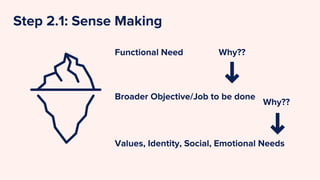
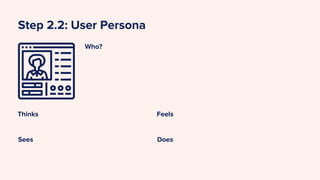
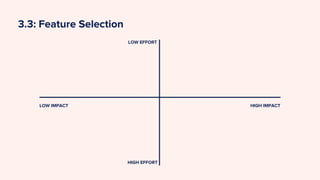
The document outlines the design thinking process tailored for tackling online dating abuse, emphasizing human-centric approaches such as empathy, problem definition, ideation, prototyping, and testing. It details steps for conducting empathetic research, framing user needs, developing personas, and brainstorming solutions while addressing the prevalence of digital dating abuse and its implications, particularly in contexts like Nepal. It encourages practitioners to apply these methodologies to understand and combat the nuances of digital dating abuse effectively.






![1.2: Empathetic Research Guide
“Hi, my name is _________ and I’m doing a project on [insert challenge]. I’m really interested in your experiences
and how you [insert activity]. I was wondering if I could ask you a few questions. It should only take 30-40 minutes.”
Starting questions:
• Can you tell me about the last time you [insert activity}?
• Can you tell me a story about your best __________ experience?
• Can you tell me a story about your worst __________ experience?
• What helped? What hindered?
• Why?
• Tell me more…
Follow up questions:
• Can you tell me more?
• Can you give me an example?
• How did that make you feel?
• What do you wish was different?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designthinkingforproductdesignslide1-221202173415-d44743de/85/Design-Thinking-for-Product-Design-Slide-pdf-7-320.jpg)