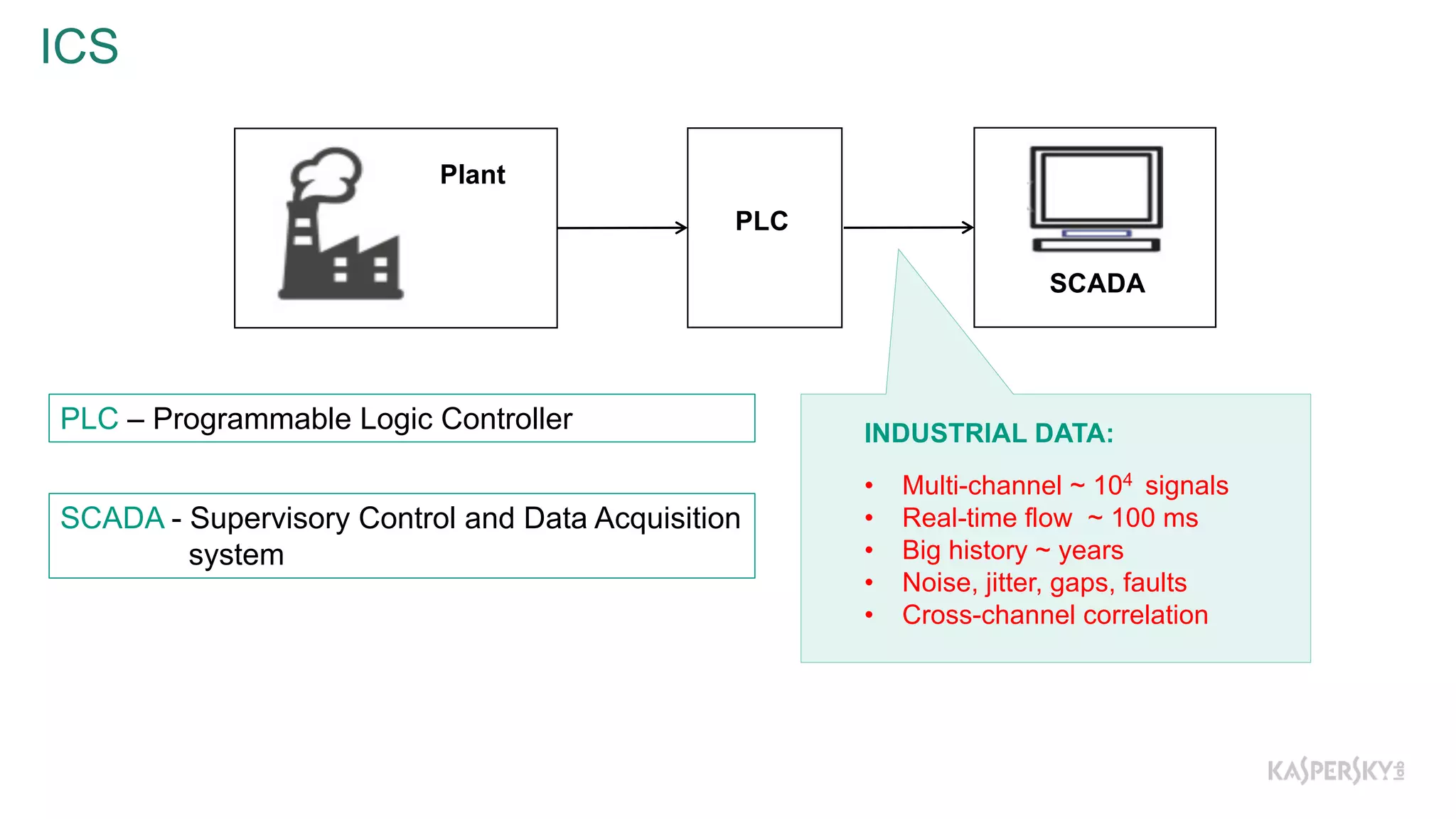
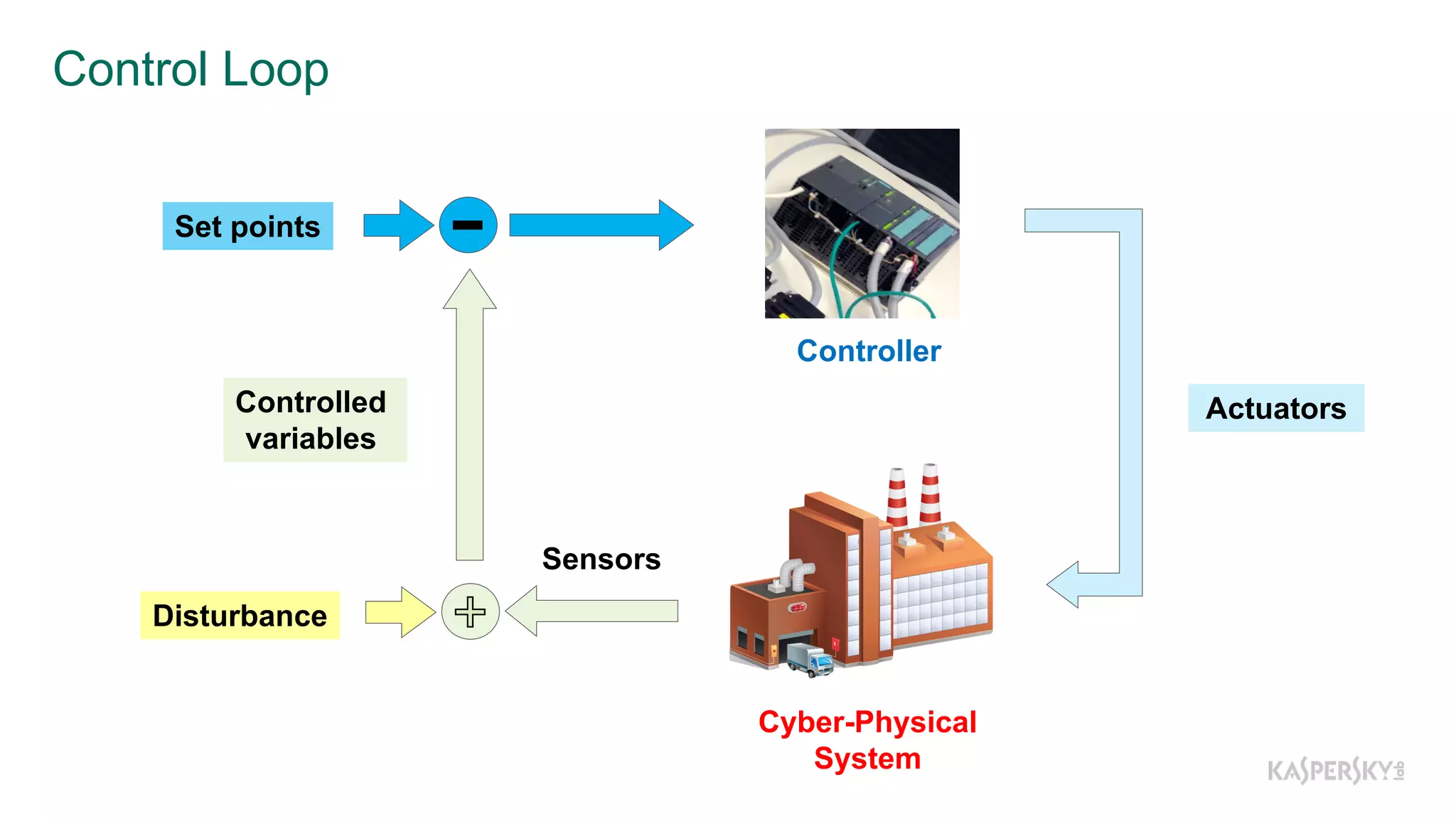
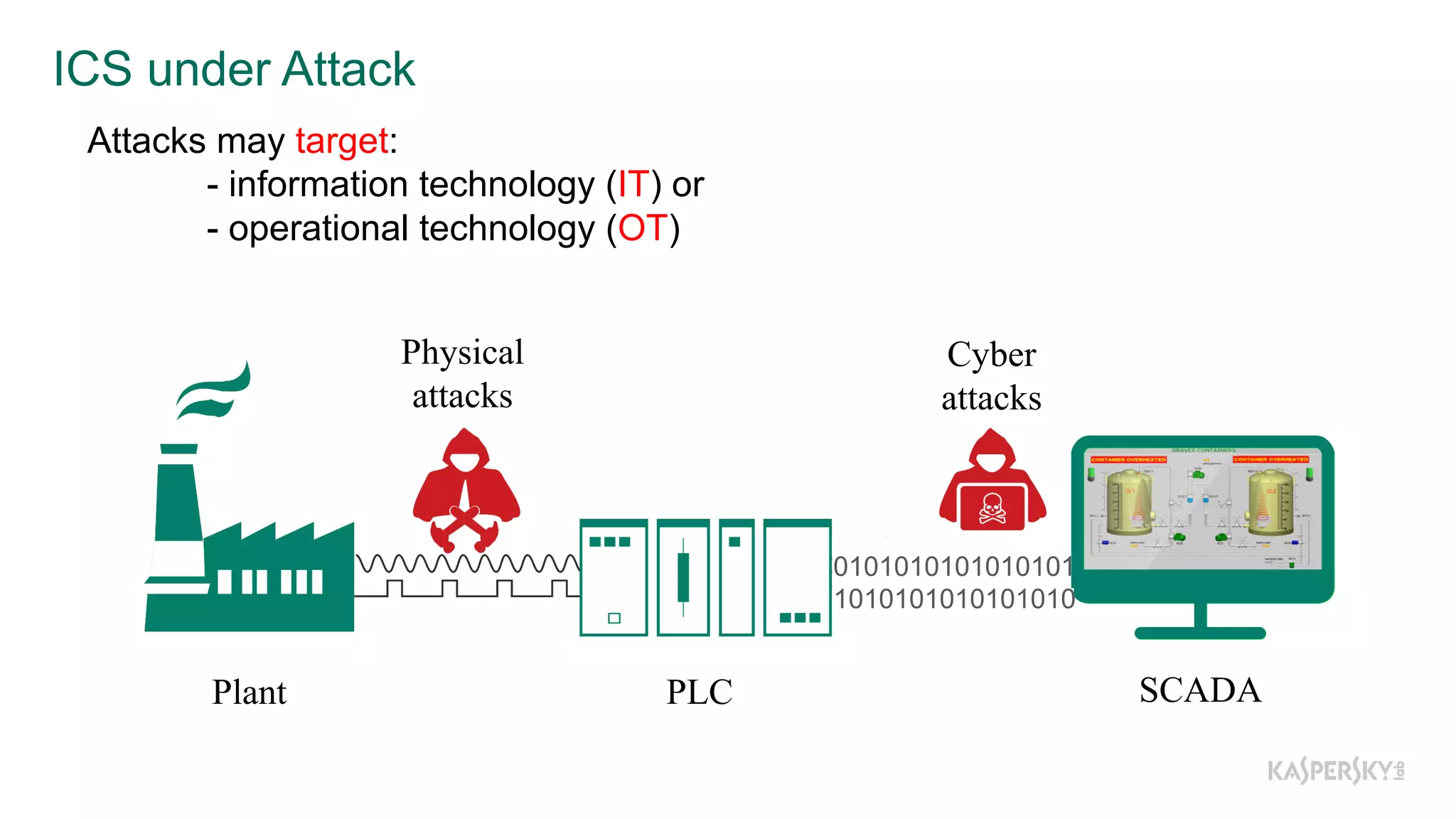
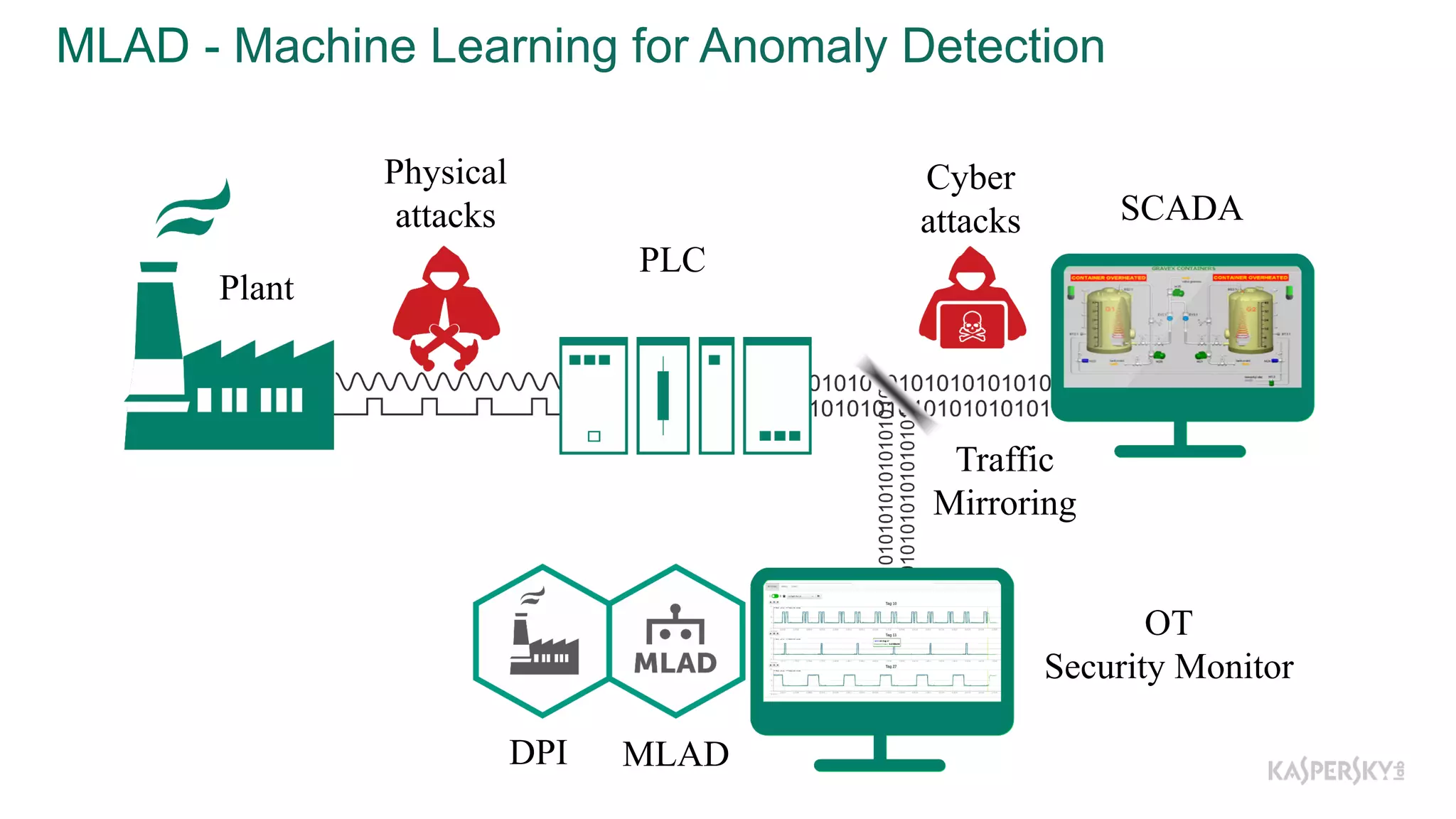
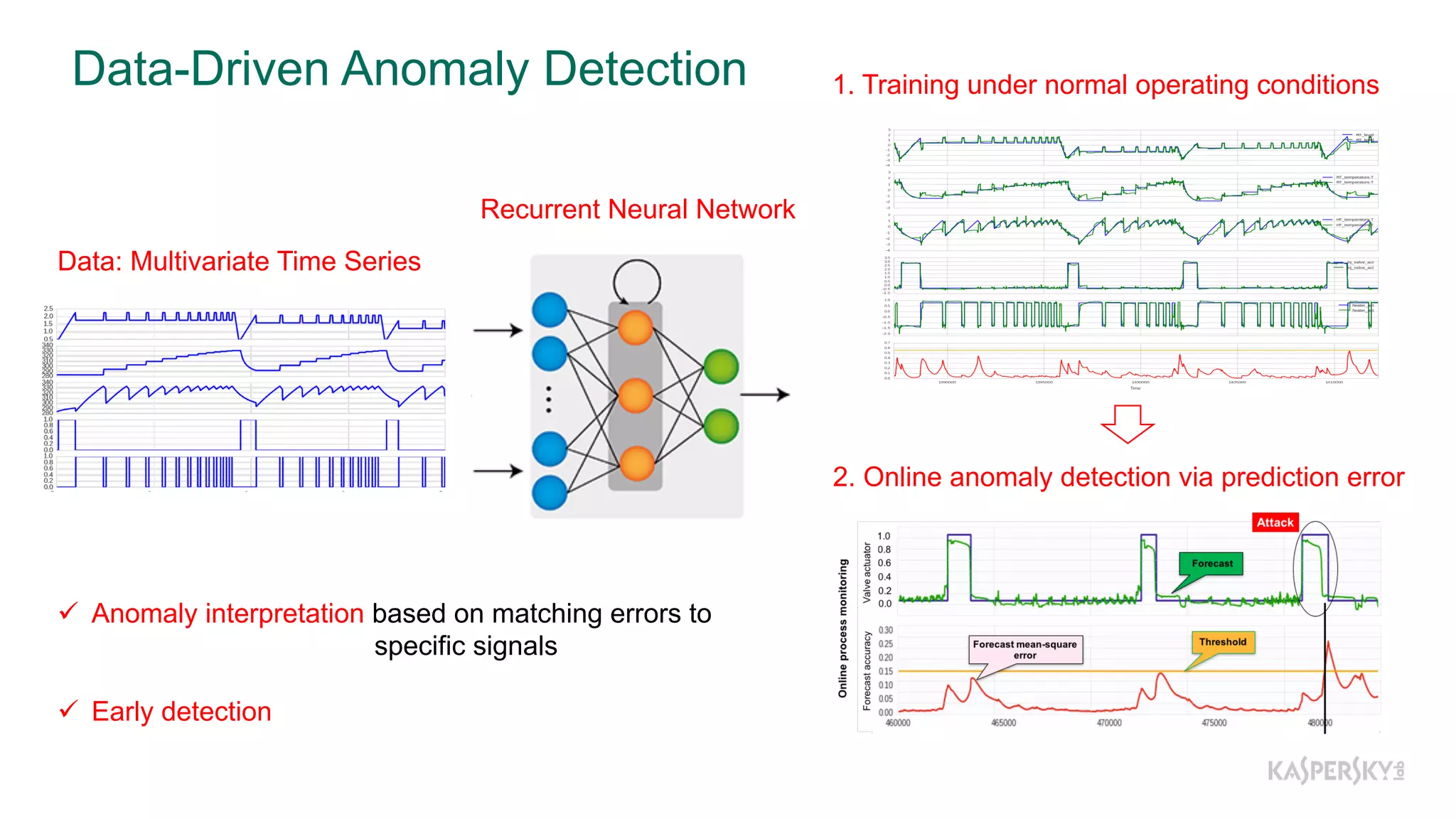
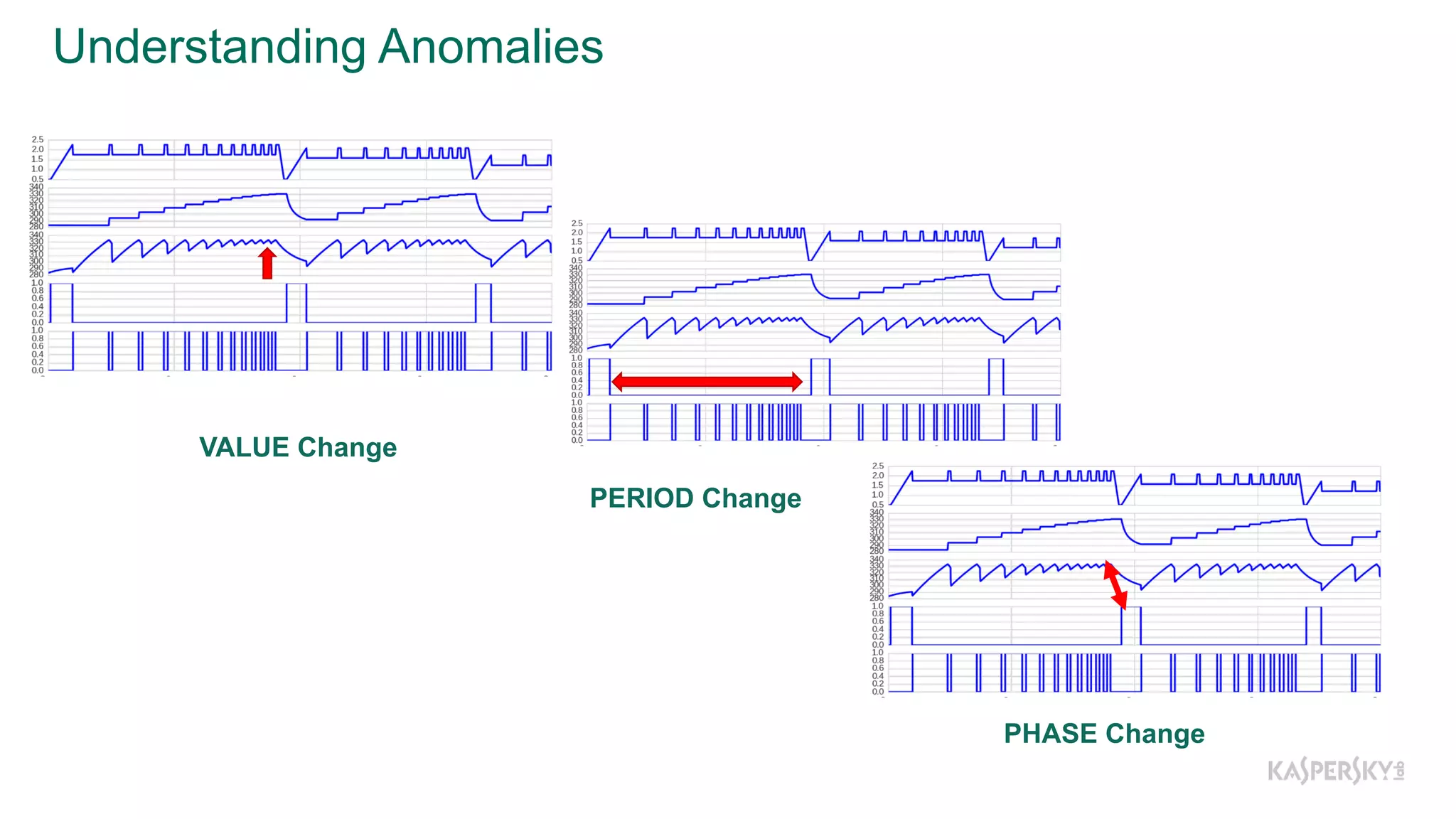
