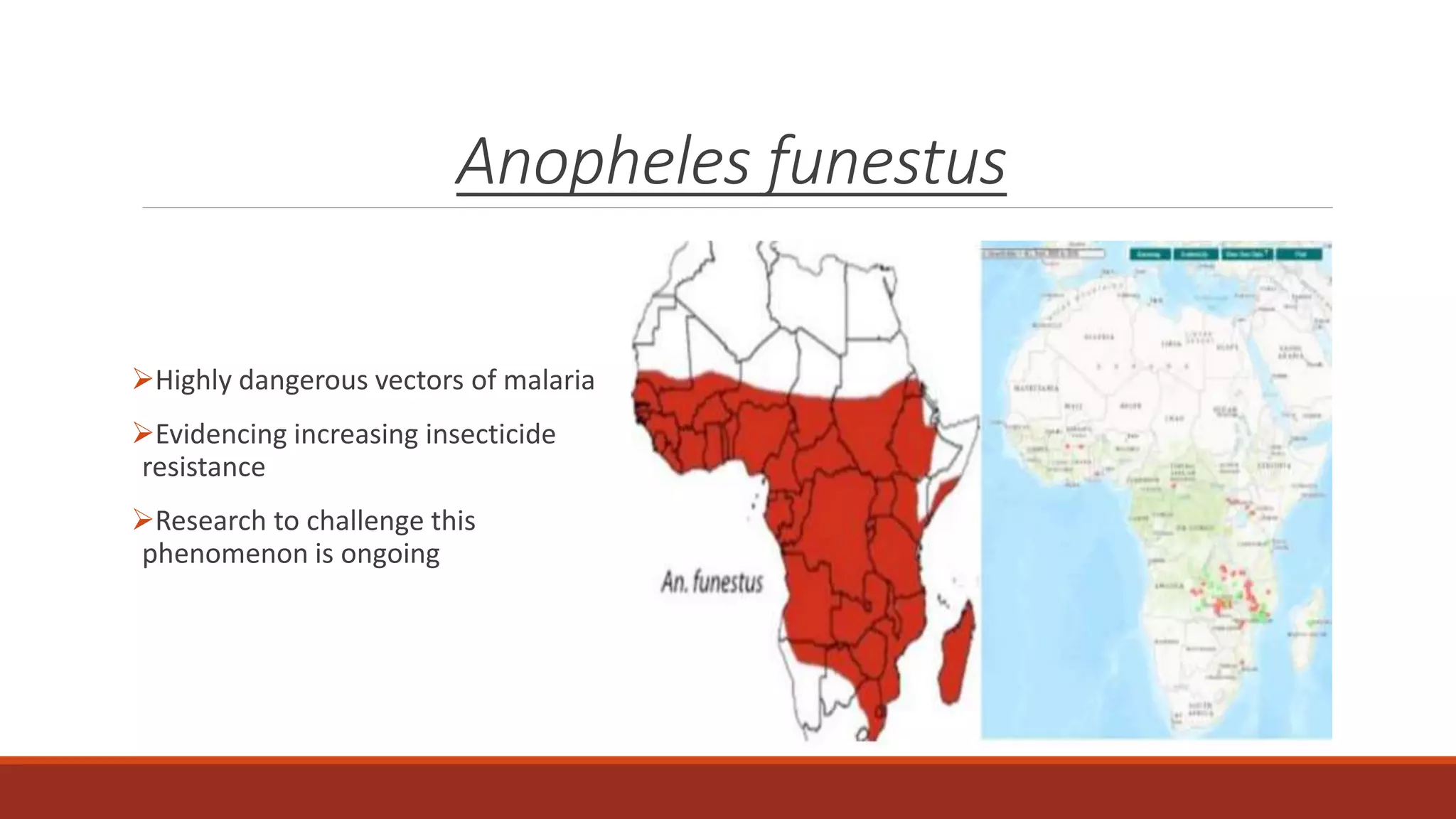
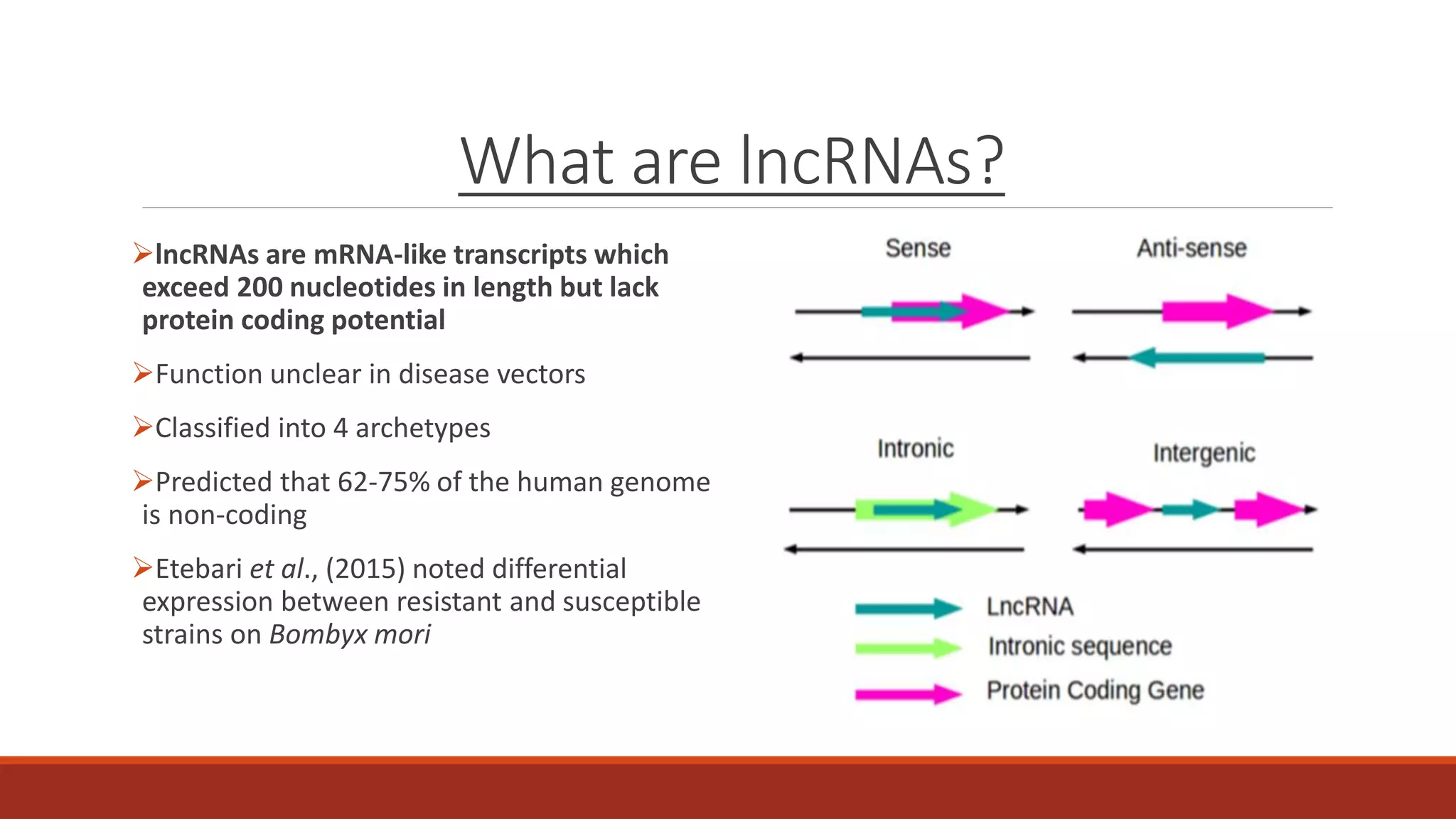
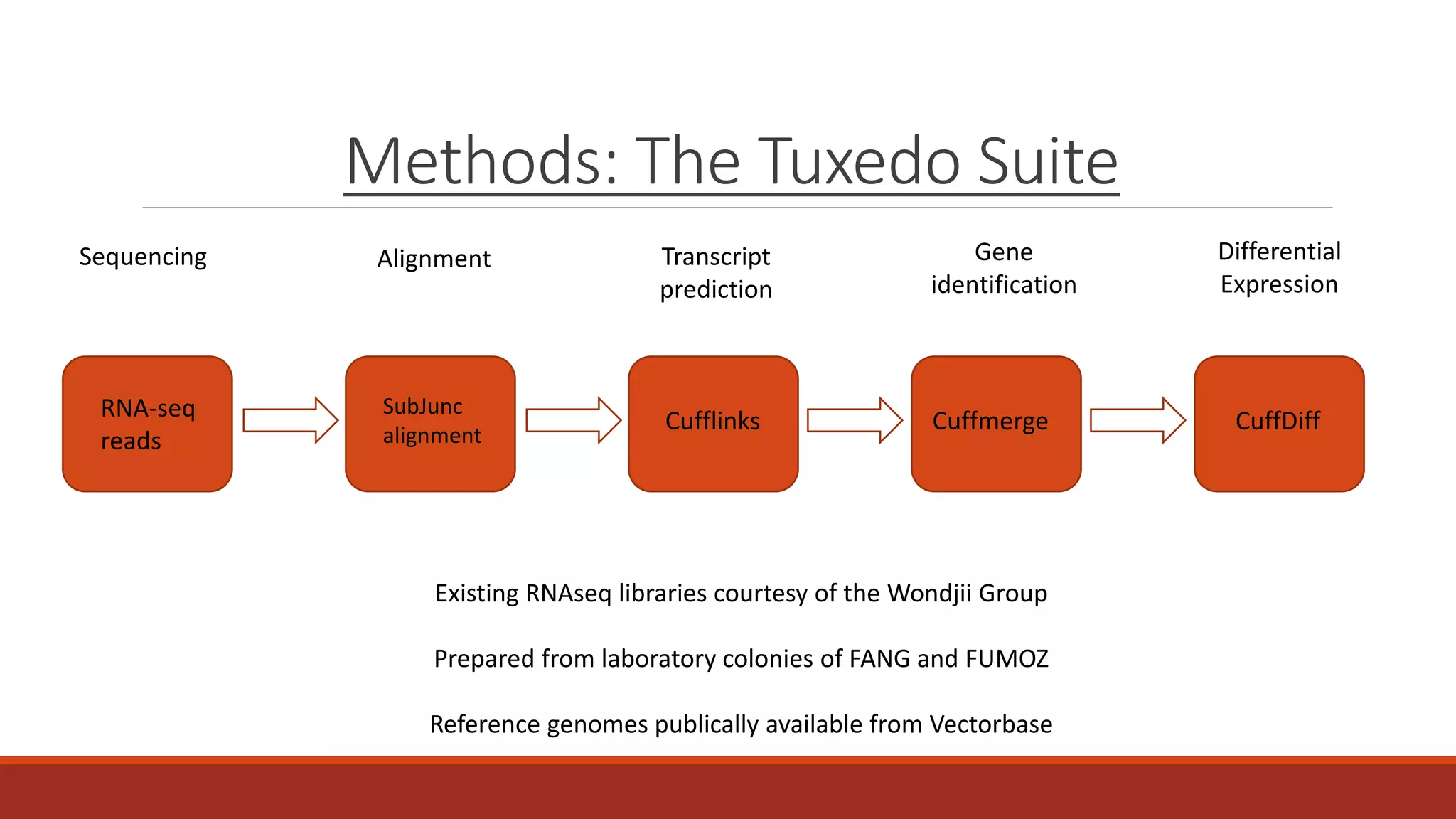
