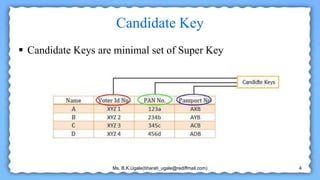
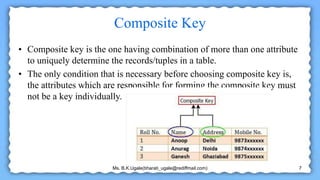
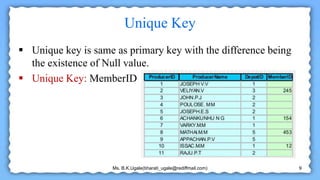
The document defines and provides examples of different types of keys used in database systems, including super keys, candidate keys, primary keys, alternate keys, composite keys, foreign keys, and unique keys. A super key can identify a tuple but contains extra attributes, while a candidate key is a minimal super key. The primary key is chosen by the administrator and must be unique. Alternate keys are other candidate keys, and composite keys comprise multiple attributes. Foreign keys link tables using primary keys, and unique keys are like primary keys but allow null values.