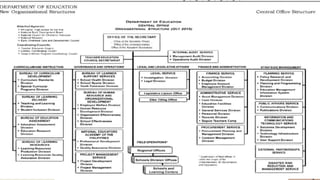
The document outlines the transformation of the Department of Education, including its new name and redefined roles for field offices. It details the governance structure, the responsibilities of the Secretary of Education, and the operational framework of regional and local offices to ensure accessible basic education. Additionally, it highlights the aims of the education system in the Philippines to develop citizens and respond to societal needs.