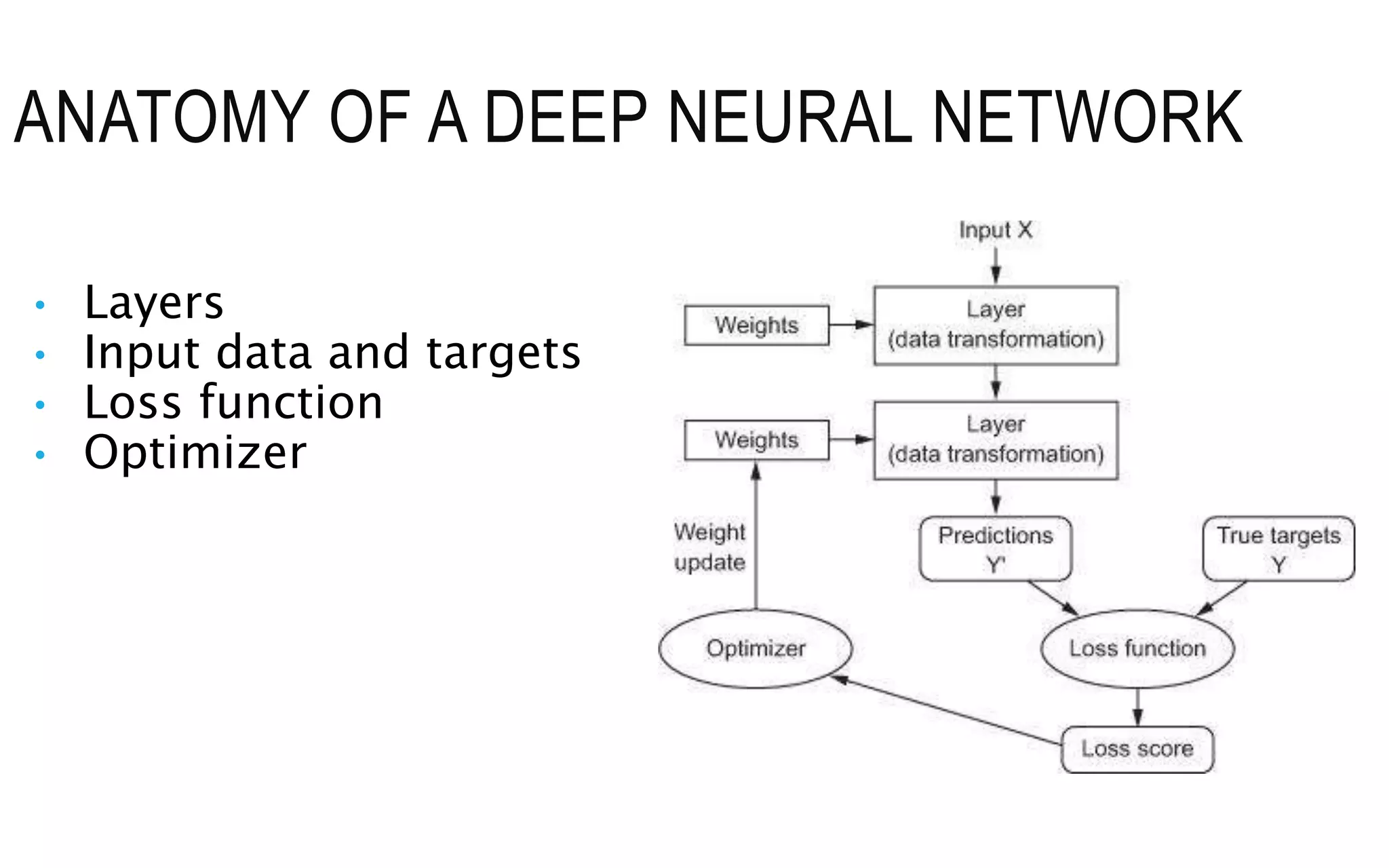
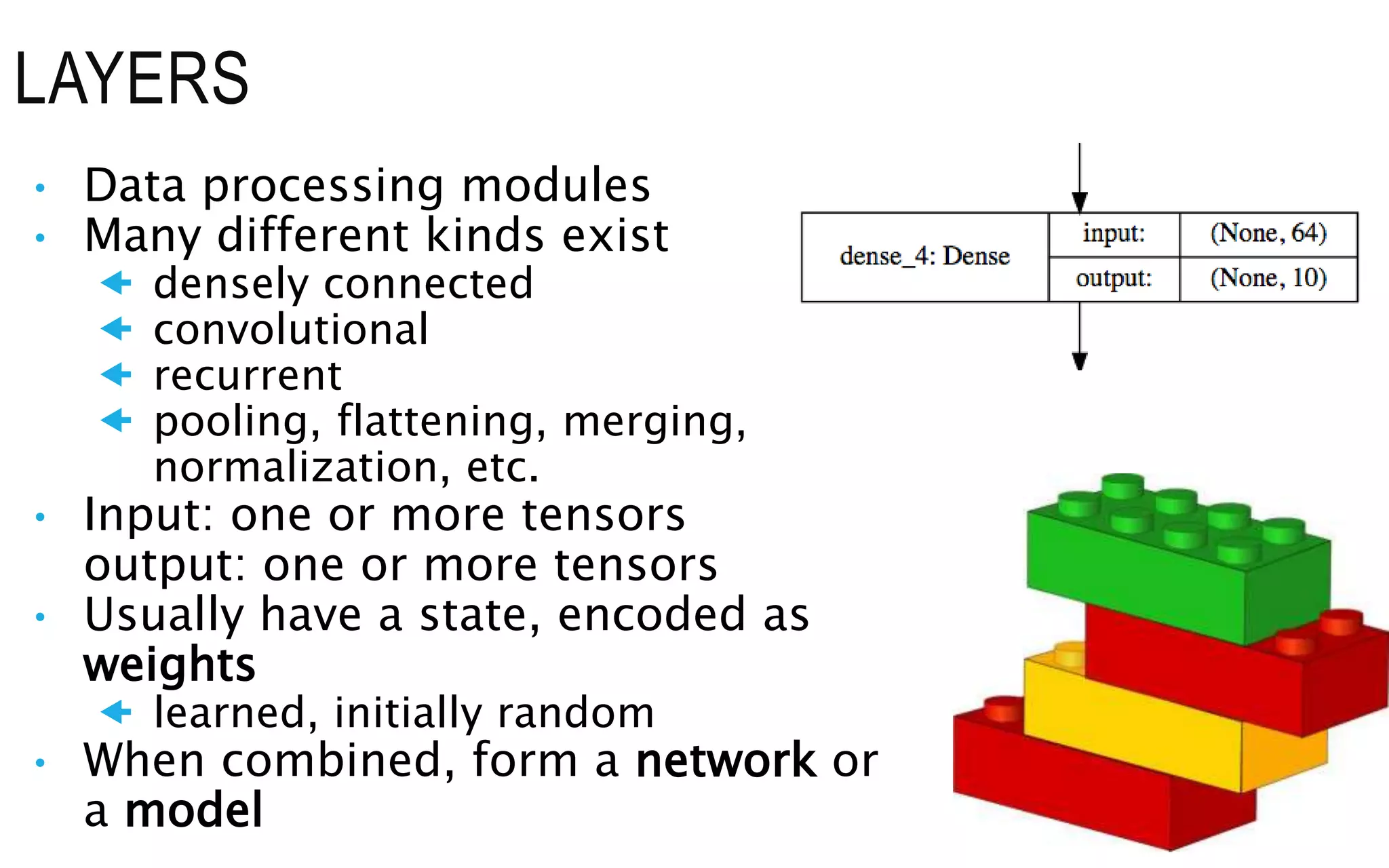
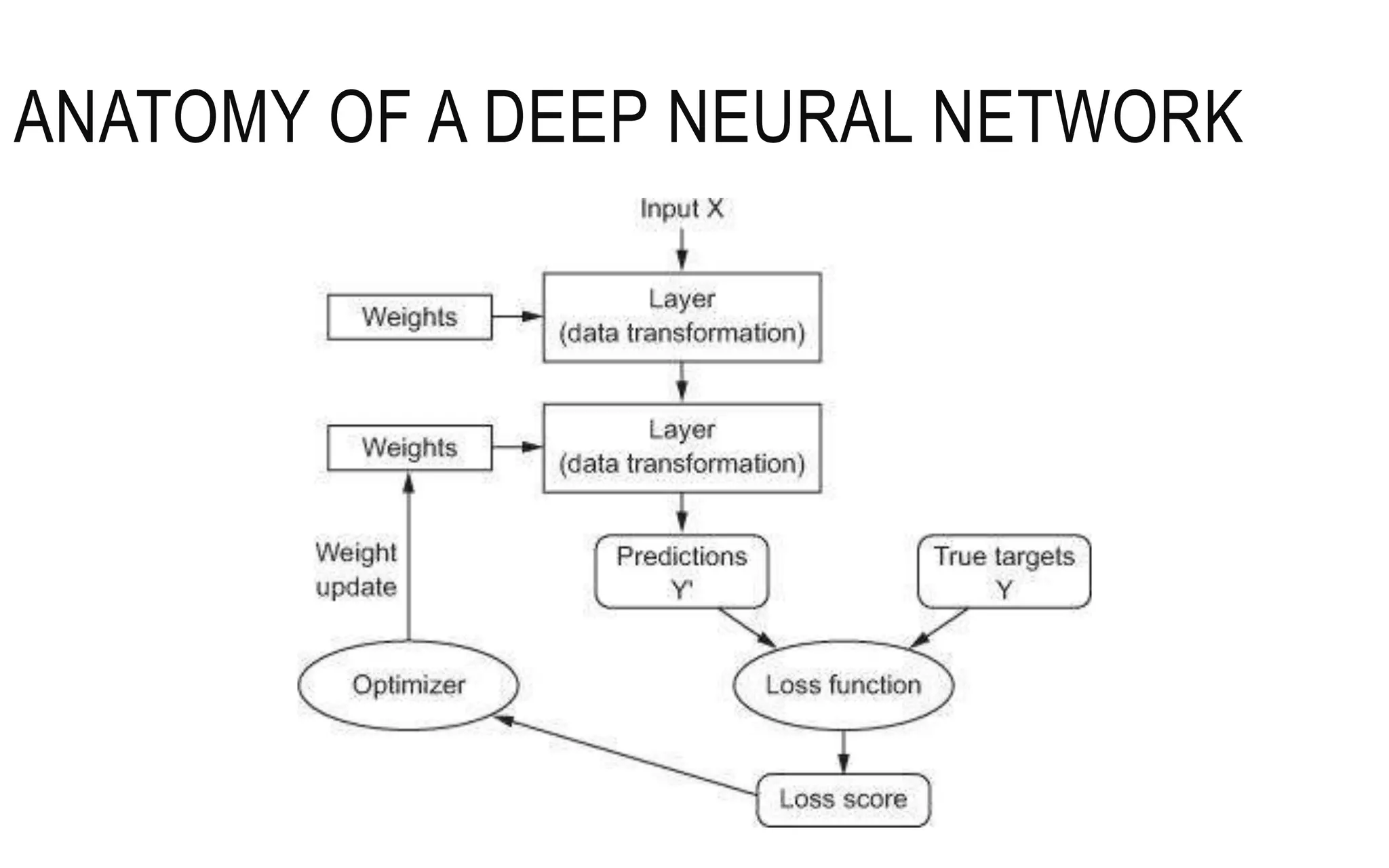
