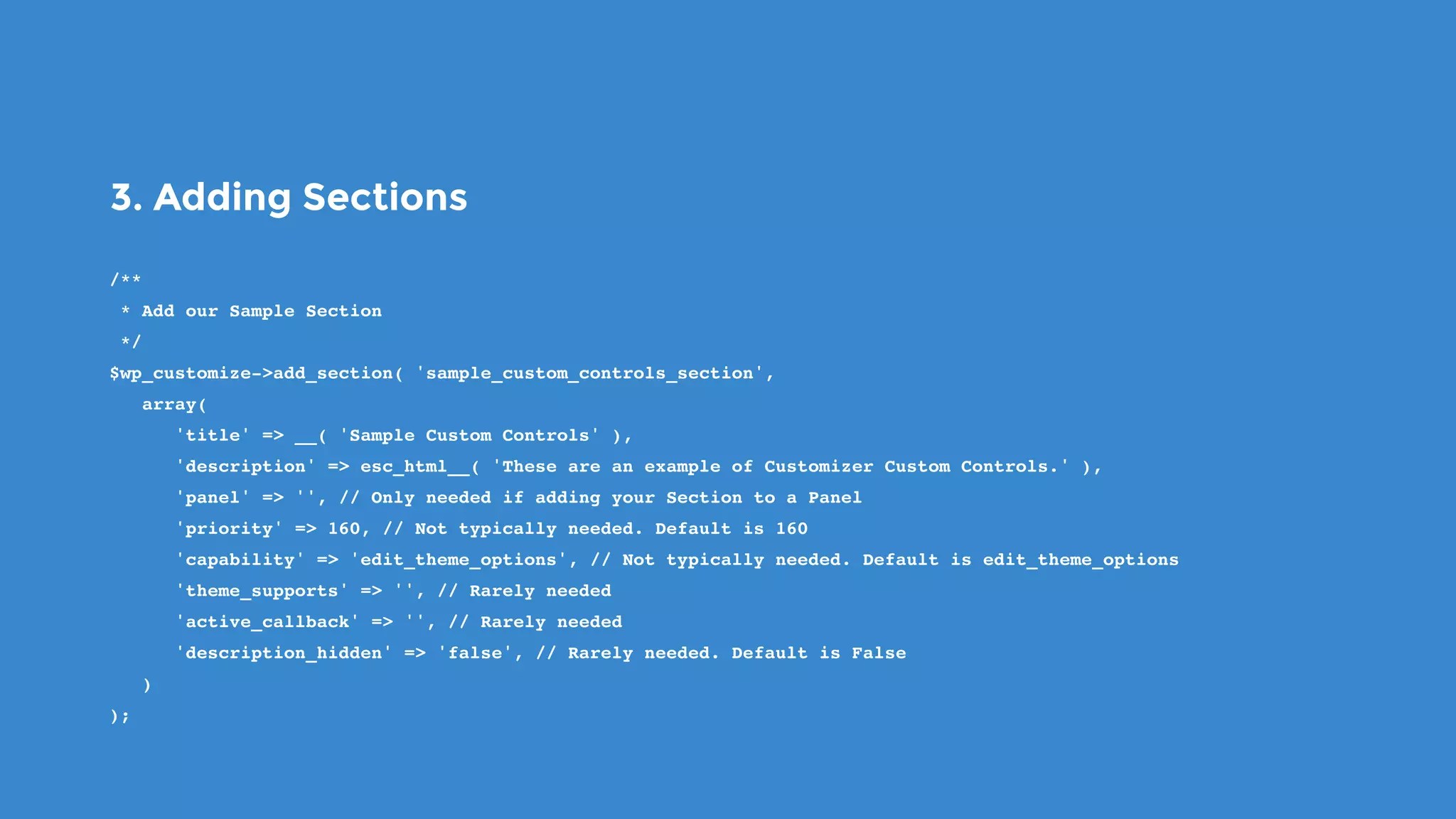
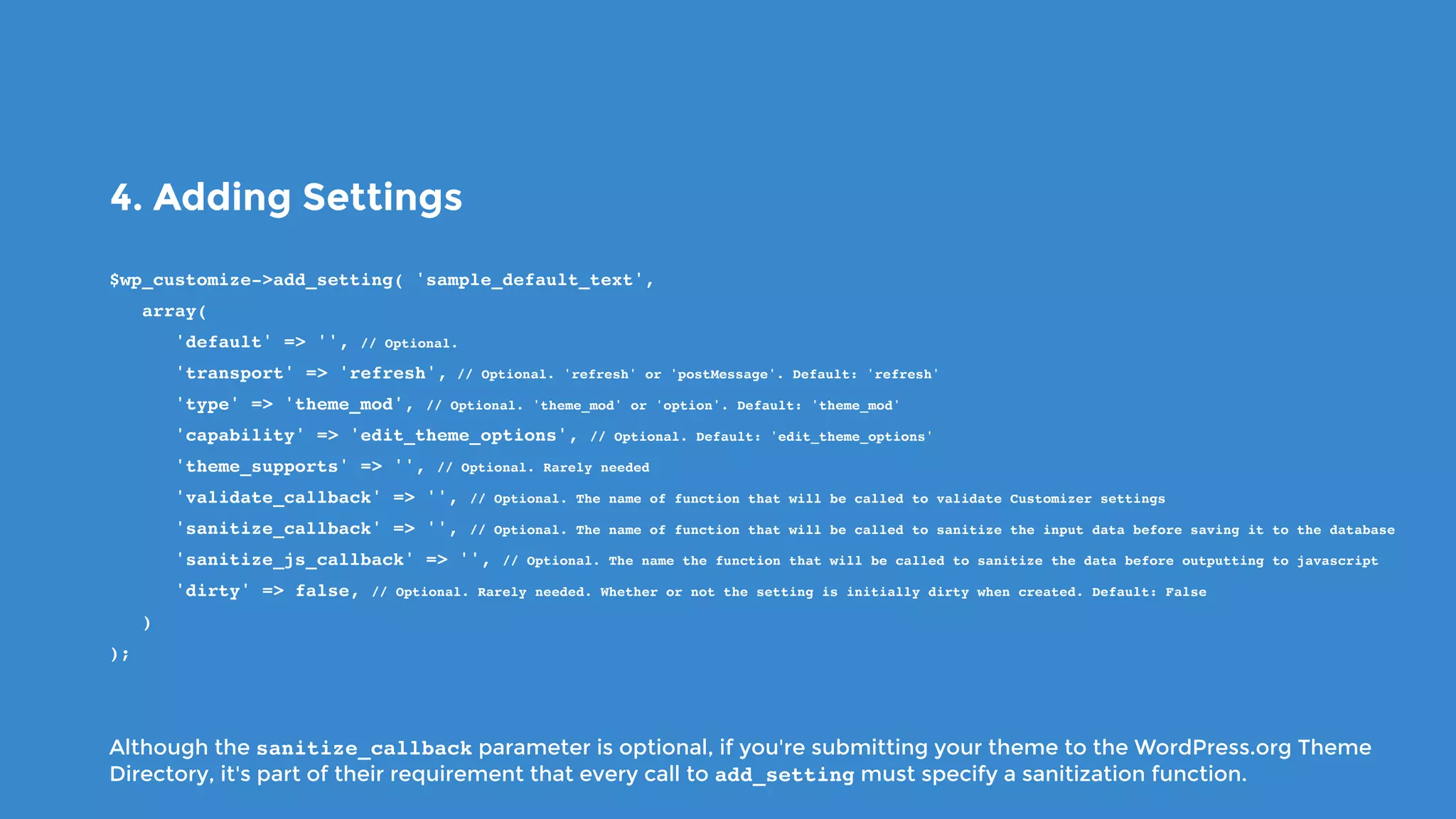
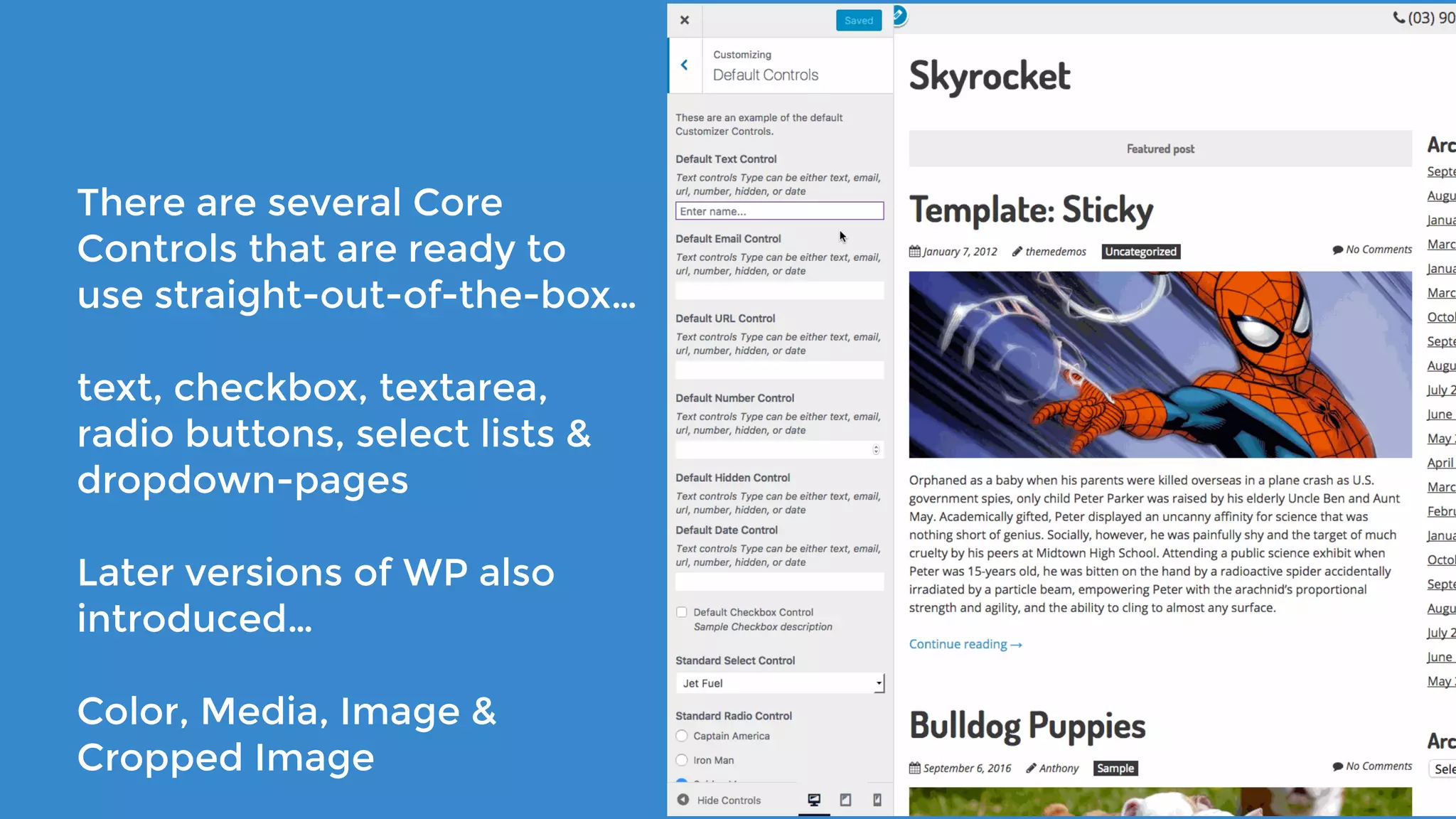
