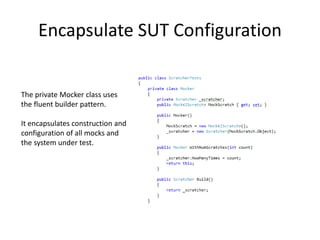
Unit testing involves testing individual components of software to ensure they function as intended when isolated from the full system. It helps identify unintended effects of code changes. While unit tests cannot prove the absence of errors, they act as an executable specification for code behavior. Writing unit tests requires designing code for testability through principles like single responsibility and dependency injection. Tests should focus on public interfaces and state transitions, not implementation details. Test-driven development involves writing tests before code to define requirements and ensure only testable code is written. Mocking frameworks simulate dependencies to isolate the system under test. Well-written unit tests keep behaviors isolated, self-contained, and use the arrange-act-assert structure.