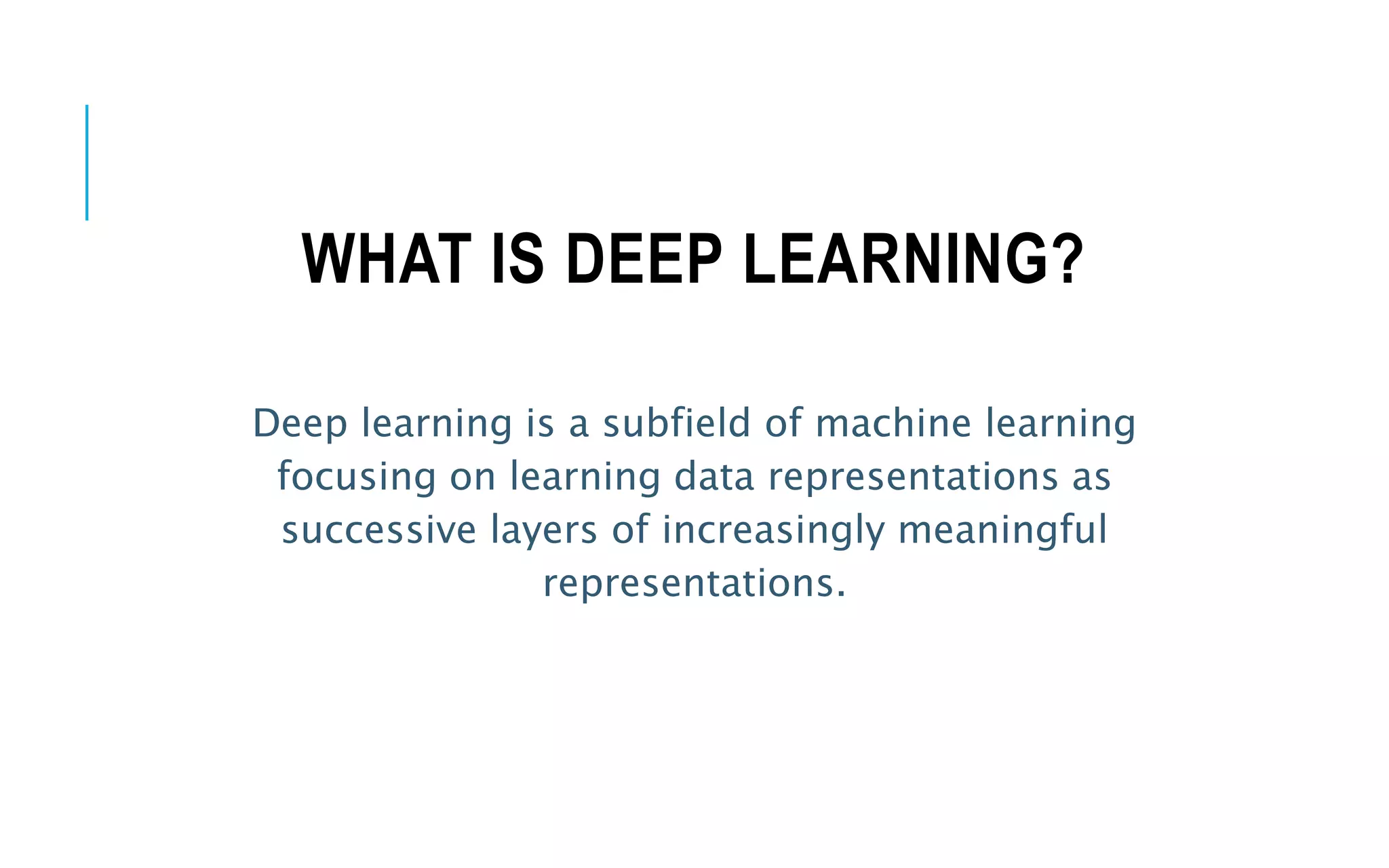
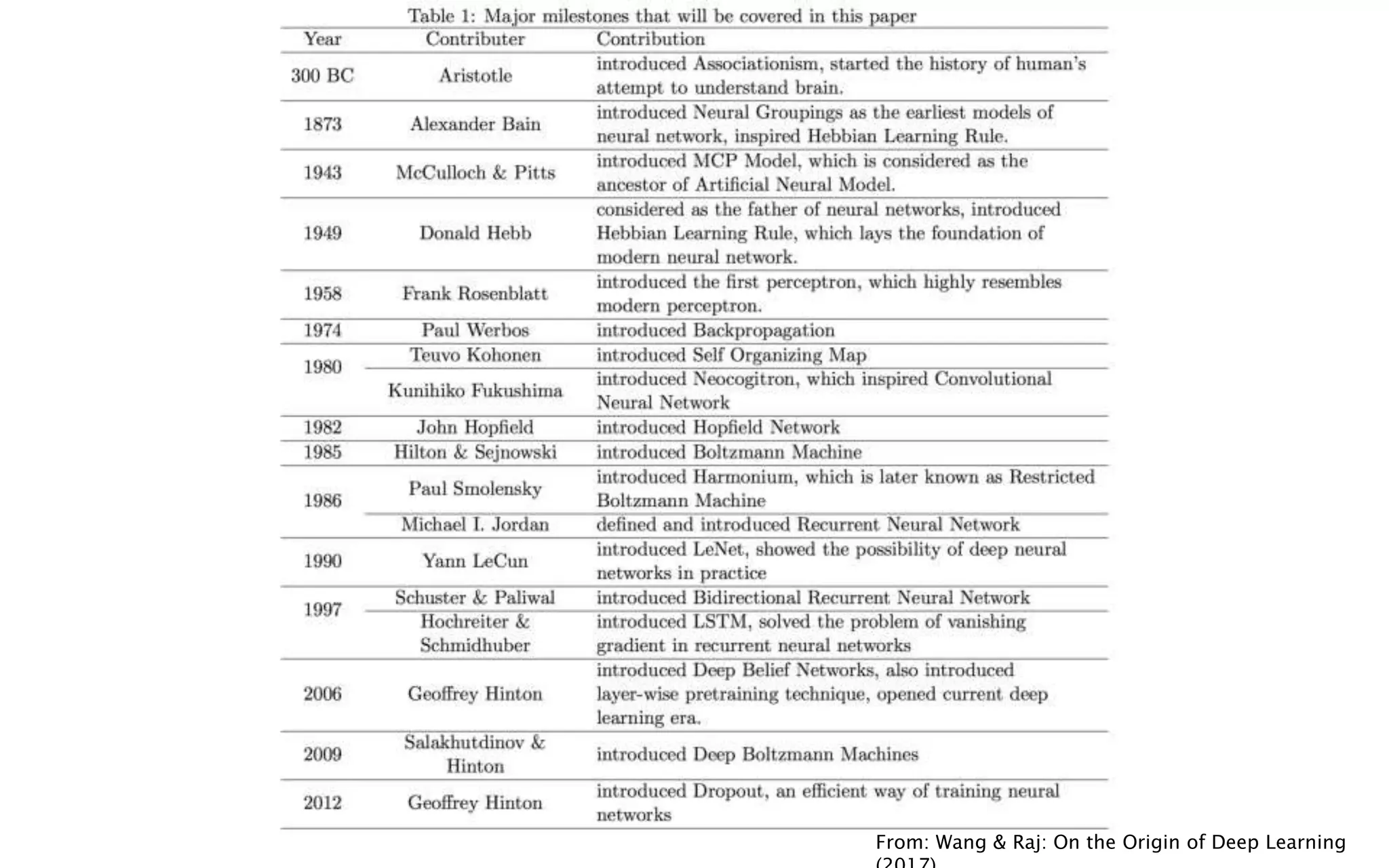