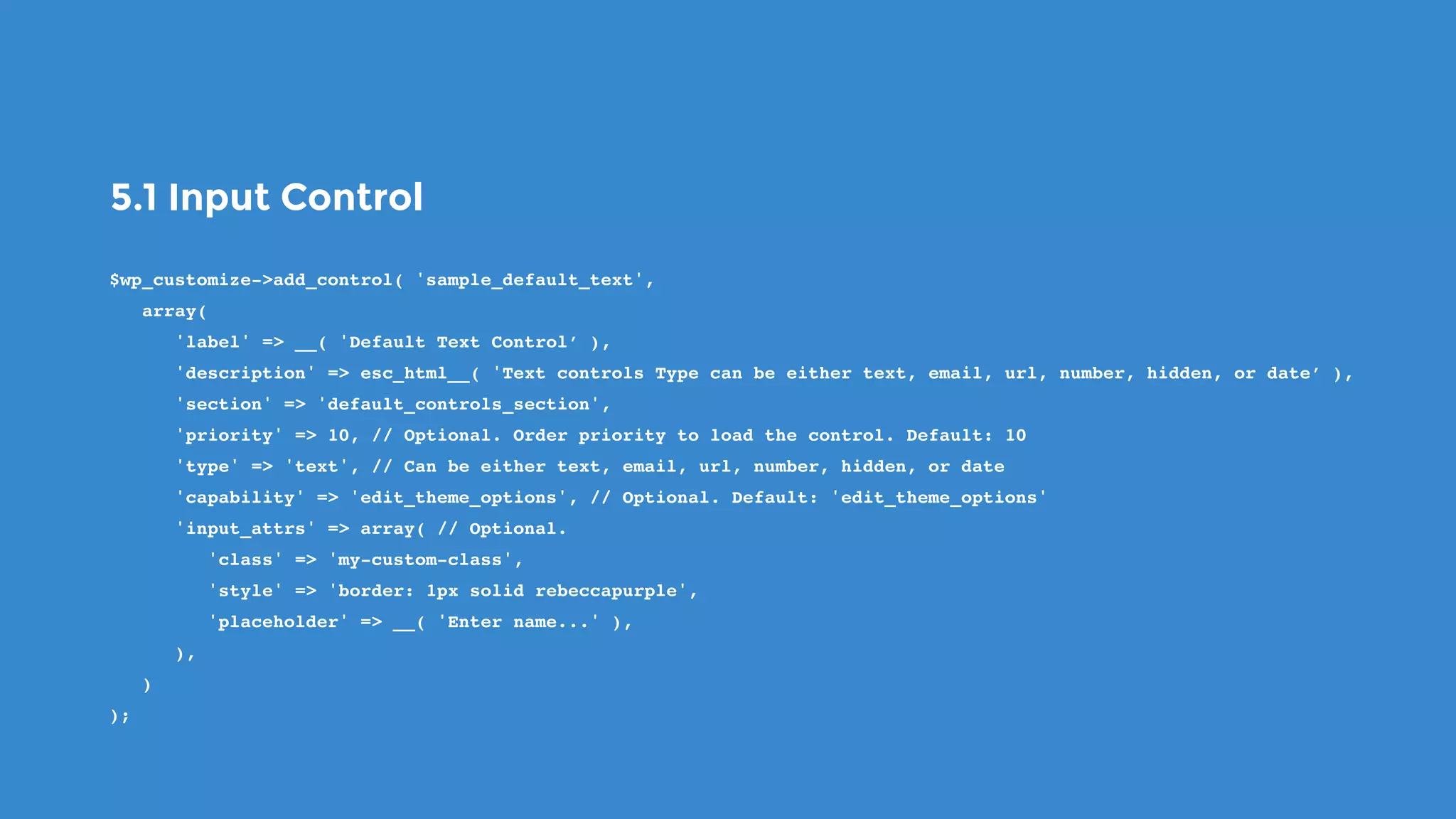
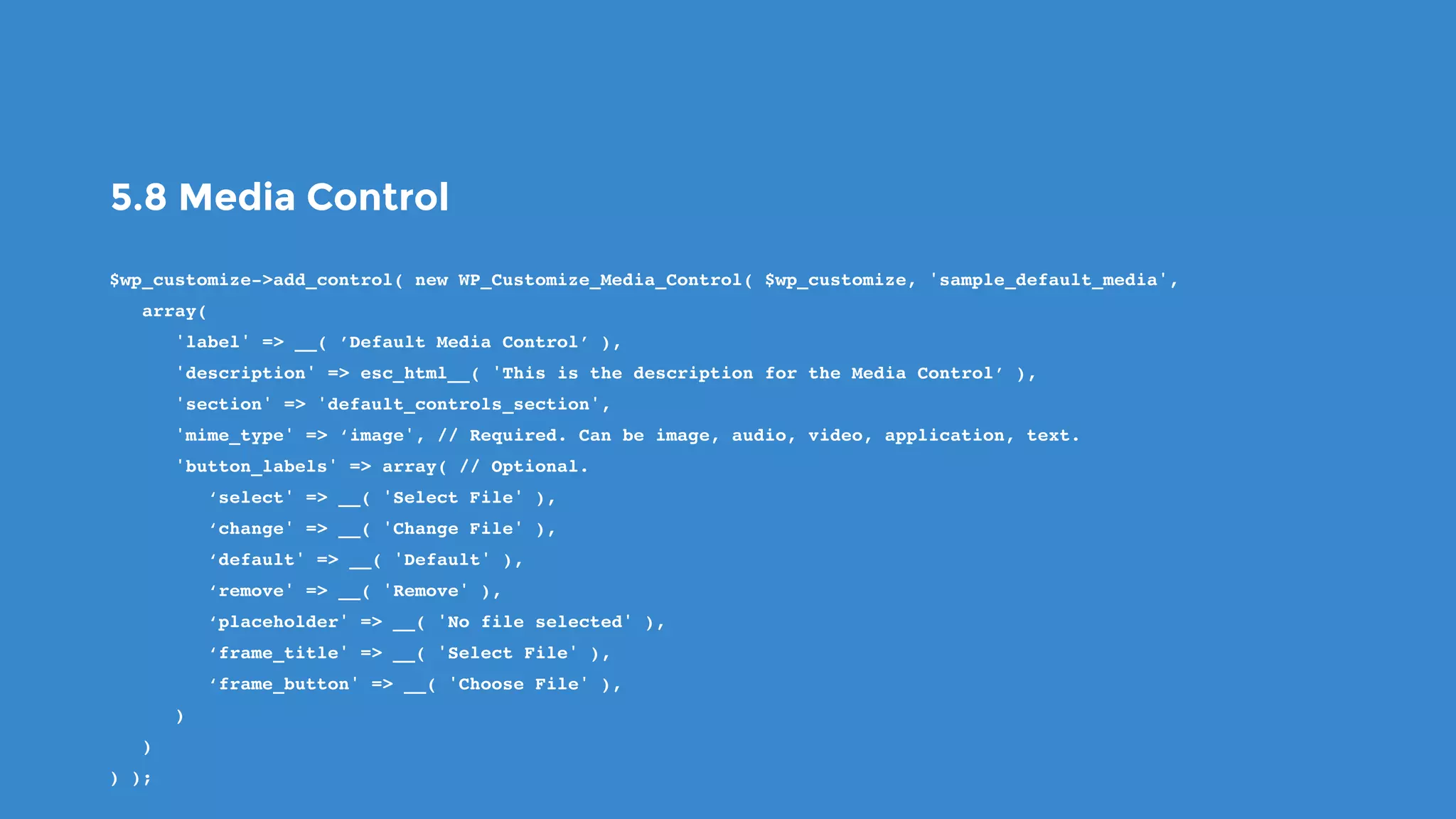
