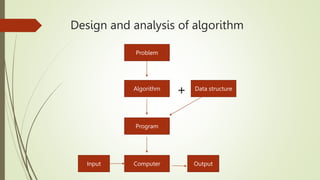
This document introduces the design and analysis of algorithms, emphasizing the importance of studying algorithms for achieving efficient computation. An algorithm is defined as a sequence of steps to transform input into output, and the analysis involves comparing algorithms based on time and space. The document also outlines fundamental characteristics of algorithms and distinguishes between algorithms, pseudo code, and programs.