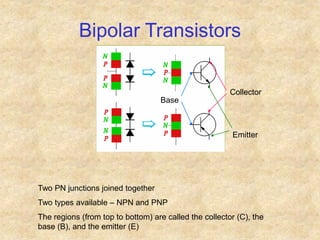
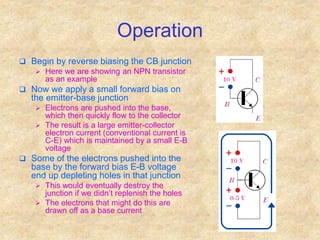
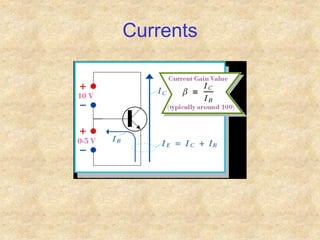
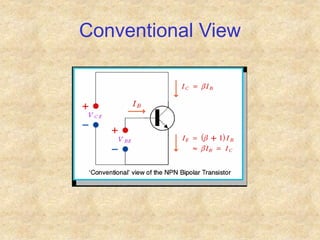
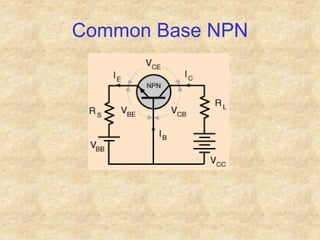
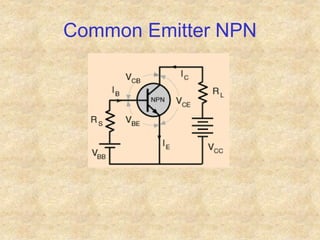
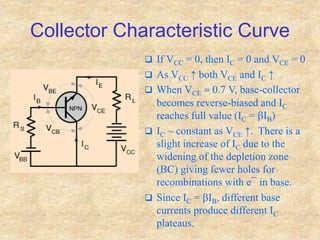
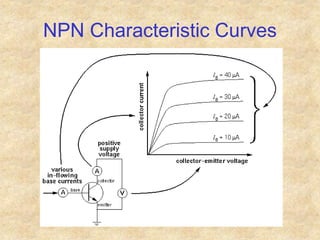
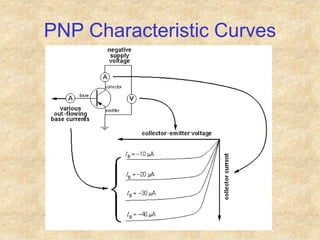
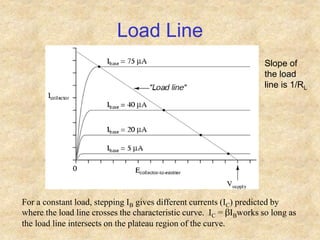
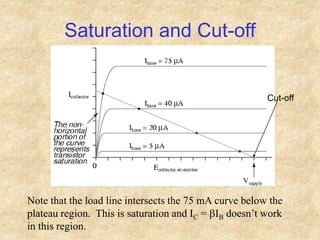
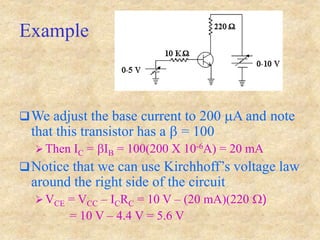
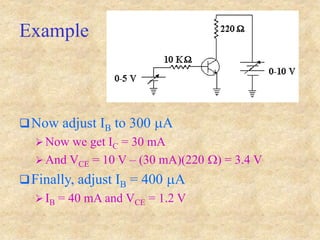
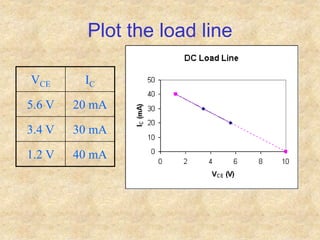
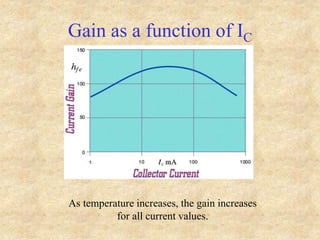
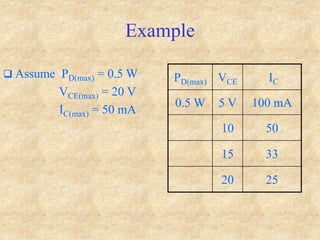
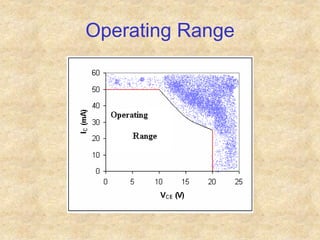
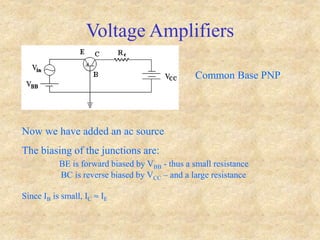
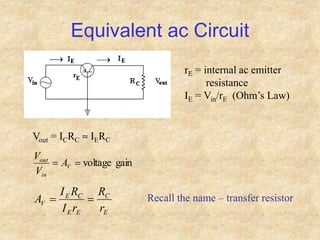