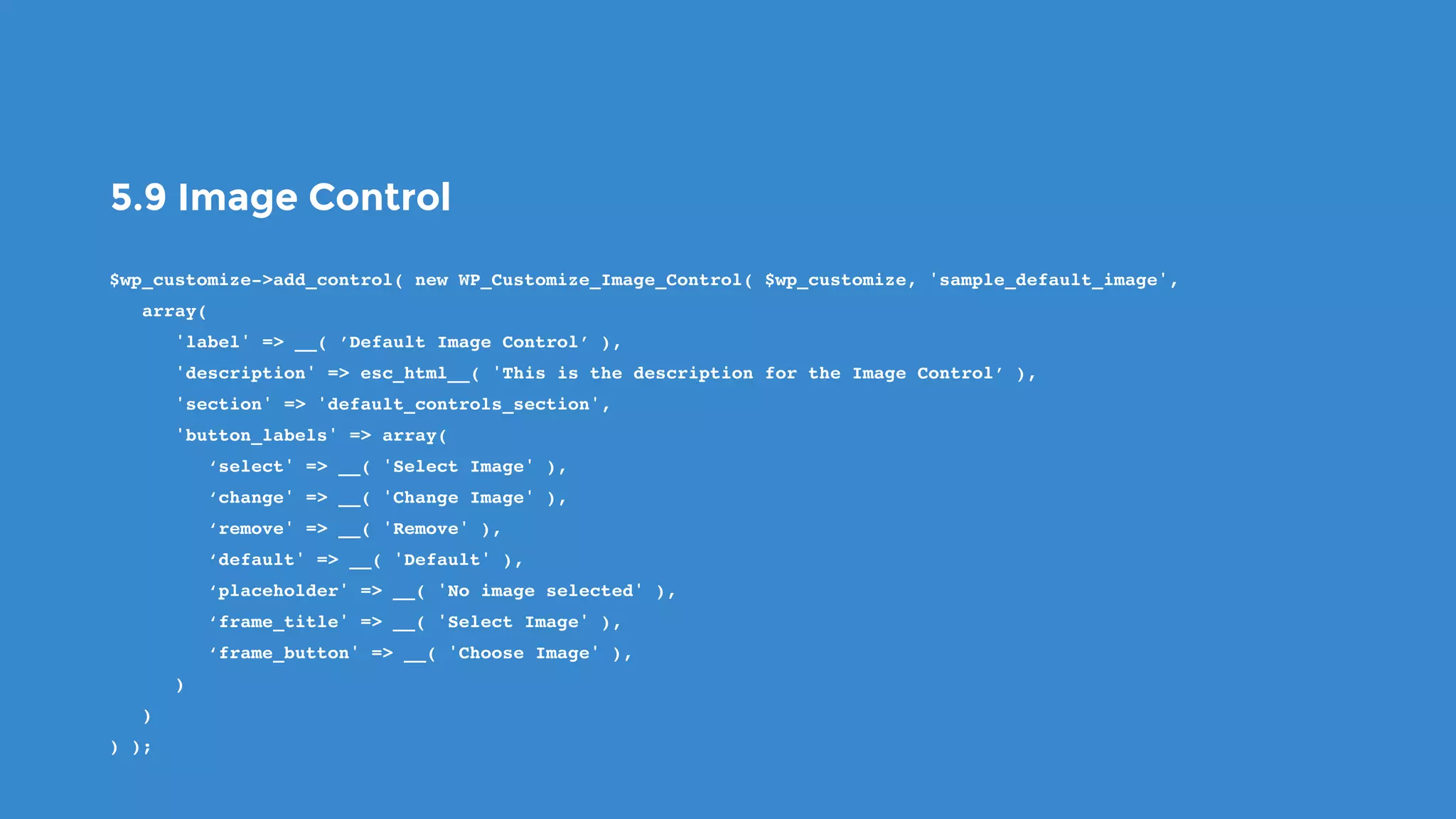
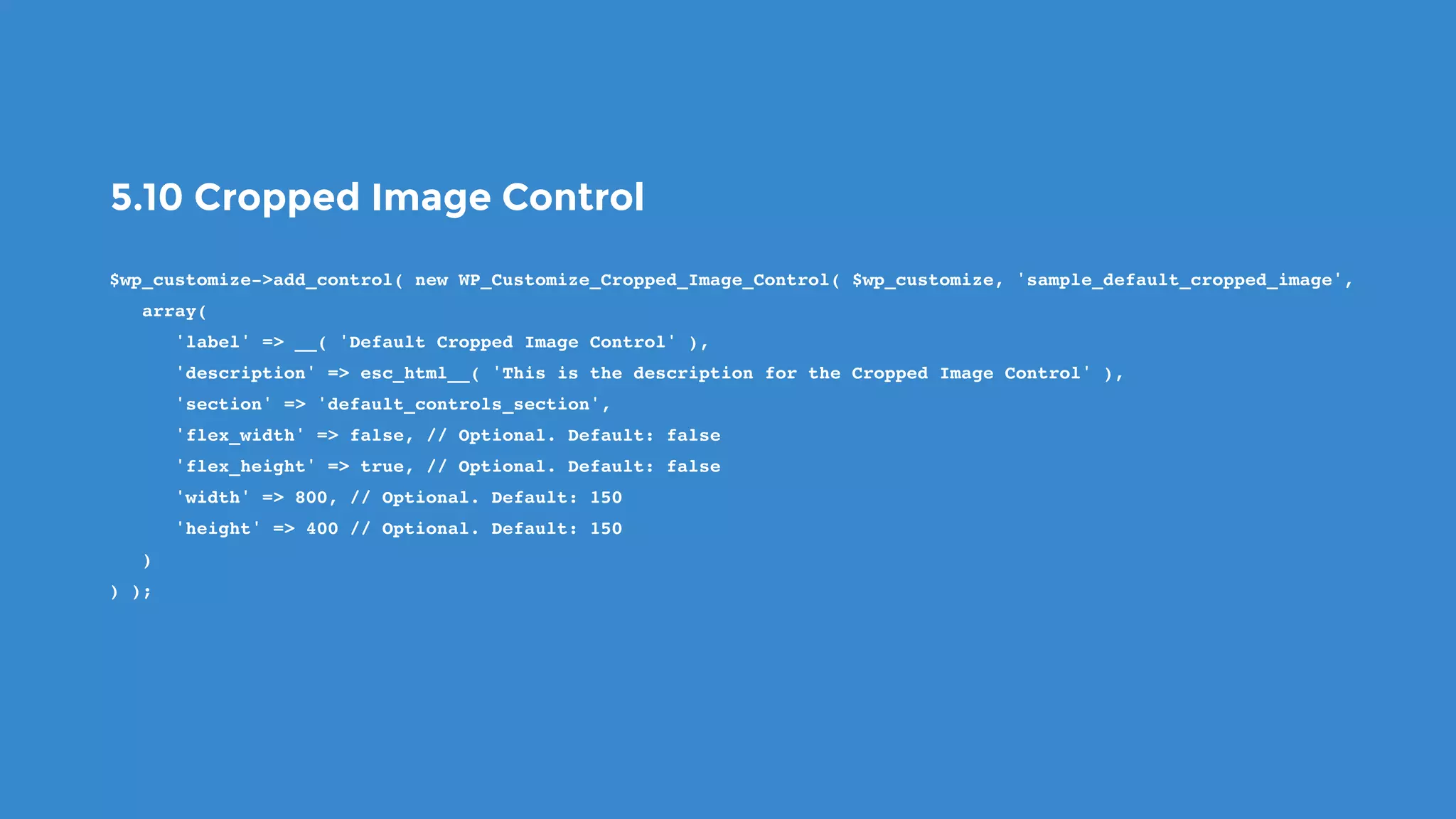
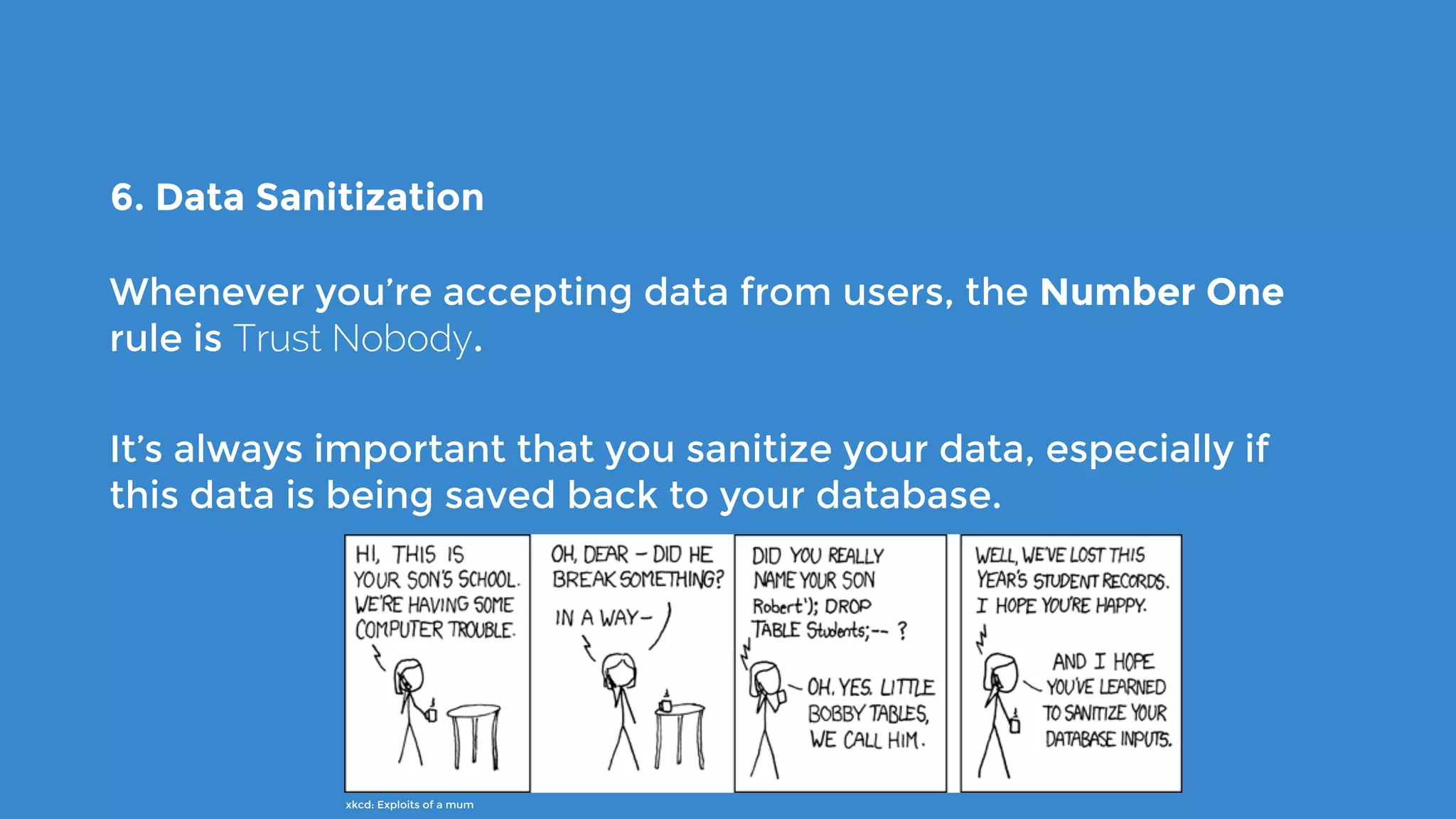