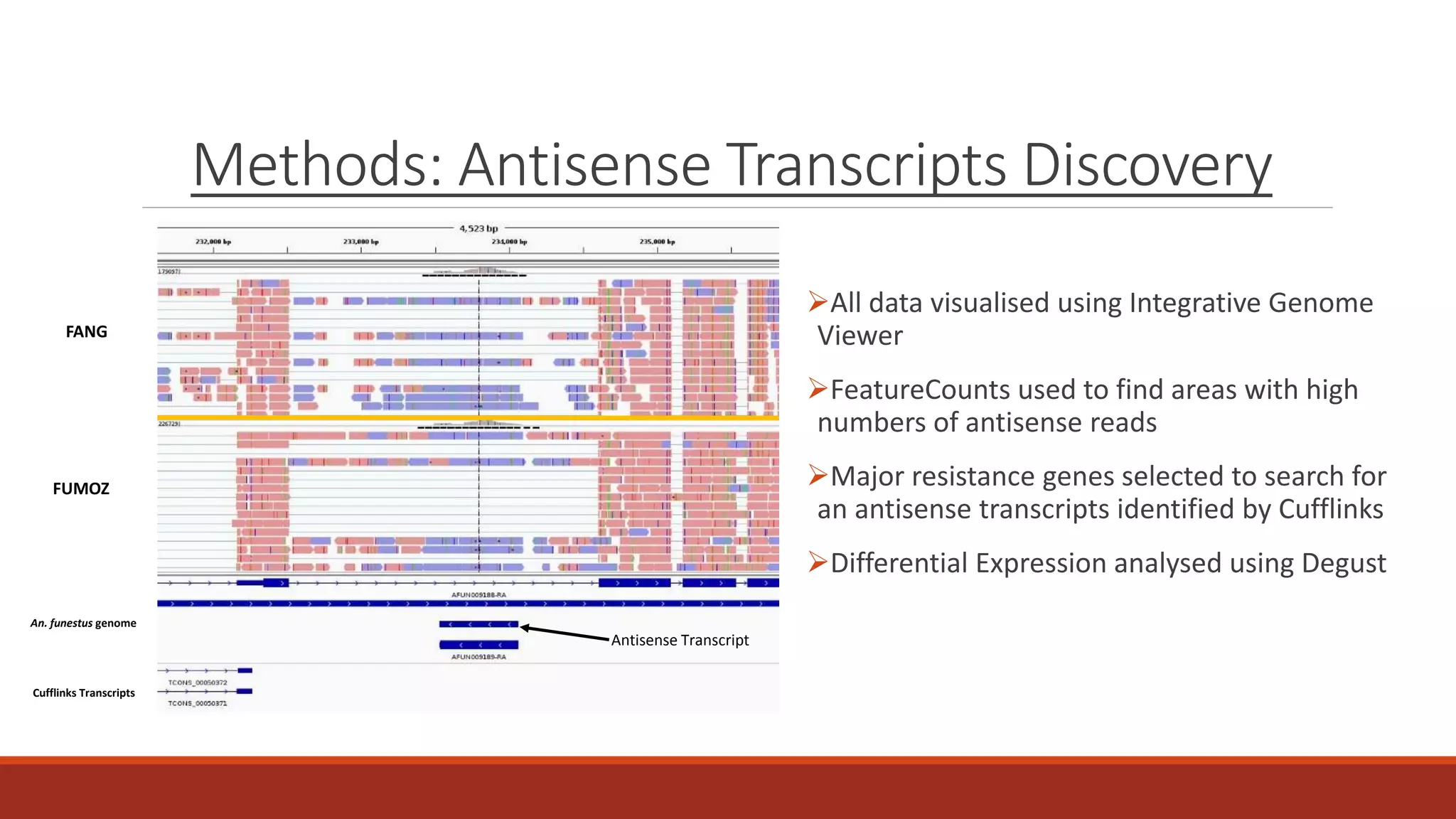
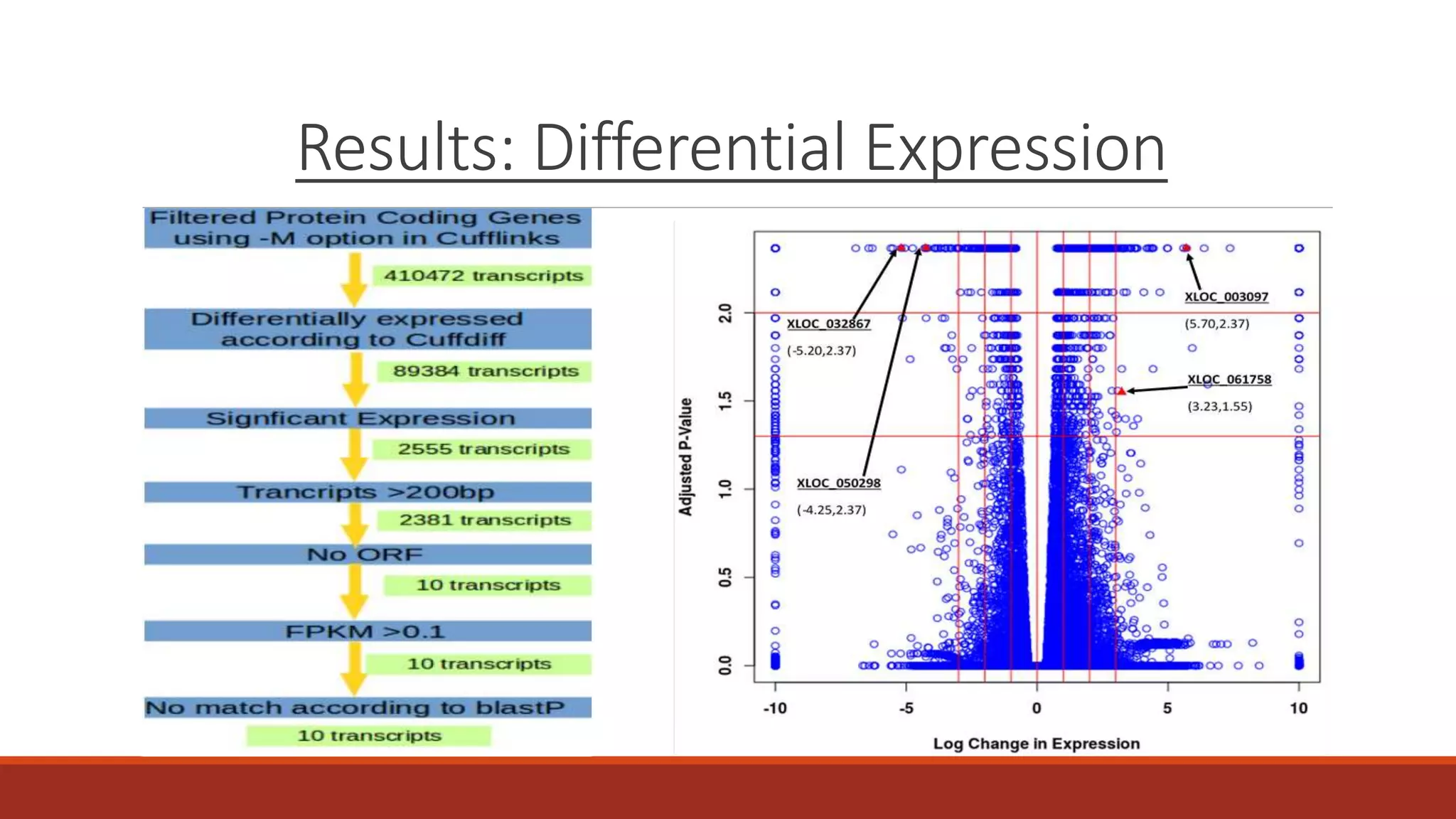
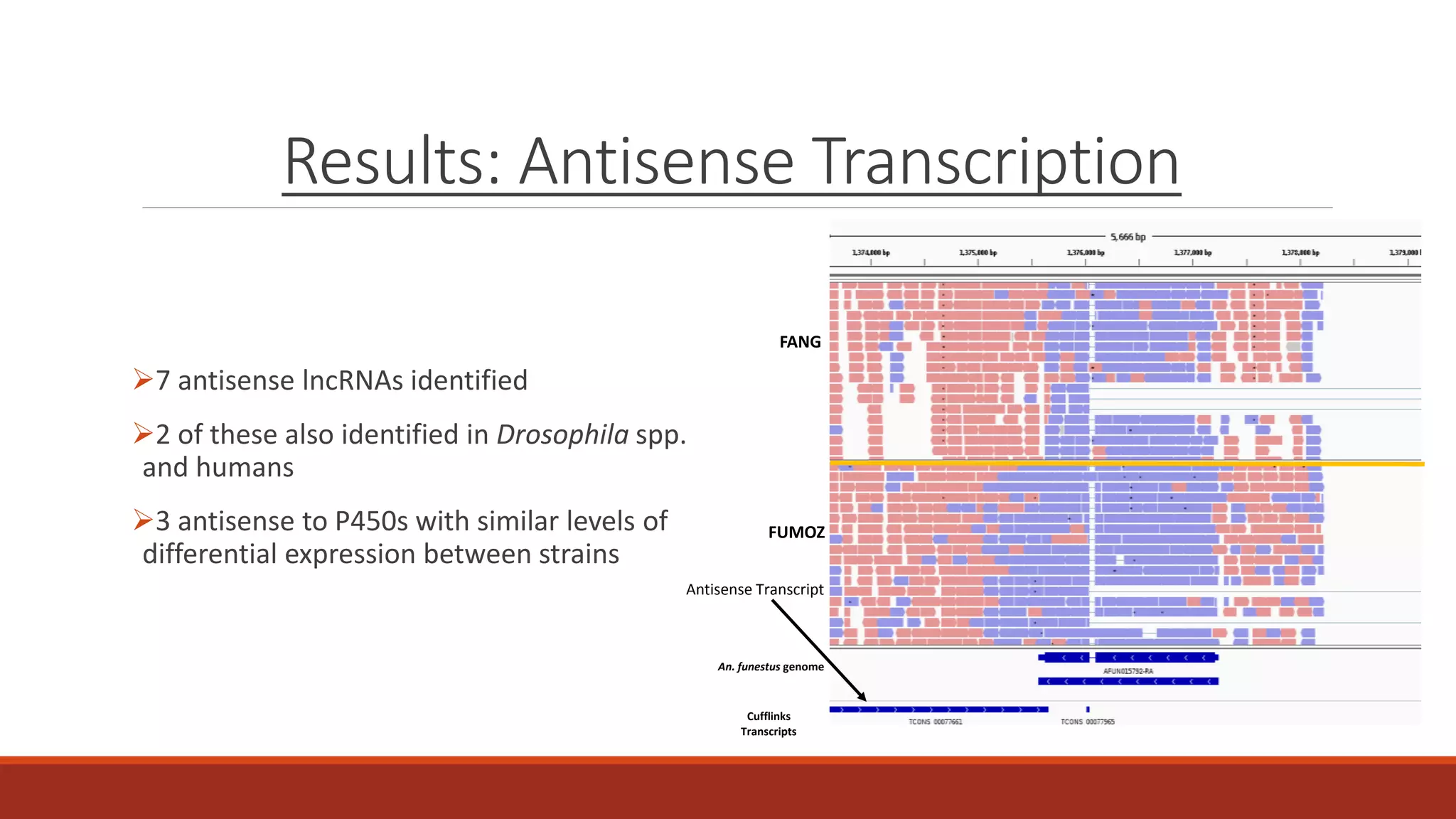
