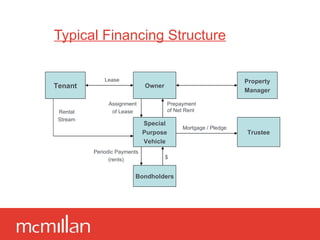
A bondable lease, also known as a credit tenant lease or hell or high water lease, is a long-term commercial lease granted to a tenant with a strong credit rating that generates a stable income stream to repay bonds. The lease transfers responsibilities from the landlord to the tenant through a triple net structure. This allows a special purpose vehicle to finance the property through bond issuances backed by the tenant's credit instead of the underlying real estate asset. Typical bondable leases have terms of 20-25 years and include provisions to mitigate risk for bondholders such as mandatory insurance policies and restrictions on the tenant's early termination rights.