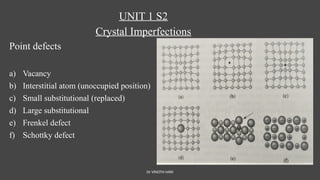
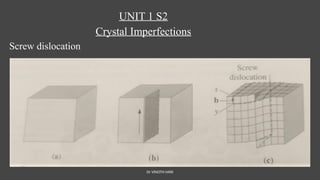
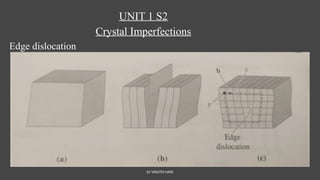
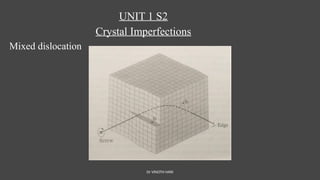
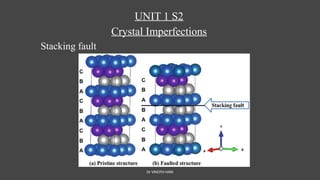
The document discusses crystal imperfections, categorizing them into point defects, line defects (dislocations), and surface defects. Point defects include vacancies, interstitial atoms, and substitutional defects, which affect the structural integrity of crystals, while dislocations are irregularities in atomic arrangement. Surface defects involve boundaries that separate regions within a material, such as grain boundaries and stacking faults.