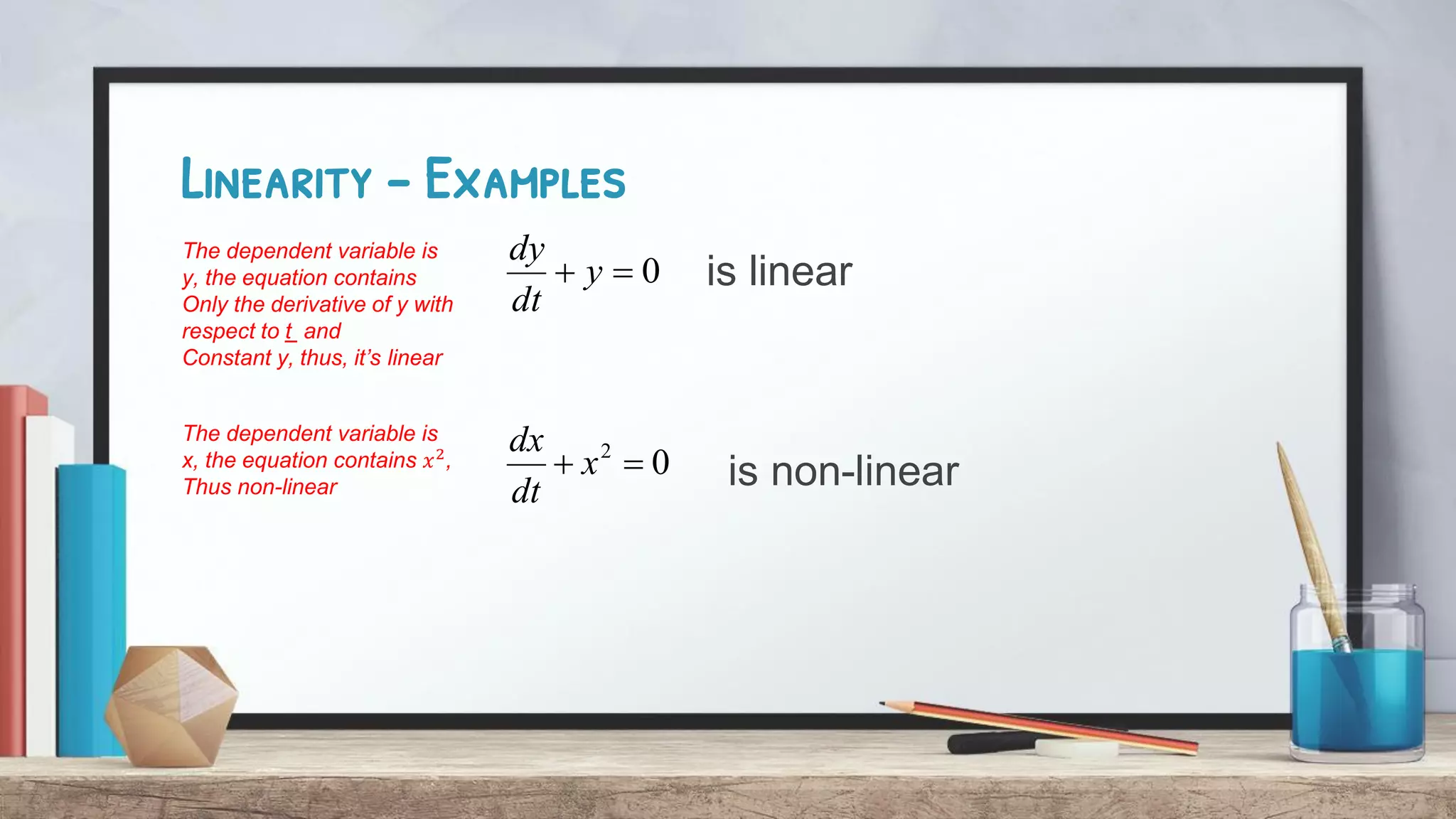
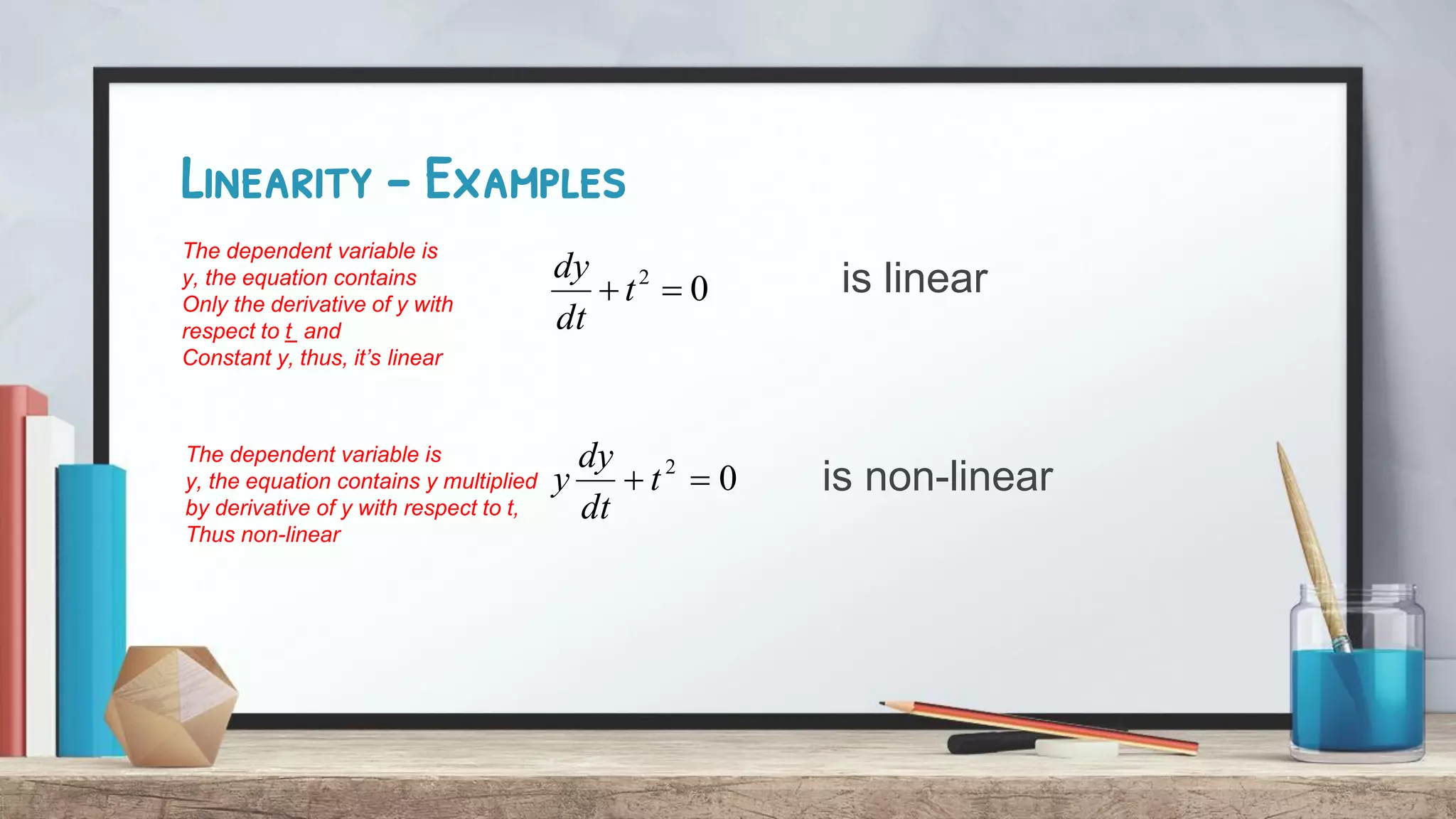
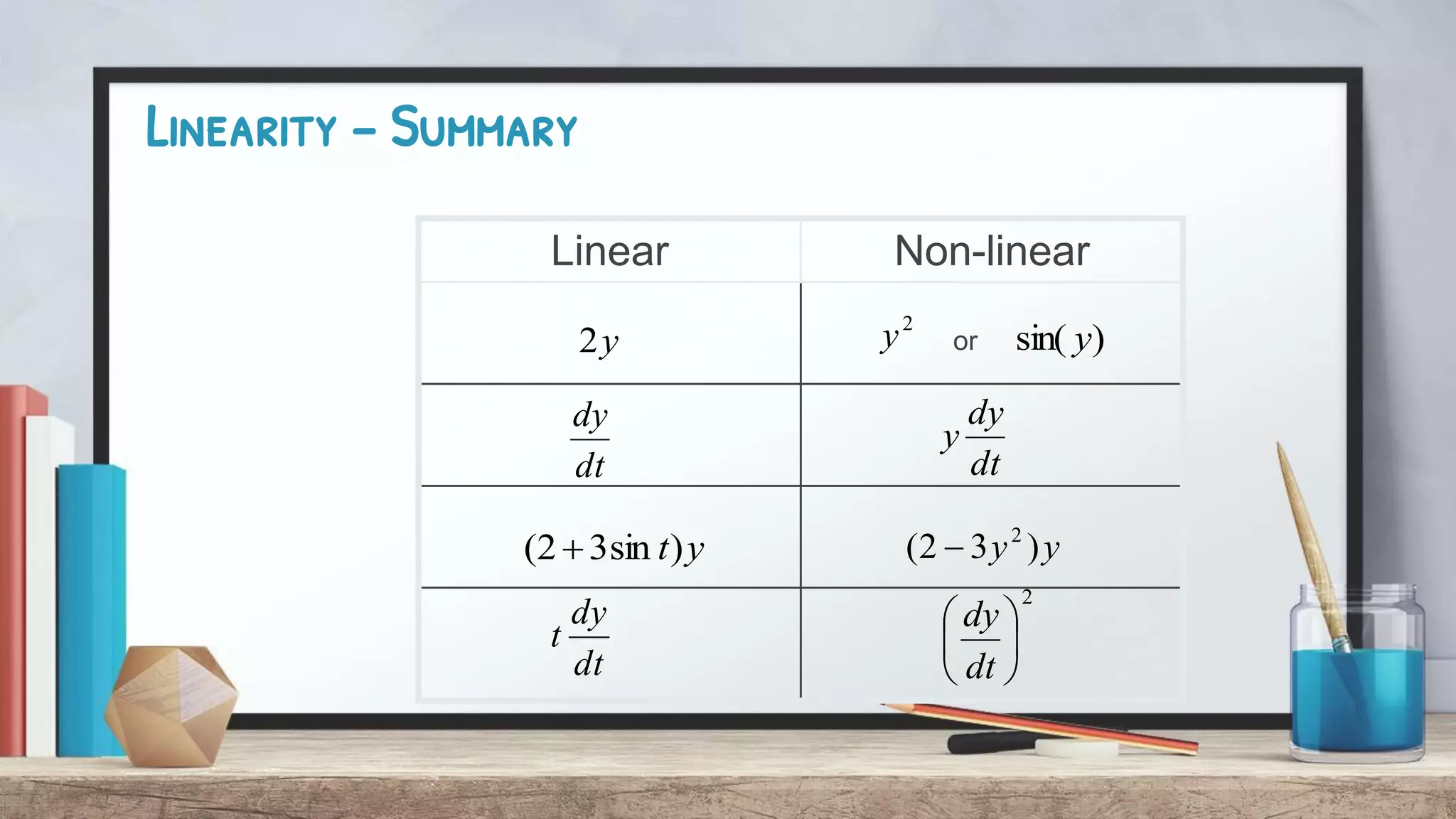
This document discusses linearity in differential equations. It defines a linear differential equation as one where the dependent variable (y) and its derivatives appear alone and are not within nonlinear functions. The coefficients must also be constants or depend only on the independent variable (t). Examples are provided of both linear and nonlinear equations to illustrate these concepts. Key factors that determine if an equation is linear or nonlinear are whether y or its derivatives are raised to powers or involved in trigonometric functions.