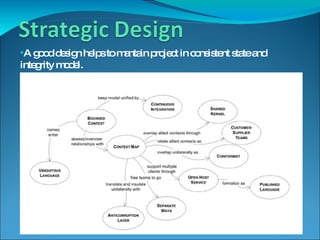
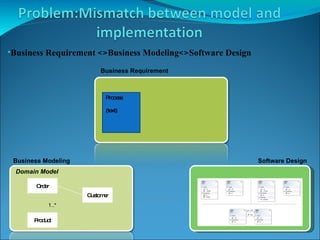
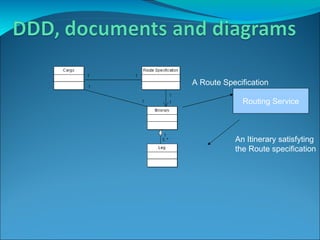
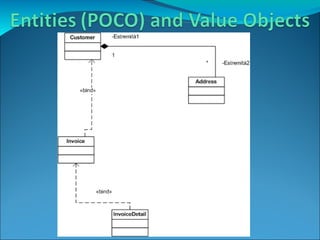
Domain-driven design (DDD) is an approach that involves using a shared domain model and ubiquitous language to support complex domains and ensure alignment between software design and business needs. It emphasizes basing the software design on an evolving model that shares common concepts with domain experts. DDD uses patterns like entities, value objects, aggregates and repositories to structure the software around domain concepts and separate domain logic from data access and external interfaces.














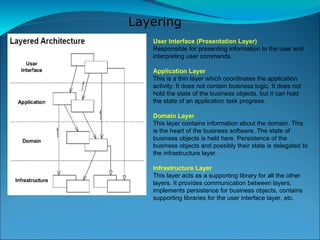

![Defines an application's boundary with a layer of services that establishes a set of available operations and coordinates the application's response in each operation. A service typically implements a business rule, generally something that software must do. Infrastructure and domain logic services A Service Layer defines an application's boundary [Cockburn PloP] and its set of available operations from the perspective of interfacing client layers. It encapsulates the application's business logic, controlling transactions and coor-dinating responses in the implementation of its operations.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ddd-1229773878275887-1/85/DDD-20-320.jpg)