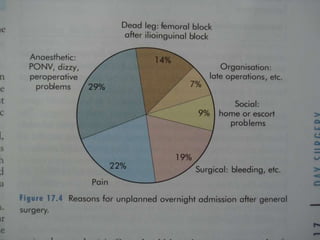
This document provides an overview of day care surgery (also known as ambulatory surgery). It discusses:
- The increasing prevalence of day care surgery globally to reduce costs and free up inpatient beds.
- Definitions and historical aspects of day care surgery.
- The benefits include reduced costs, morbidity, and disruption to patients' lives.
- Considerations for setting up a successful day surgery unit including appropriate patient and procedure selection, pre-admission processes, standards of care, and post-discharge follow up.
- Key factors for minimizing complications and ensuring safe and effective day care surgery.