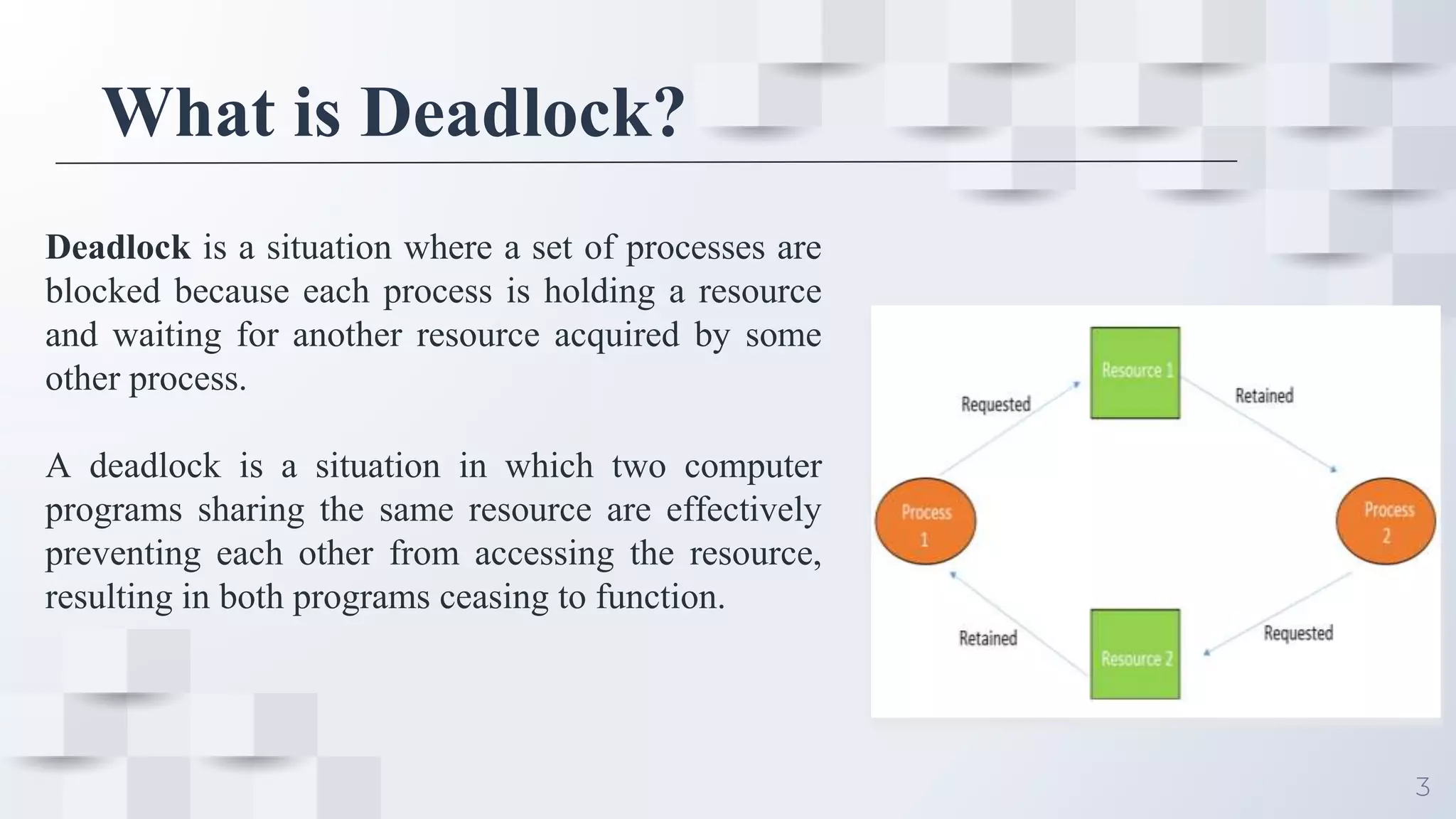
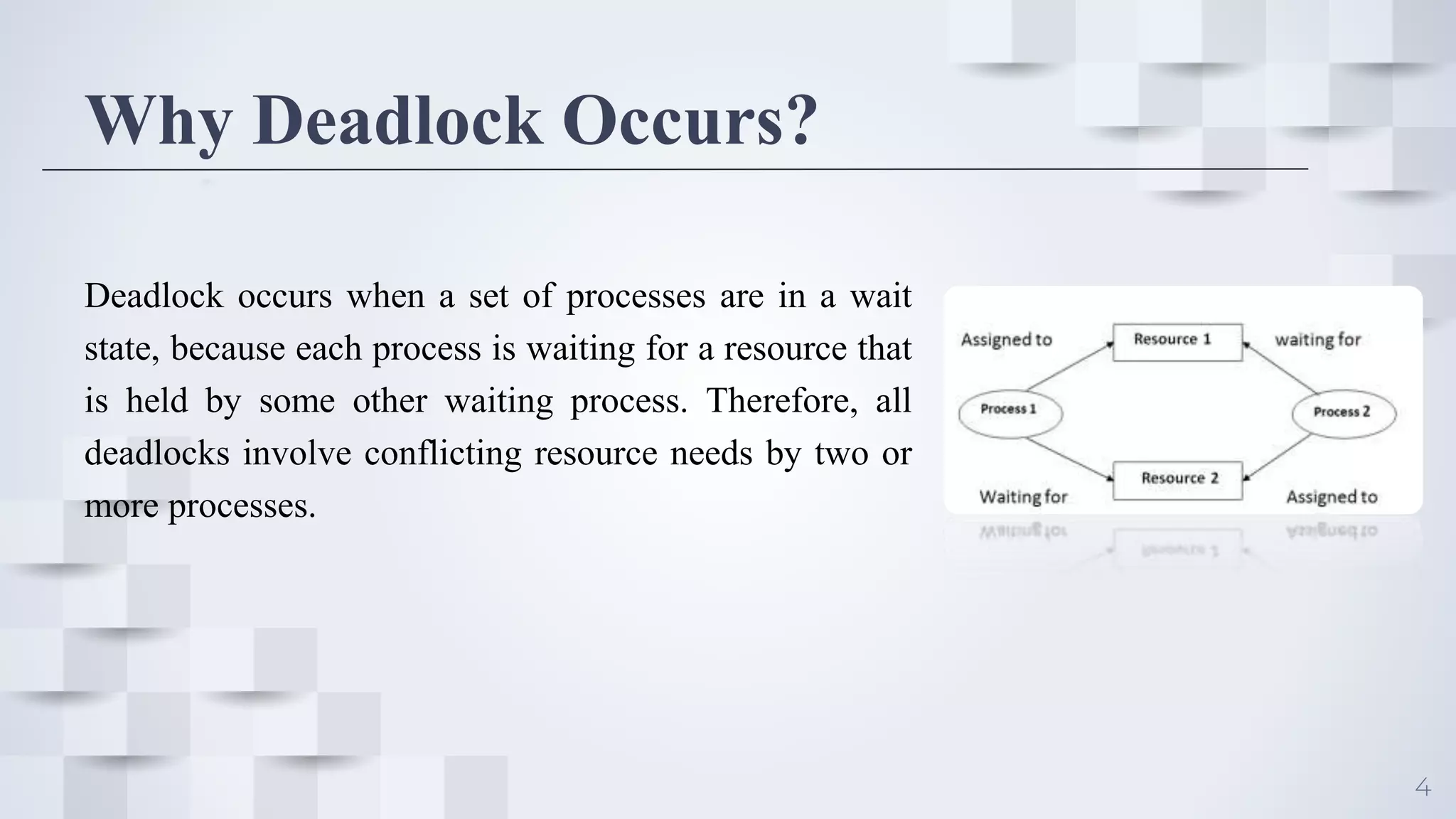
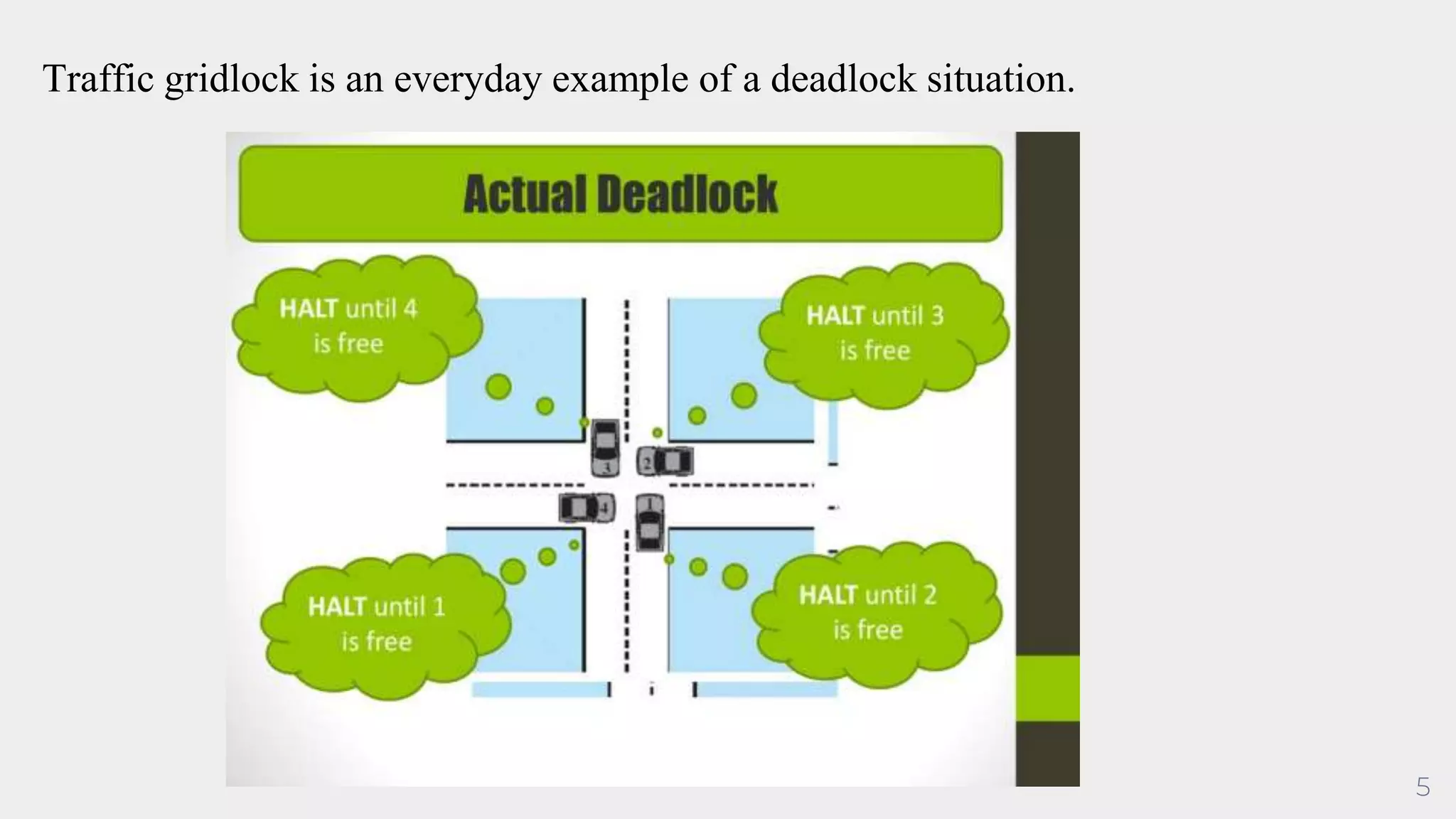
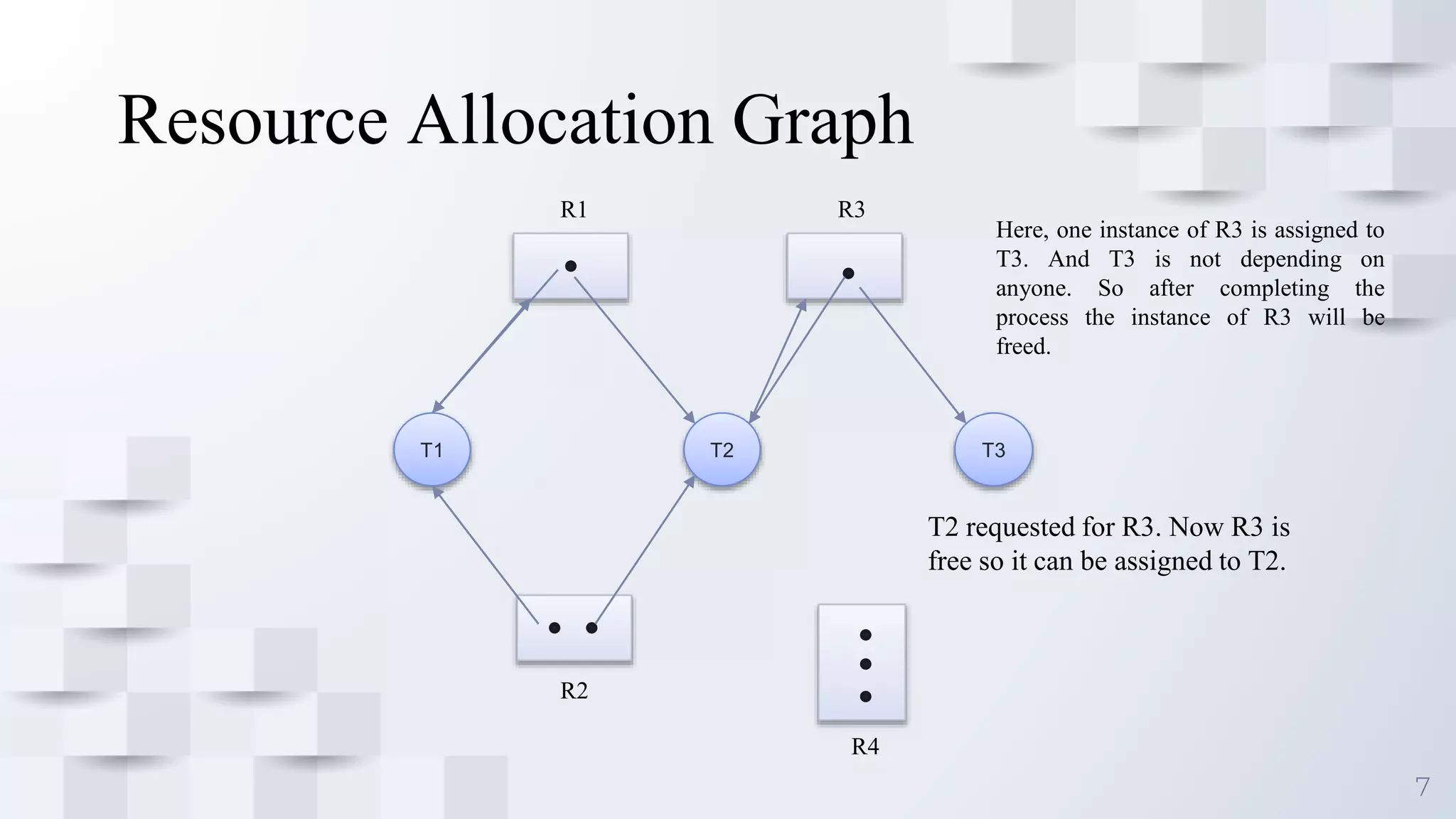
