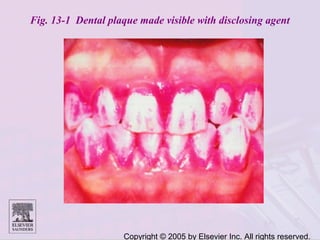
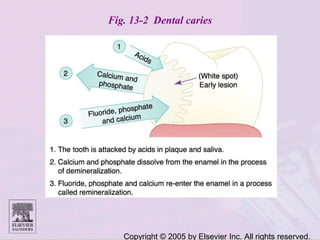
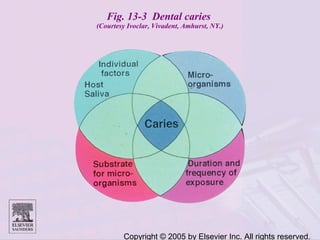
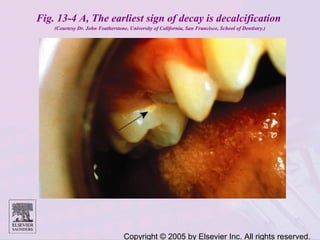
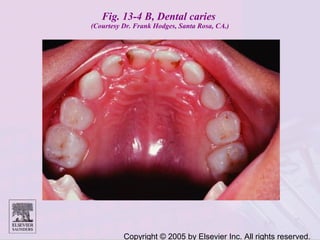
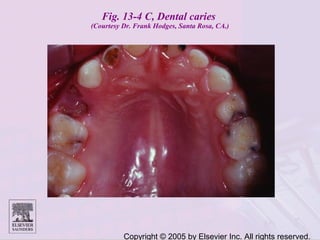
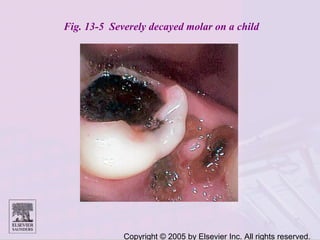
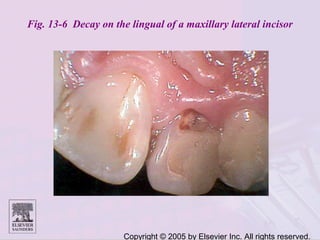
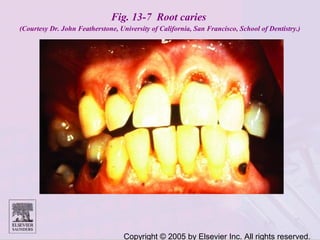
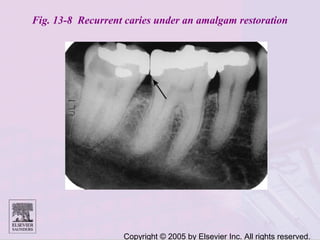
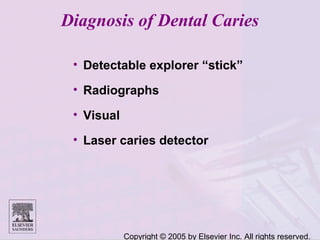
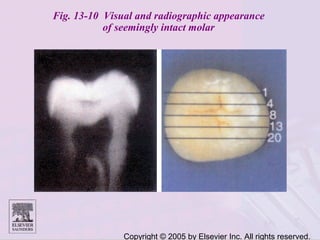
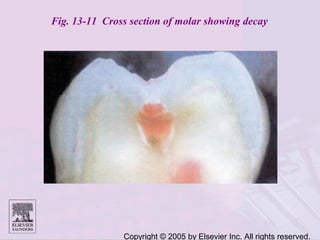
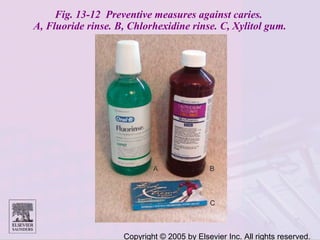
Dental caries is caused by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugars and produce acids. Over time, the acids dissolve minerals in the enamel of teeth causing cavities. The document discusses the bacteria responsible, how caries develops in stages, risk factors like sugar intake and low saliva flow, prevention methods like fluoride and gum, and tools for diagnosis and risk assessment.