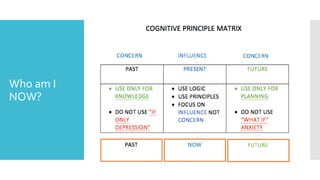
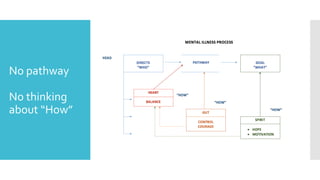
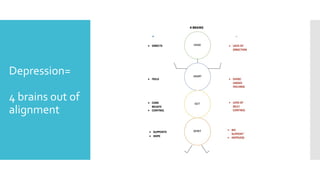
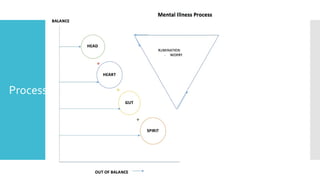
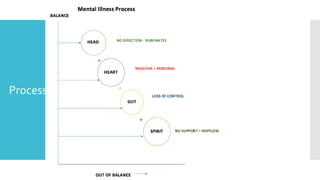
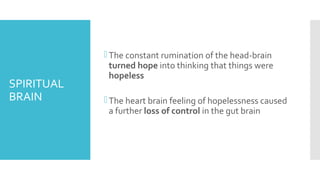
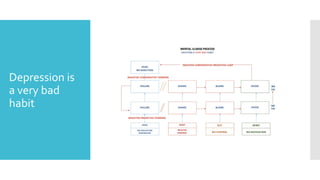
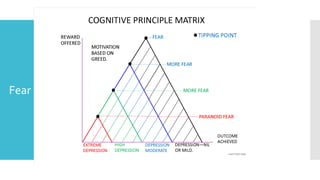
This document discusses Cognitive Principle Therapy for treating depression. It describes depression as having four brains - the head brain, heart brain, gut brain, and spiritual brain - operating out of alignment. Each brain contributes differently to depression. The head brain engages in negative rumination. The heart brain attaches fear to negative thoughts. The gut brain triggers a fight-or-flight response and loss of intuition. The spiritual brain leads to a loss of hope and inability to forgive. The therapy aims to explain how depression occurs, refocus negative thoughts, and pass unsolved problems to the subconscious mind to find solutions. Clients are told to stop thinking and let their faster subconscious minds work on problems instead of ruminating.







![DEPRESSION-
WHAT TO DO
Spiritual brain
Give the client hope, through awareness [ education that
depression occurs through process, which can be reversed]
Model hope to the depressed client
Head brain
Explain the process that leads to depression
Explain how fear works when taken as a physical threat
Gut brain
Give the exercise of emotional threat- physical threat [requires no
decision making]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/depression-170218223917/85/Depression-A-new-treatment-using-cognitive-principle-therapy-15-320.jpg)