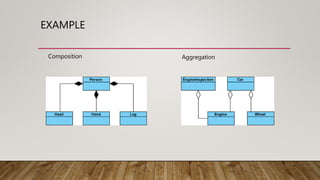
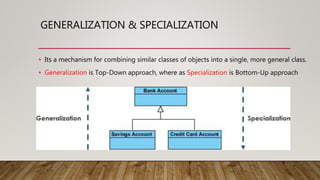
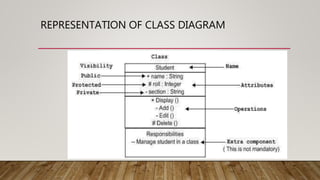
The document discusses low level design (LLD) as a component-level design process that provides the internal logical structure of software, facilitating direct code development with minimal debugging. It also covers object-oriented analysis and design (OOAD), UML as a modeling language, and various UML diagrams that represent classes and relationships within a system. Key concepts like association, aggregation, composition, generalization, and specialization are outlined to illustrate relationships between objects.