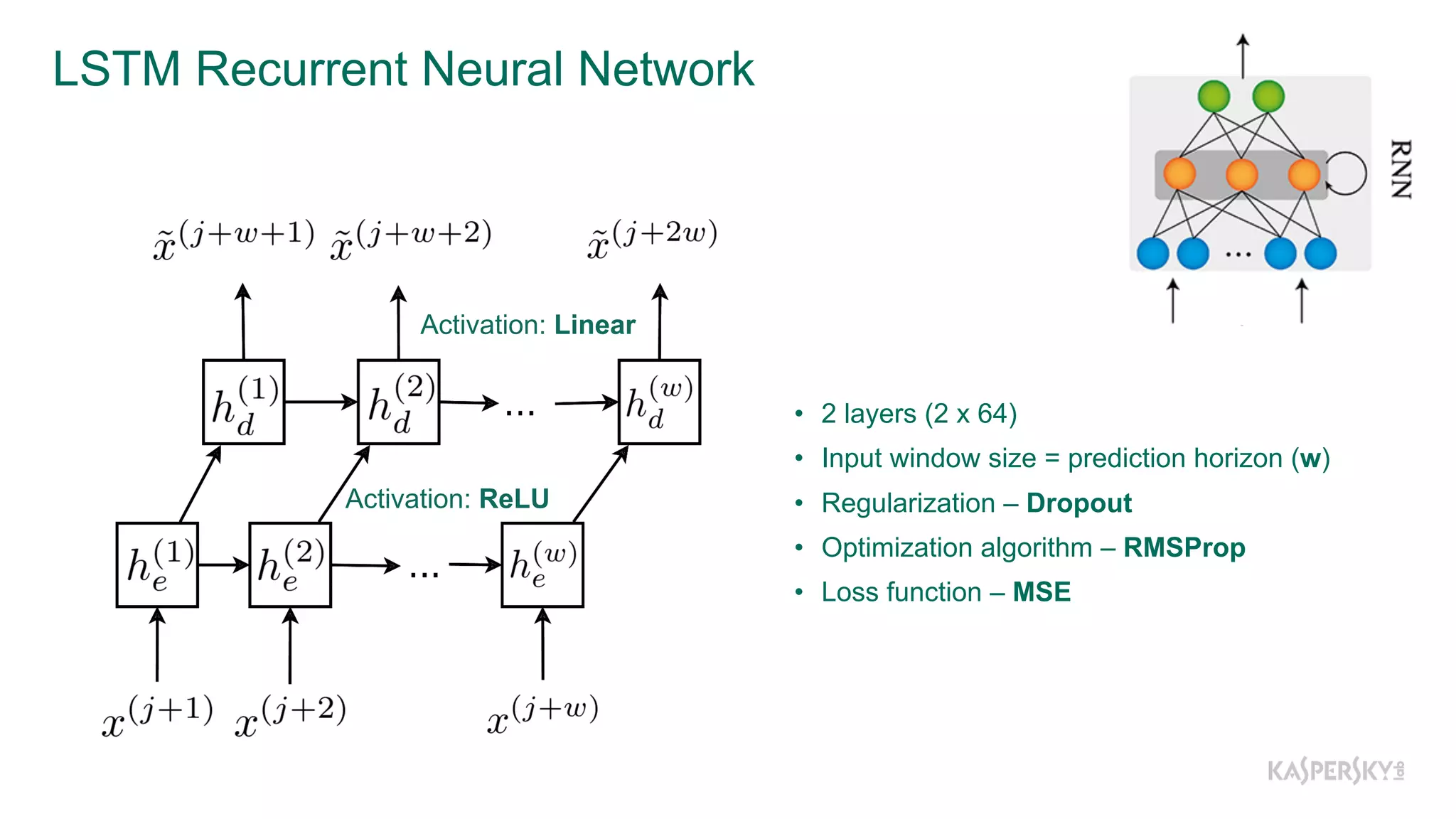
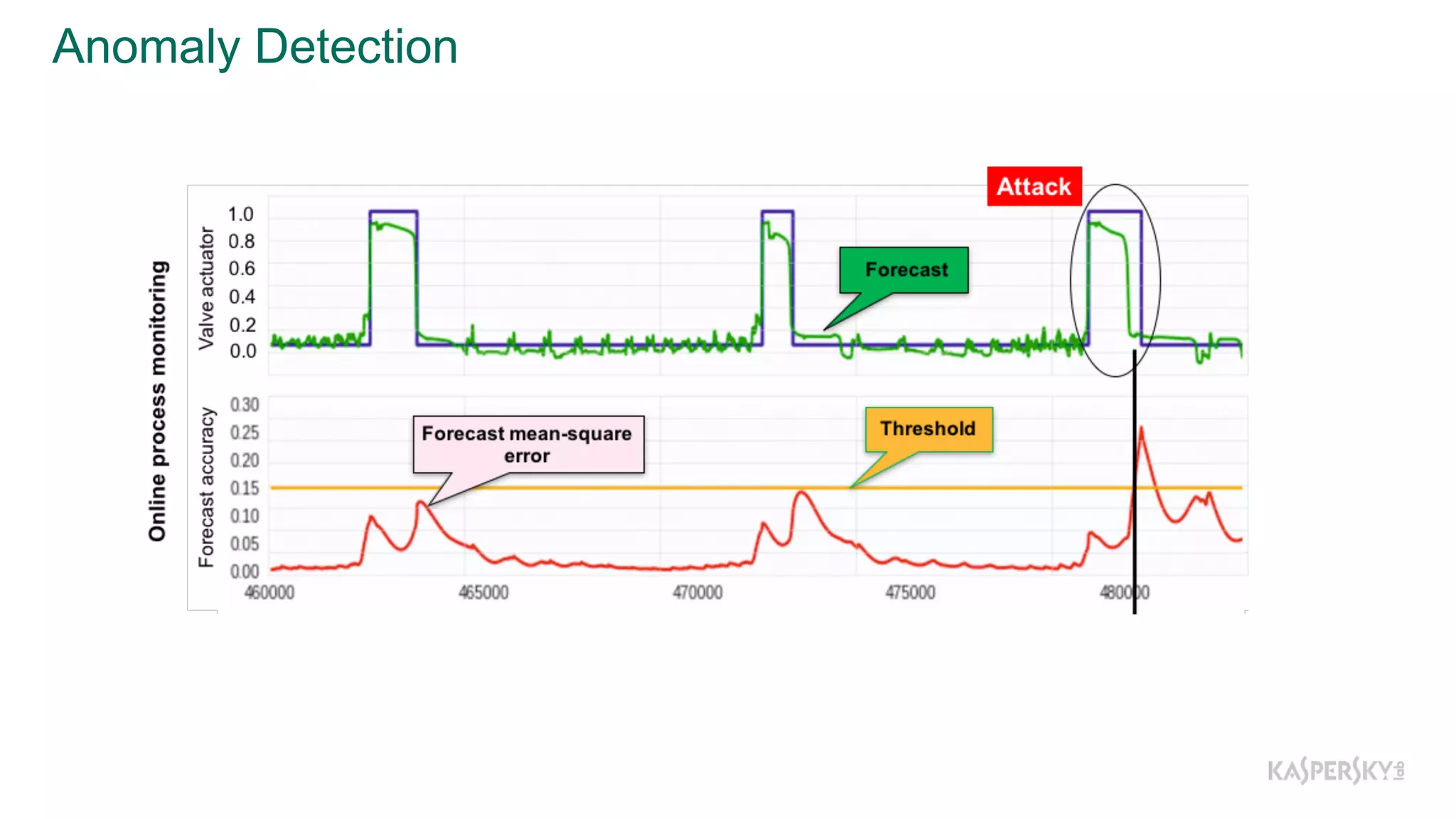
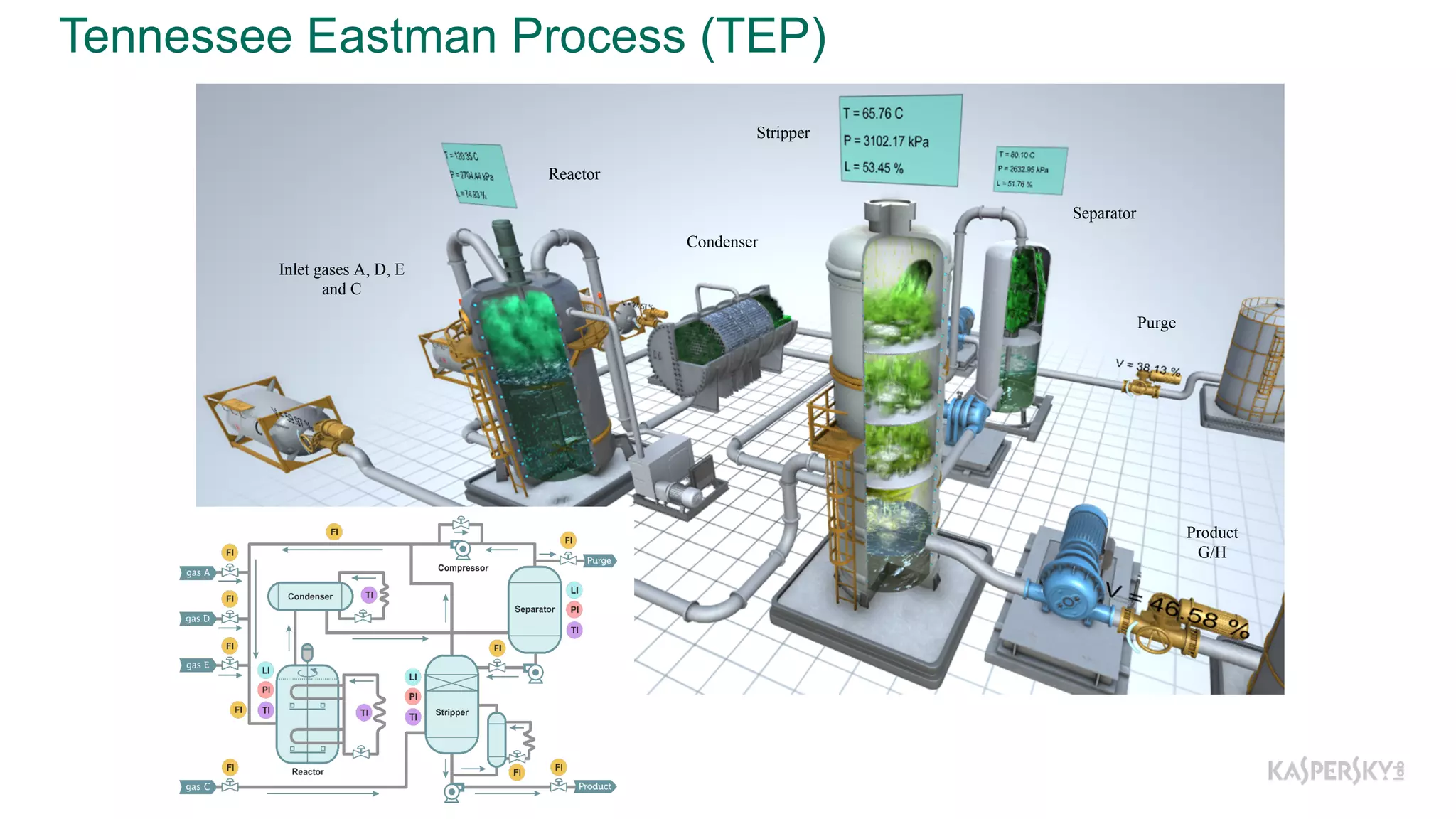
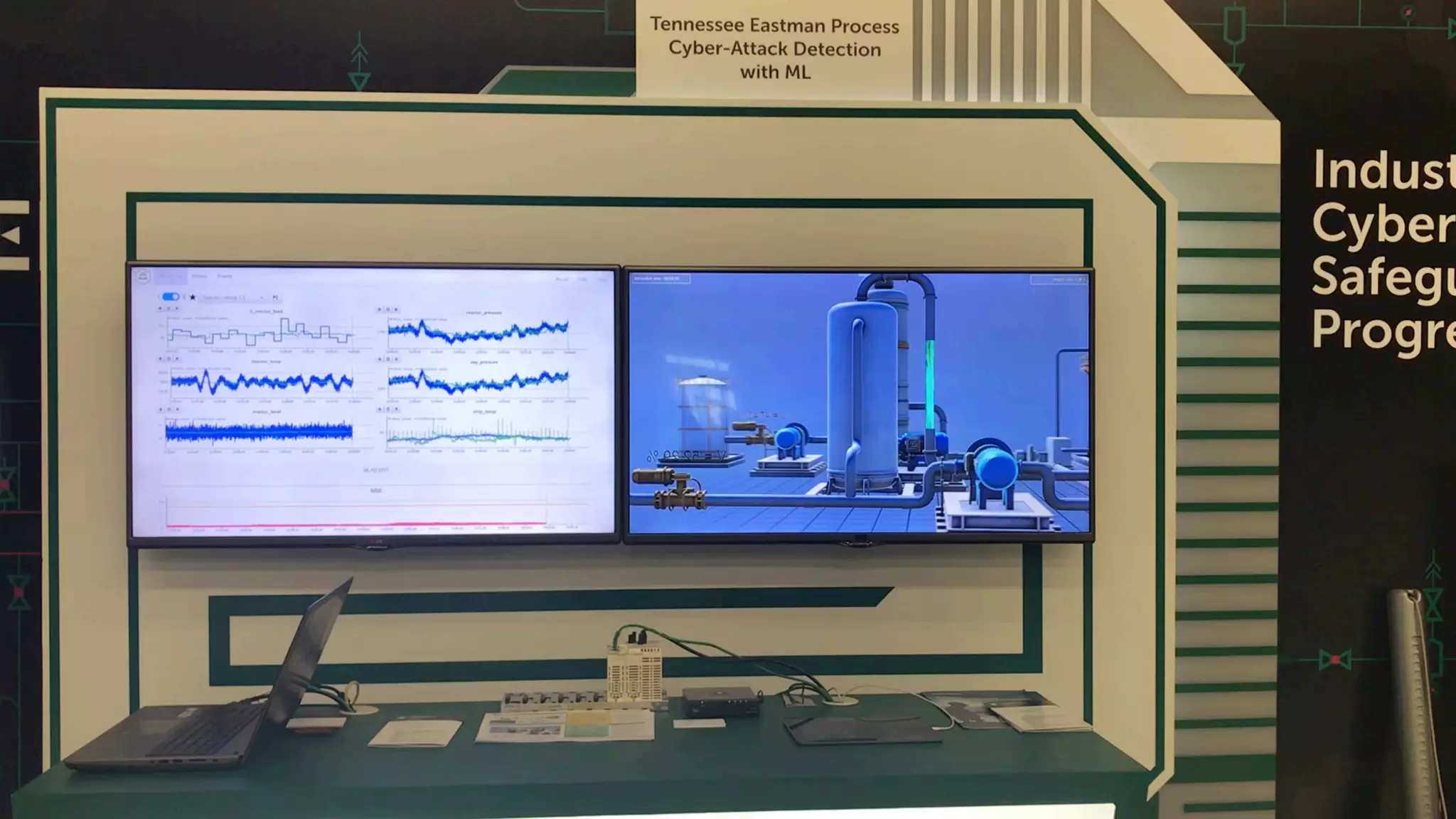
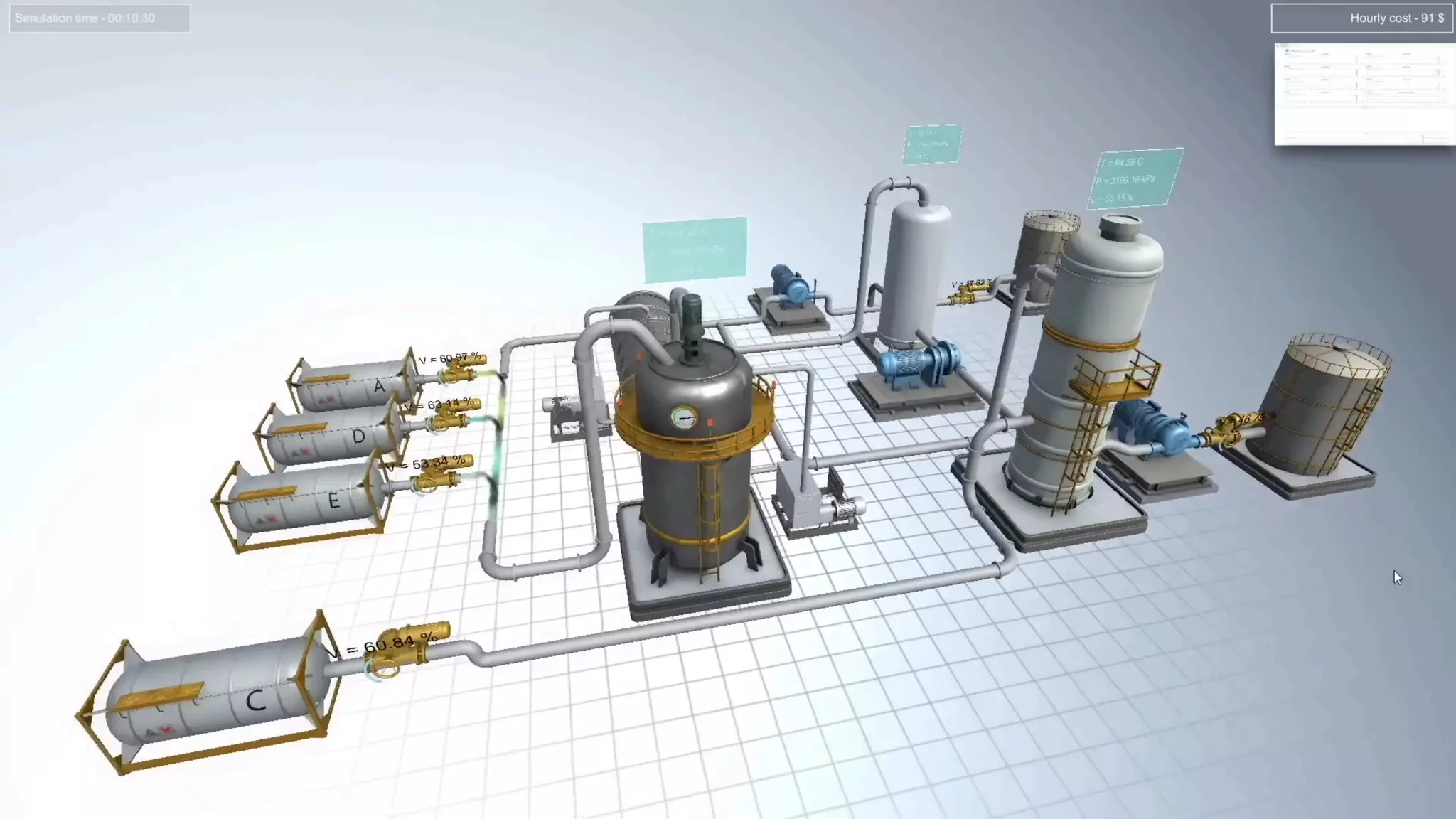
