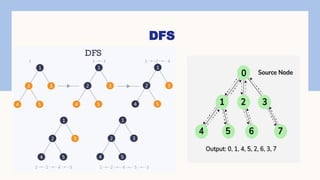
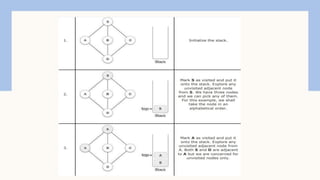
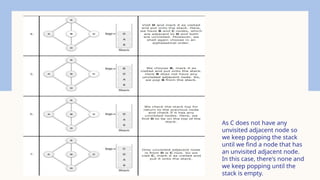
The document explains the depth-first search (DFS) algorithm for graph traversal, emphasizing its systematic approach to visiting vertices using a stack. It outlines the key rules for implementation, including visiting unvisited adjacent vertices and backtracking when necessary. A step-by-step algorithm is provided for initializing vertex states and processing them until the stack is empty.