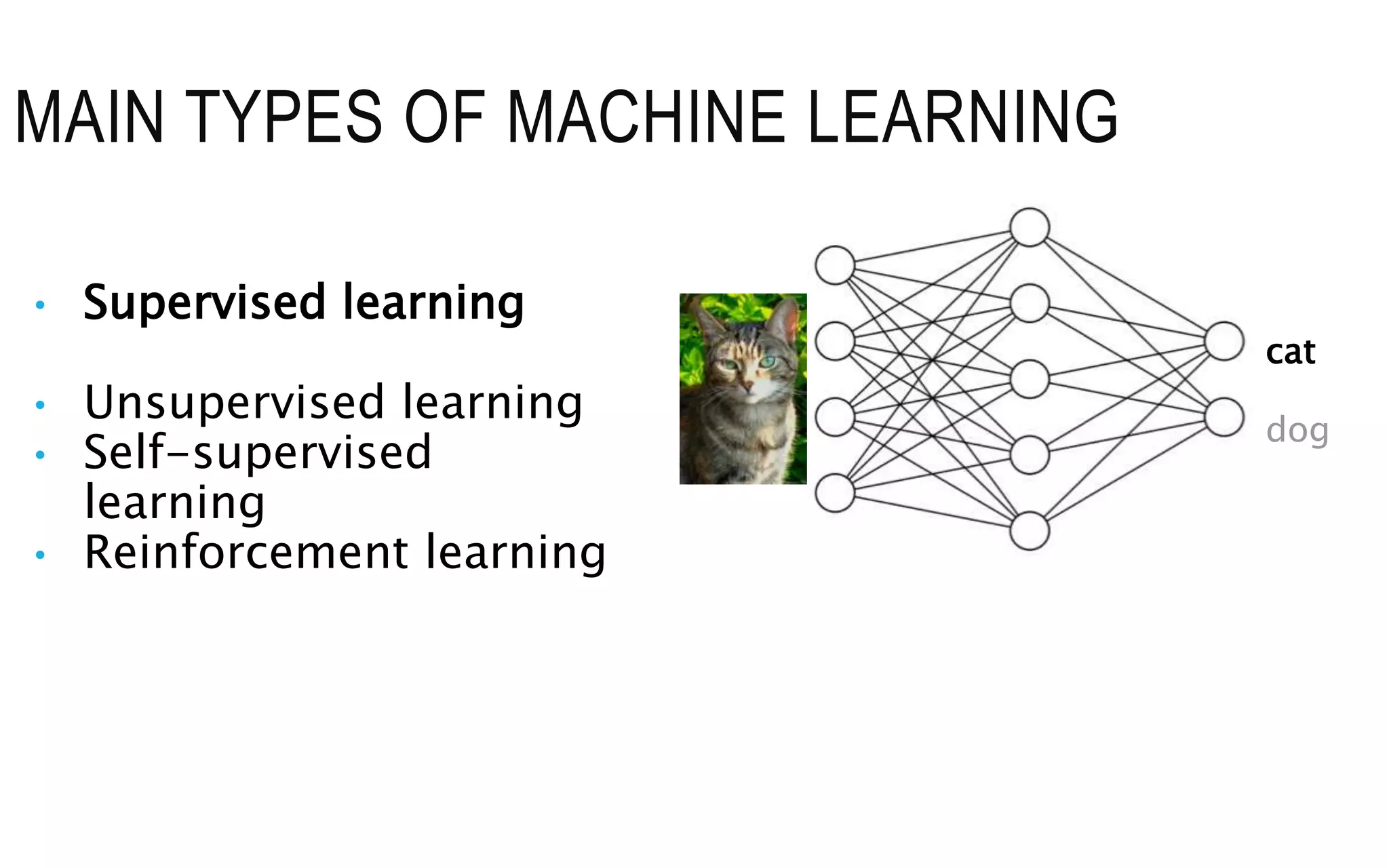
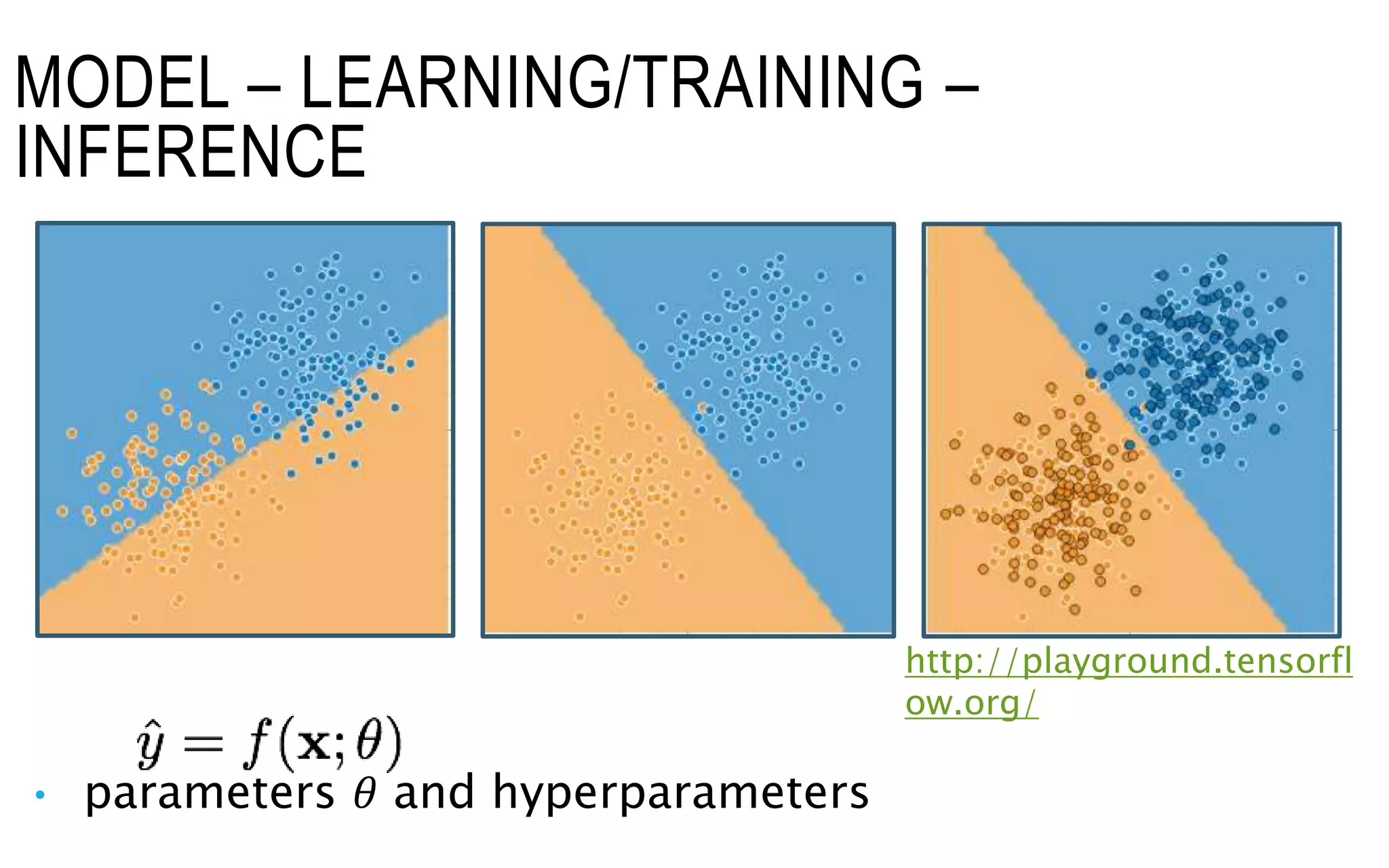
The document is an introduction to deep learning, exploring key concepts such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning. It outlines the main types of machine learning—supervised, unsupervised, self-supervised, and reinforcement learning—and discusses fundamental components including data, models, training processes, loss functions, and deep learning frameworks. Notable frameworks mentioned include TensorFlow and PyTorch for building and training neural networks.