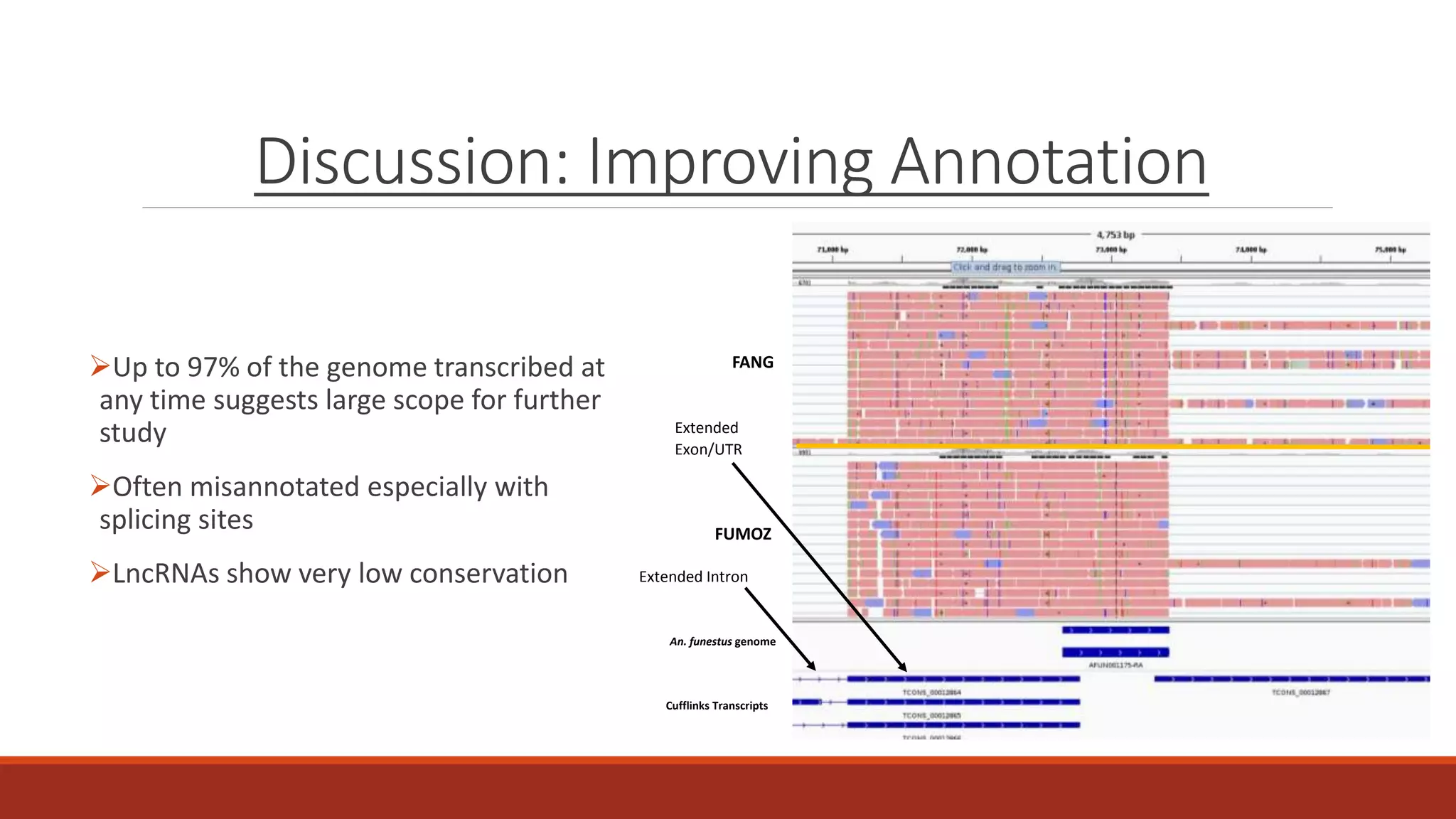
The document discusses the investigation of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in Anopheles funestus, a malaria vector, particularly focusing on their differential expression between insecticide-resistant and susceptible strains. Researchers identified several lncRNAs and suggested their potential roles as transcription regulators and biomarkers for disease. The findings indicate a significant scope for further study and validation of the lncRNAs' functionality and therapeutic relevance.