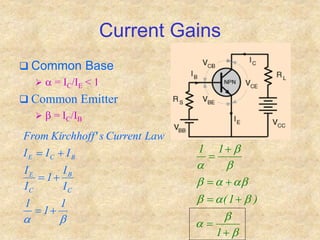
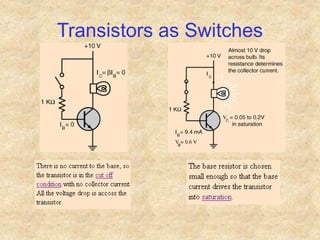
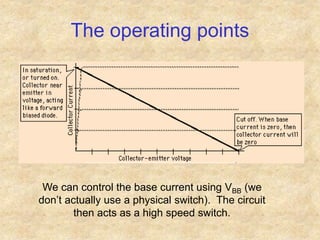
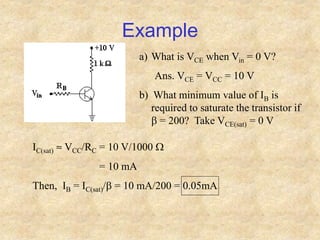
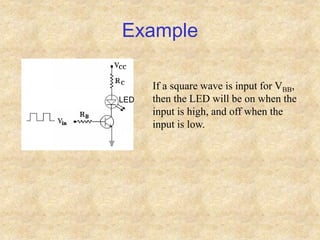
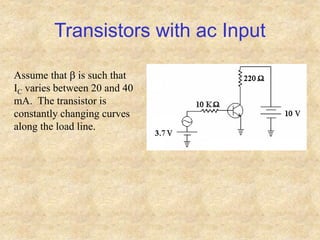
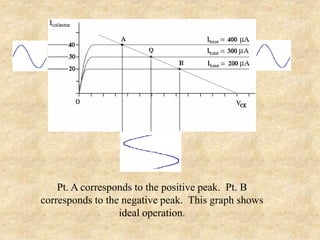
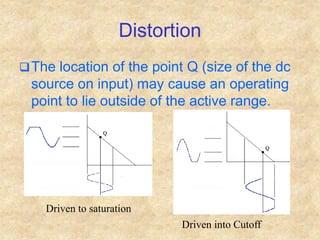
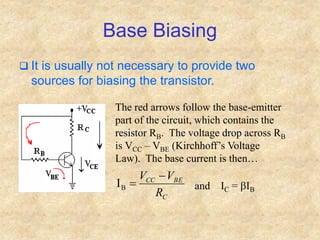
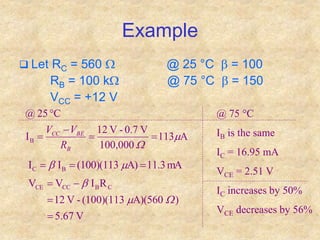
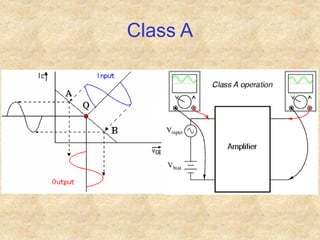
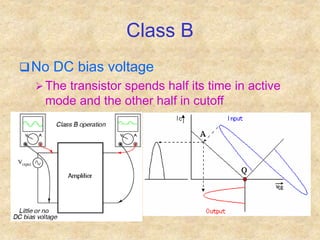
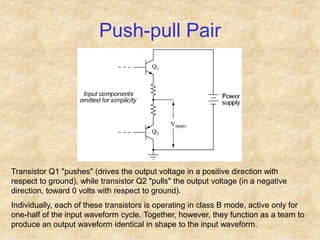
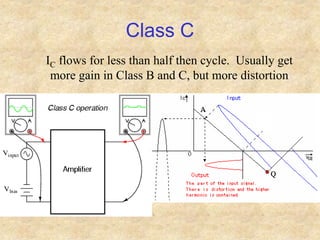
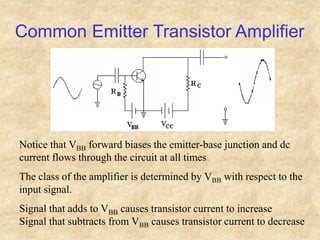
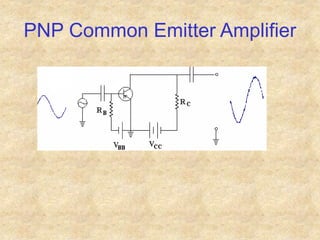
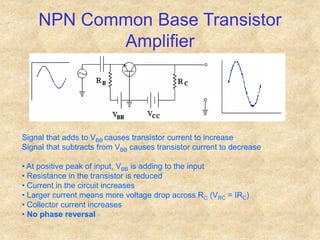
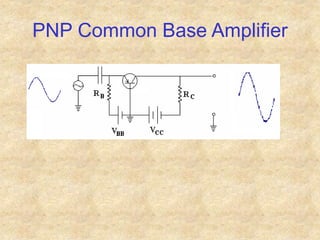
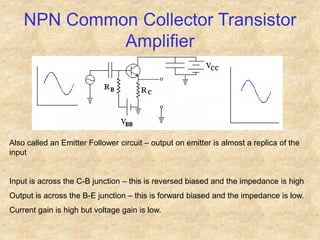
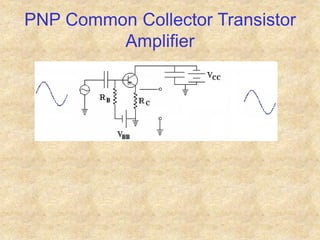