![OPTIMIZATION
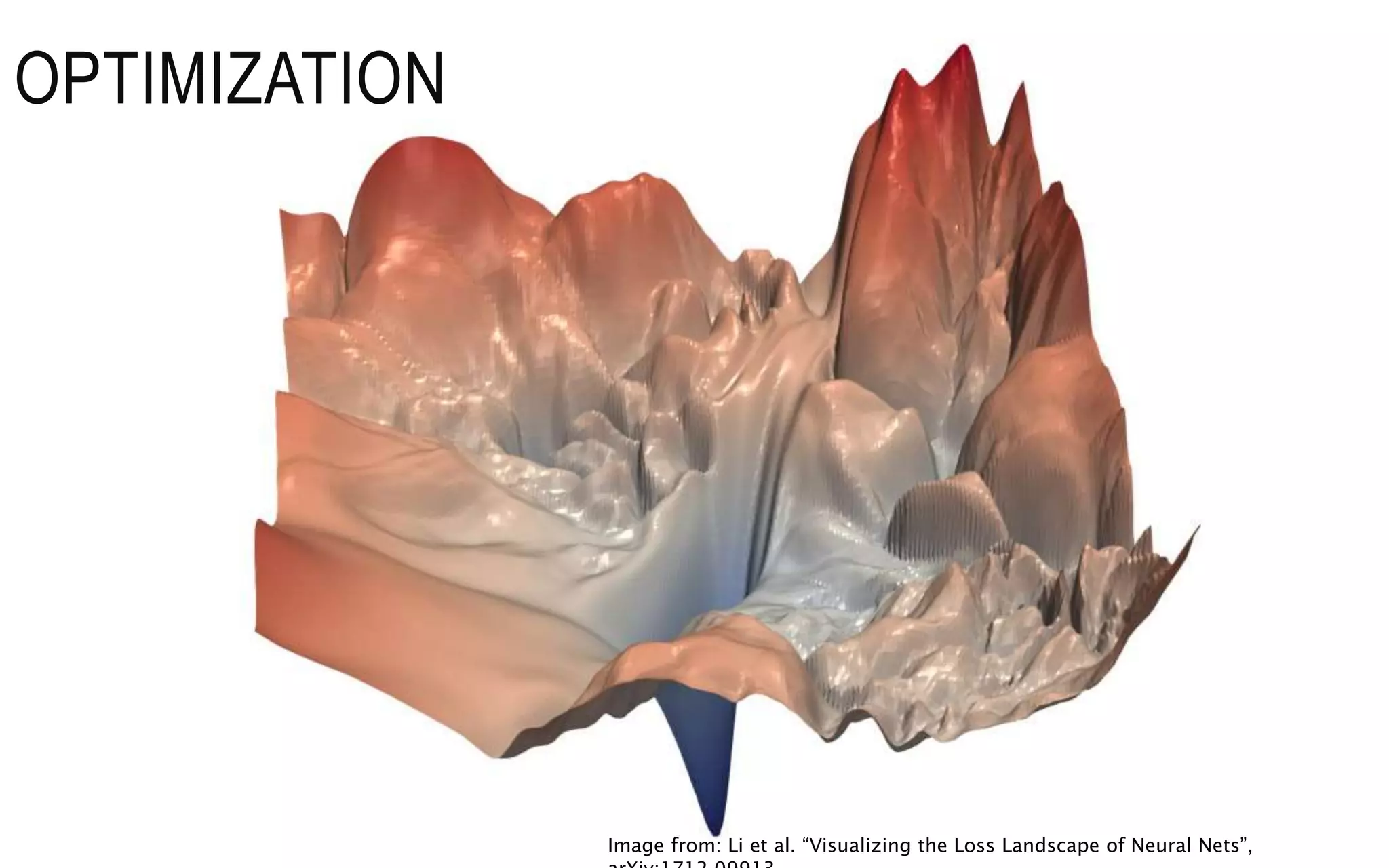
• Mathematical optimization:
“the selection of a best element (with
regard to some criterion) from some
set of available alternatives”
(Wikipedia)
• Main types:
finite-step, iterative, heuristic By Rebecca Wilson (originally posted to Flickr as Vicariously) [CC BY 2.0], via Wikimedia
Commons
los
s
regularizati
on
• Learning as an optimization problem
• cost function:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deeplearning-230325042831-23fbd141/75/deep-learning-pptx-15-2048.jpg)