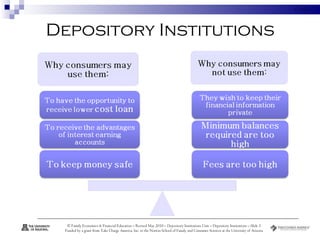
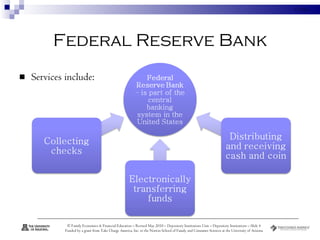
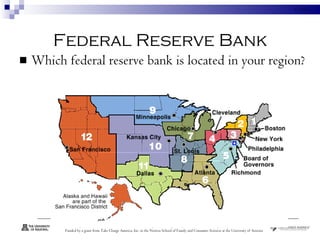
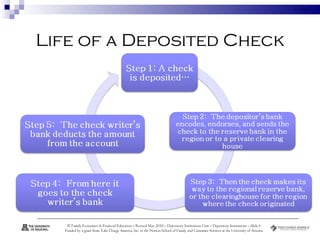
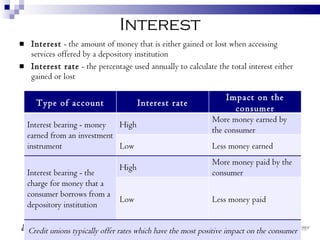
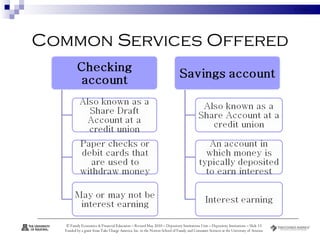
Depository institutions, commonly known as banks, provide multiple financial services including banking, savings, loans, and insurance. They include commercial banks, credit unions, and savings and loan associations. These institutions are regulated and offer services like interest-bearing accounts, loans, credit cards, safe deposit boxes, and financial counseling. Depositors' accounts are insured by agencies like the FDIC and NCUA up to $250,000 to protect consumers from loss of funds if an institution fails.