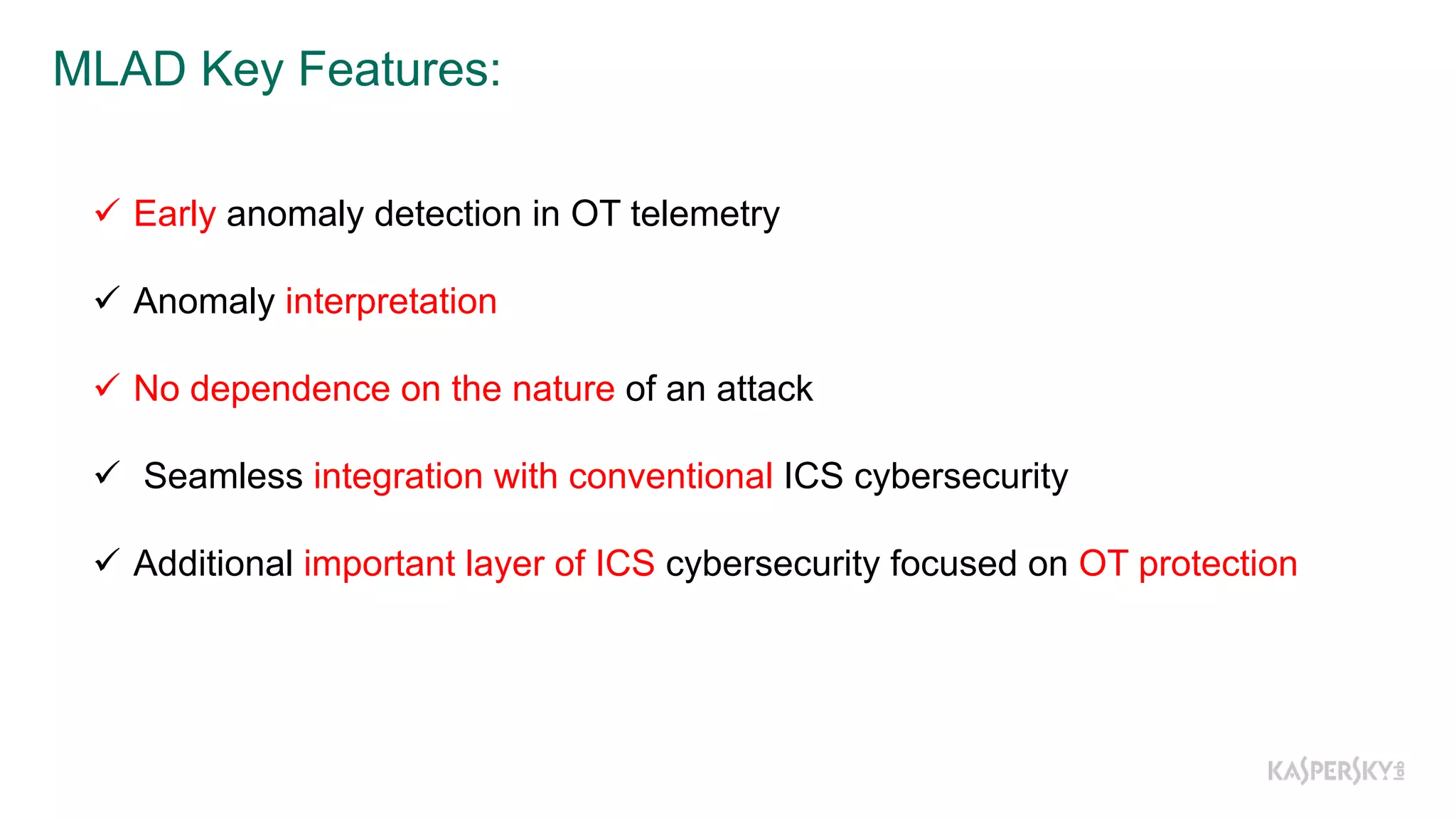
The document discusses a methodology to detect industrial control system (ICS) attacks using recurrent neural networks (RNN), focusing on correlations between signals in operational technology (OT). It emphasizes the significance of early anomaly detection to prevent physical damage and financial losses from such attacks, particularly by utilizing machine learning for processing multivariate time series data. The approach integrates seamlessly with existing ICS cybersecurity measures, targeting specific anomalies in OT telemetry without relying on attack nature.



![References
www.kaspersky.com
mlad@kaspersky.com
[1] MLAD Presentation
https://youtu.be/xXWjfYcPi_Q
[2] RNN-based Early Cyber-Attack Detection for the Tennessee Eastman Process. ICML 2017
Time Series Workshop, Sydney, Australia, 2017.
https://arxiv.org/abs/1709.02232
[3] Multivariate Industrial Time Series with Cyber-Attack Simulation: Fault Detection Using an
LSTM-based Predictive Data Model. NIPS 2016 Time Series Workshop, Barcelona, Spain, 2016.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1612.06676
[4] ICS Anomaly Detection Panel
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jeepkpqdurc&t=306s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kls4x18mladtalklavrentiev-180124081610/75/Detecting-ICS-Attacks-Using-Recurrent-Neural-Networks-16-2048.jpg)