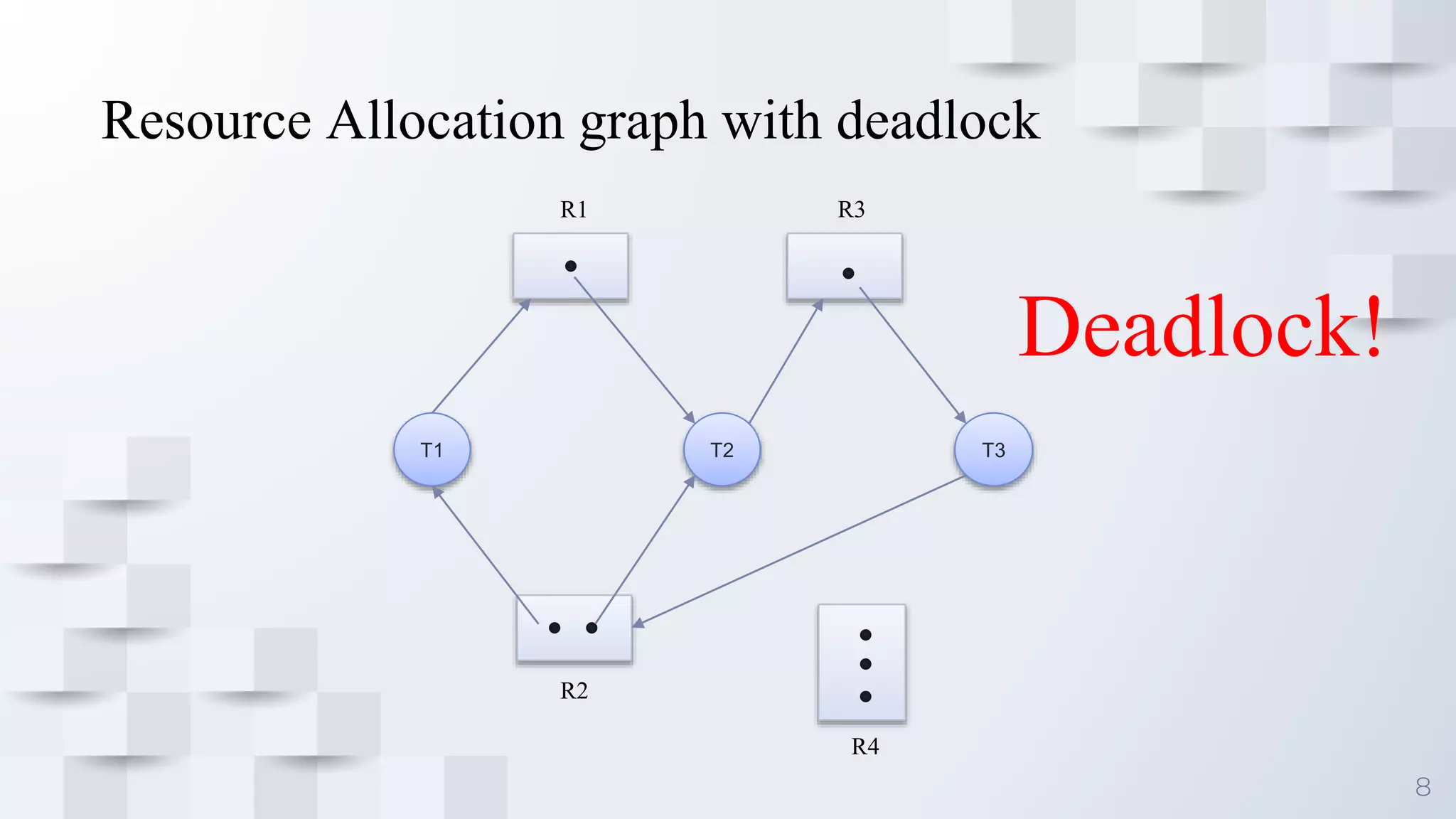
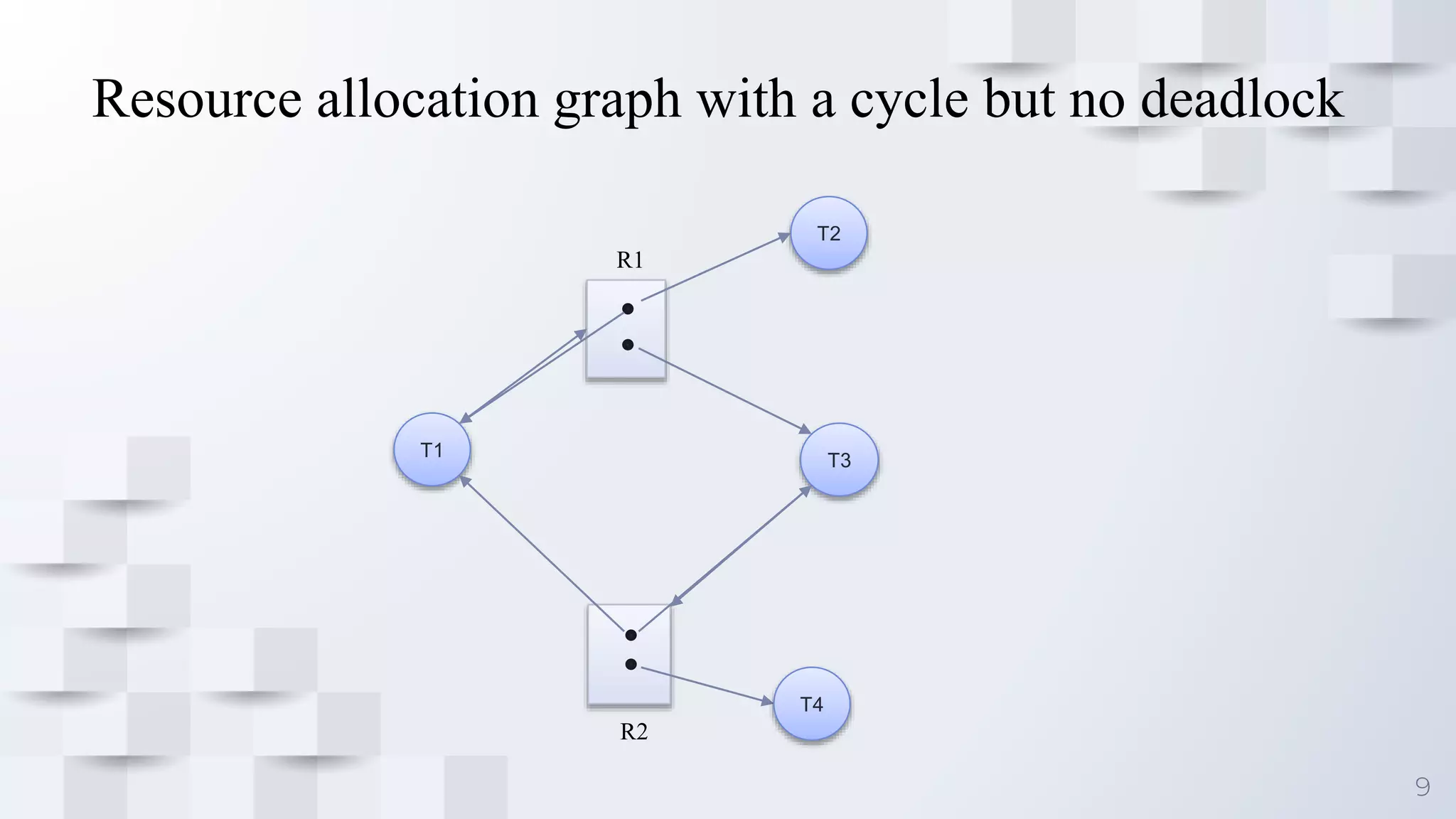
Deadlock occurs when a set of processes are blocked because each process is holding a resource and waiting for another resource acquired by some other process, resulting in all processes ceasing to function. For deadlock to occur, four conditions must be satisfied simultaneously: mutual exclusion, where only one process can use a resource at a time; hold and wait, where processes are holding resources while waiting for other resources; no preemption, where a resource cannot be forcibly removed from a process; and circular wait, where there is a cycle in resource allocation. Deadlock can be represented using a resource allocation graph that shows resource dependencies between processes.