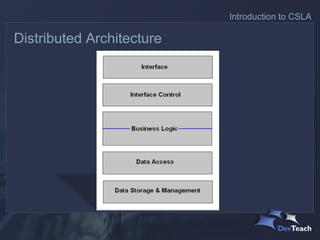
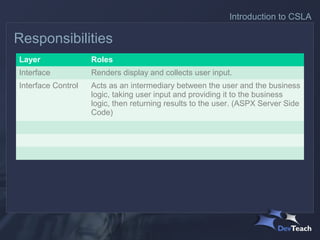
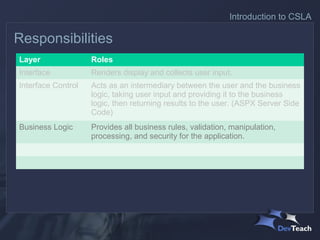
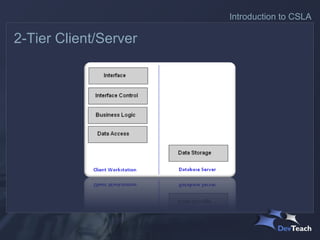
The document discusses CSLA .NET, a development framework designed to facilitate the creation of scalable and maintainable business applications through a structured architecture. It outlines the key features and responsibilities of different application layers, emphasizing the need for a formal business layer that allows for easier management of changes and promotes object-oriented design. The framework aims to reduce development costs while providing flexibility in deployment and data access technologies.