This document is a lesson on decimals that includes:
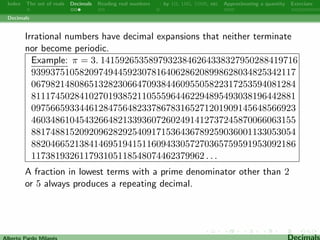
1. An introduction to decimals and their properties including terminating, repeating, and non-repeating decimals.
2. How to read and write decimal numbers.
3. How multiplying or dividing decimals by powers of ten affects their value.
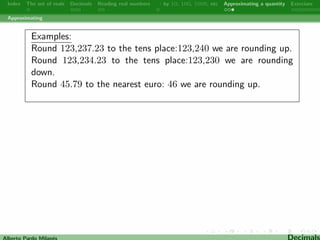
4. Techniques for approximating decimals like rounding and truncating.
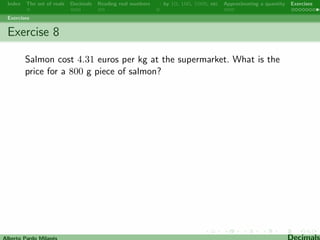
5. Several exercises for students to practice skills with decimals.