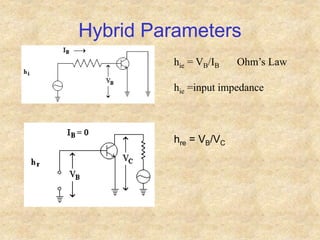
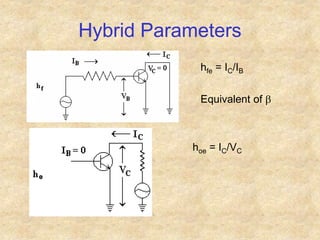
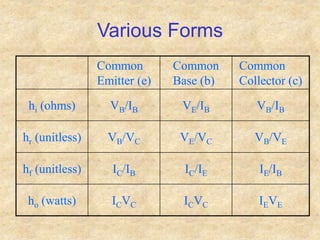
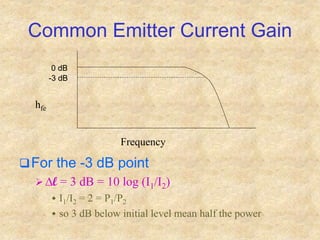
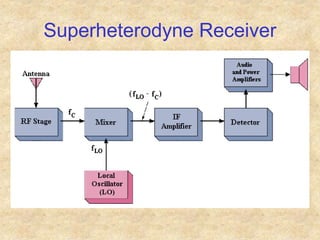
Transistors are semiconductor devices with three terminals - collector, base, and emitter. There are two main types, NPN and PNP, which differ in the doping of the semiconductor regions. Bipolar transistors can operate as amplifiers, switches, or oscillators depending on the biasing conditions. The common emitter configuration provides voltage gain but inverts the phase, while common base and common collector configurations do not invert phase. Transistor gain is determined by factors like current gain (beta) and varies based on operating point and temperature.