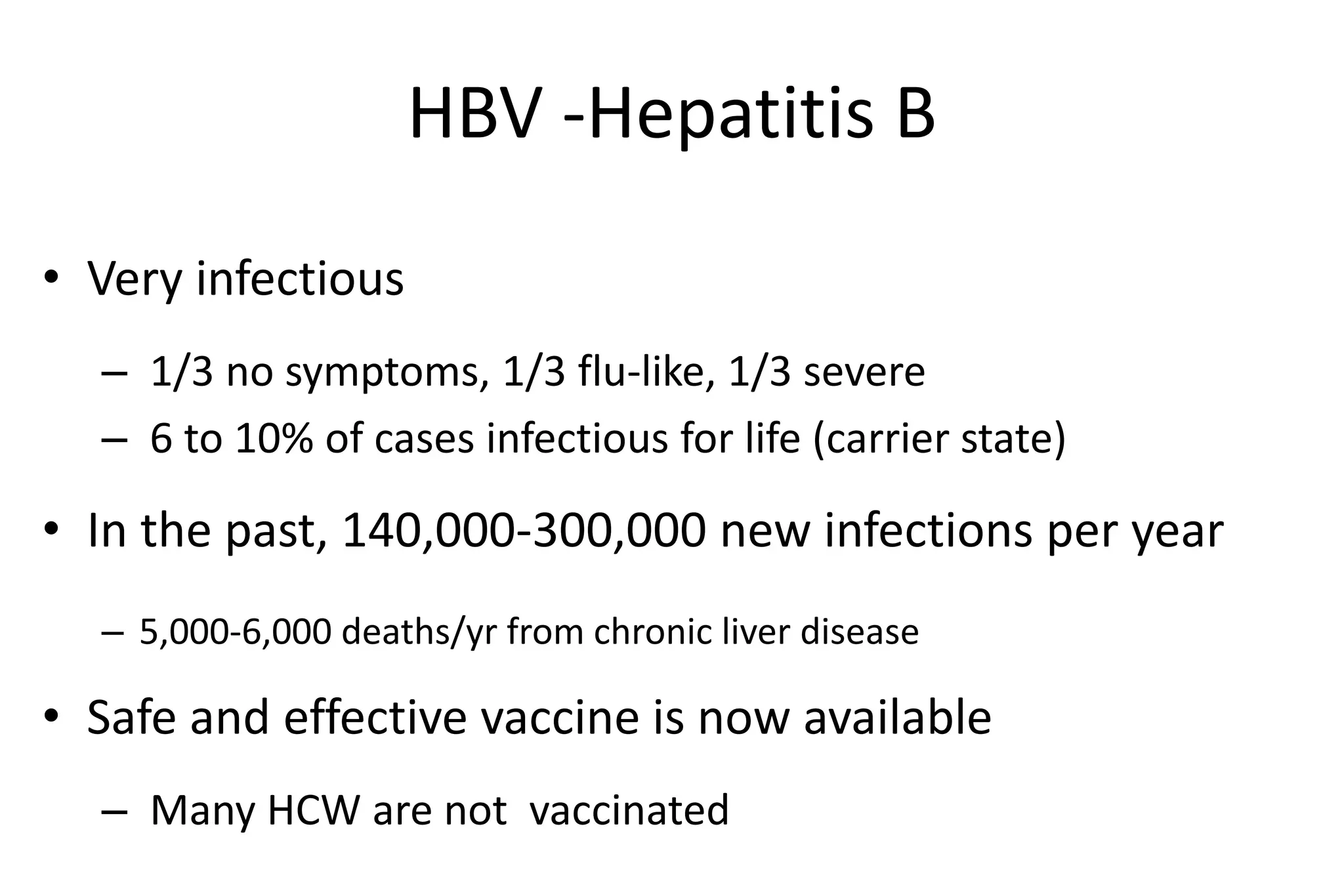
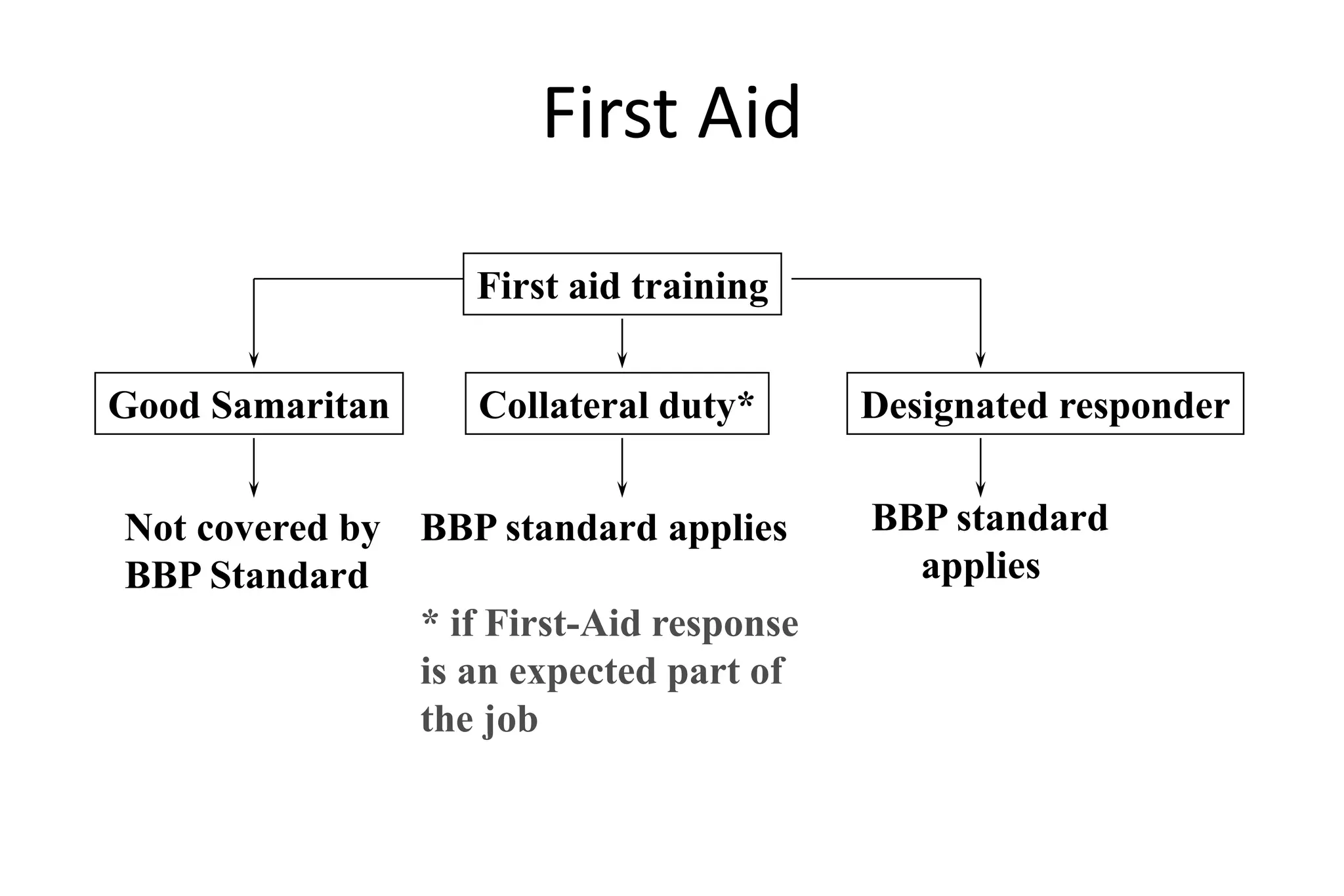
Bloodborne pathogens like hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and HIV can be transmitted through contact with infected blood or body fluids. Standard precautions like universal precautions and personal protective equipment are used to prevent exposure. An exposure control plan outlines steps to eliminate or minimize occupational exposure to bloodborne pathogens through methods like engineering controls, work practice controls, personal protective equipment, housekeeping, hepatitis B vaccination, post-exposure evaluation, and recordkeeping. The plan is reviewed annually and when changes in exposure risk occur.