Embed presentation
Download to read offline
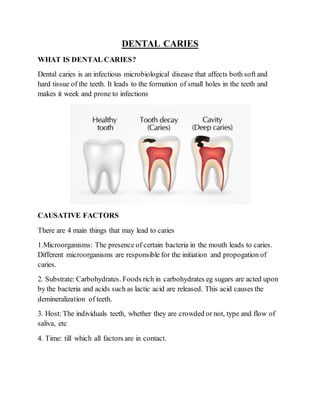



Dental caries is caused by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugars and produce acids, leading to demineralization of tooth enamel over time. The four main factors that contribute to dental caries are: 1) certain microorganisms in the mouth, 2) carbohydrates that the bacteria feed on, 3) individual risk factors like tooth structure or saliva, and 4) prolonged exposure time allowing the factors to interact. Early symptoms include discolored spots on teeth that can develop into cavities if left untreated. Treatment ranges from fillings for superficial cavities to root canals if infection has spread deeper. Regular brushing, fluoride use, and limiting sugary foods can help prevent dental caries.