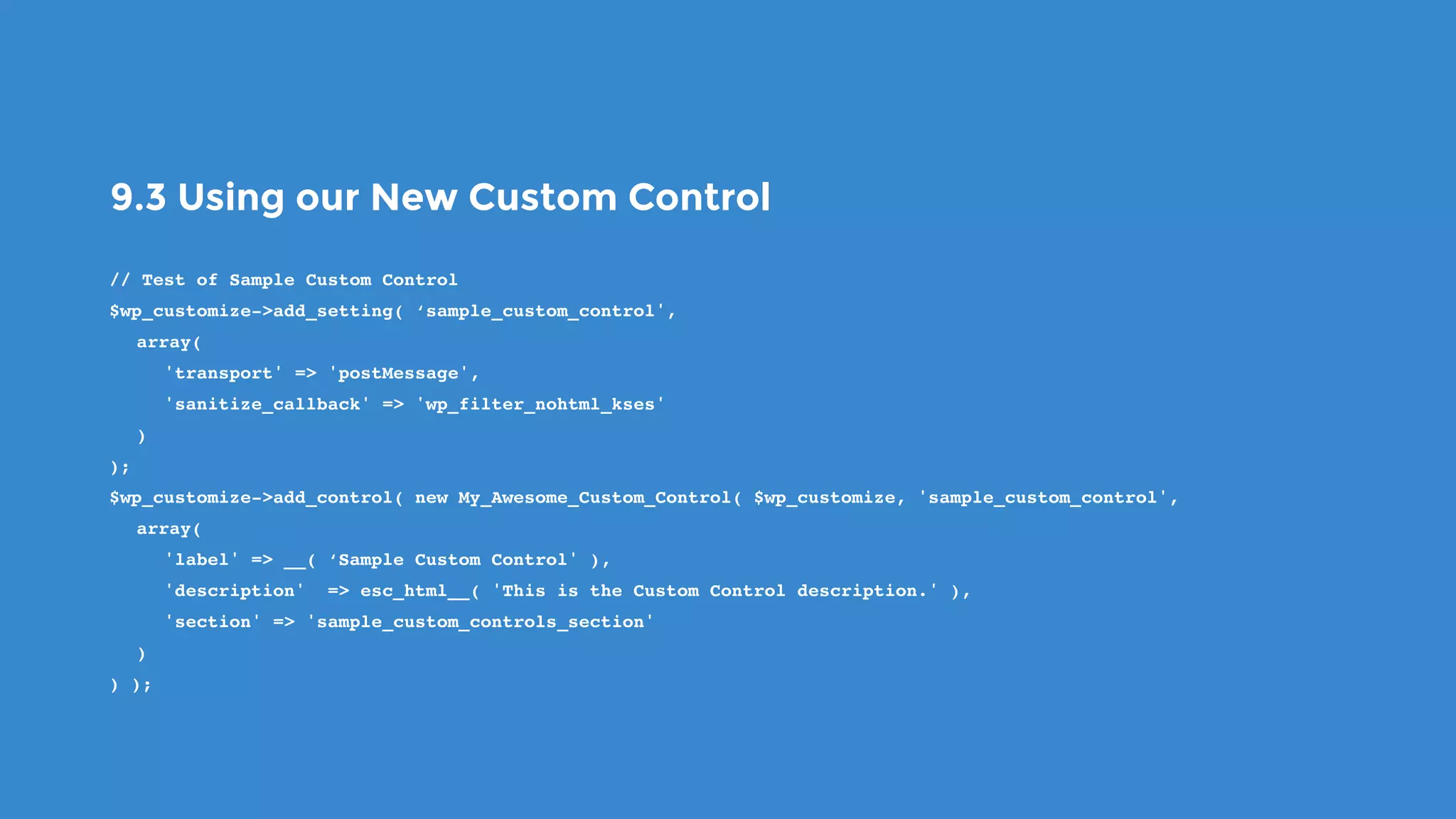
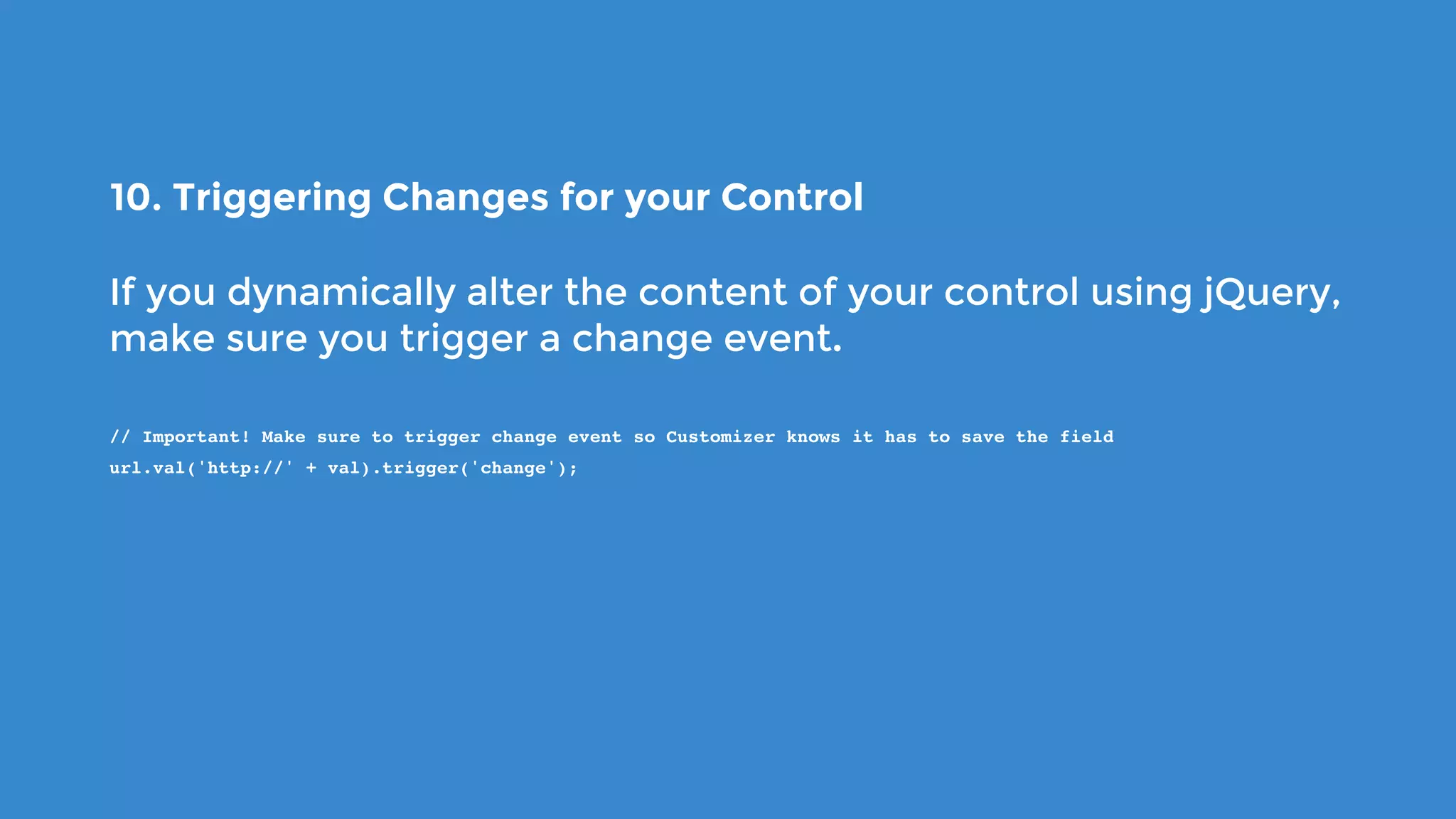
The document outlines the process for developing custom WordPress themes using the Customizer API, detailing how to register and manage panels, sections, settings, and controls. It emphasizes the importance of data sanitization and includes code examples for creating various UI elements, such as text fields, checkboxes, and custom controls. Additionally, it explains how to implement live previews and customize control behavior through JavaScript.