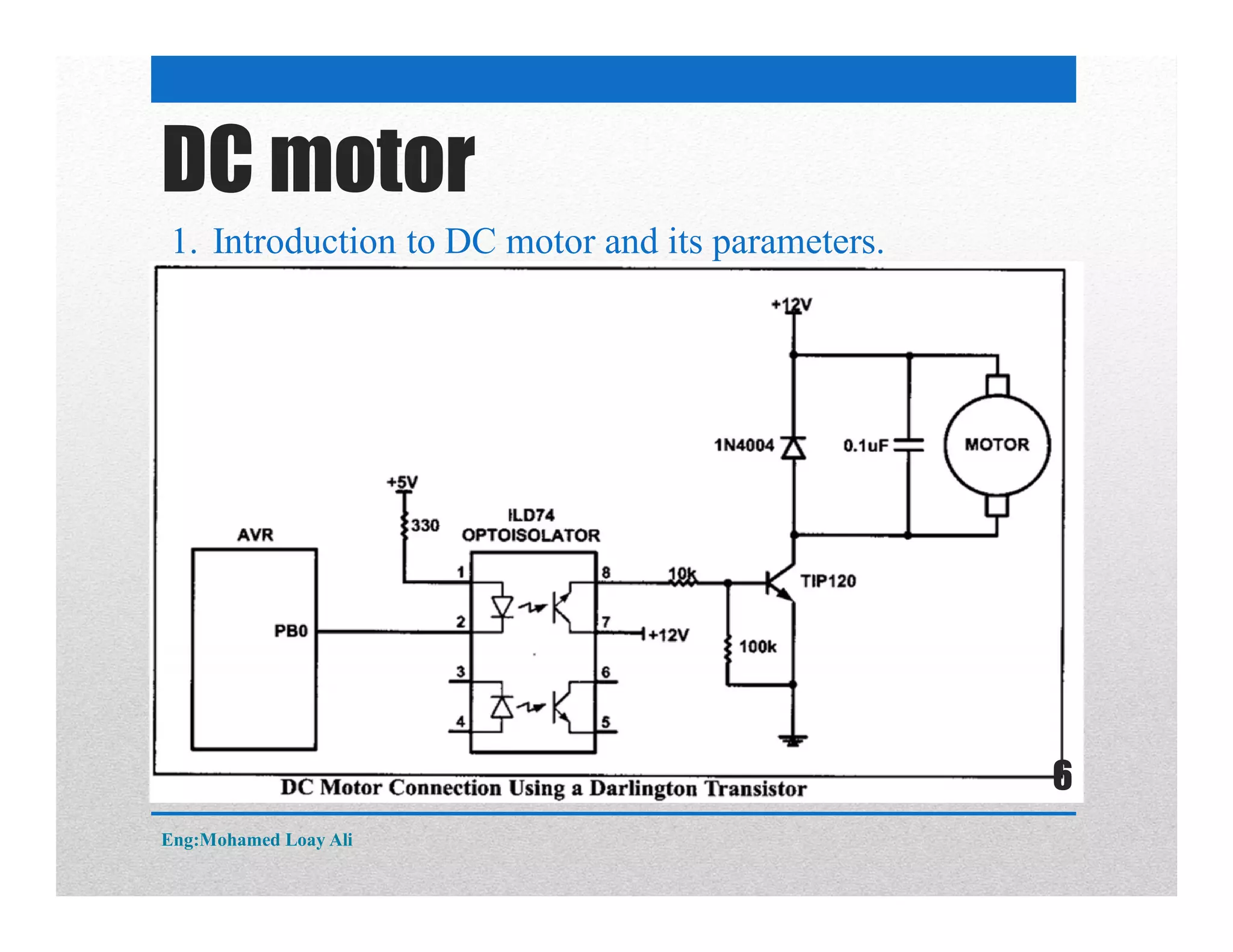
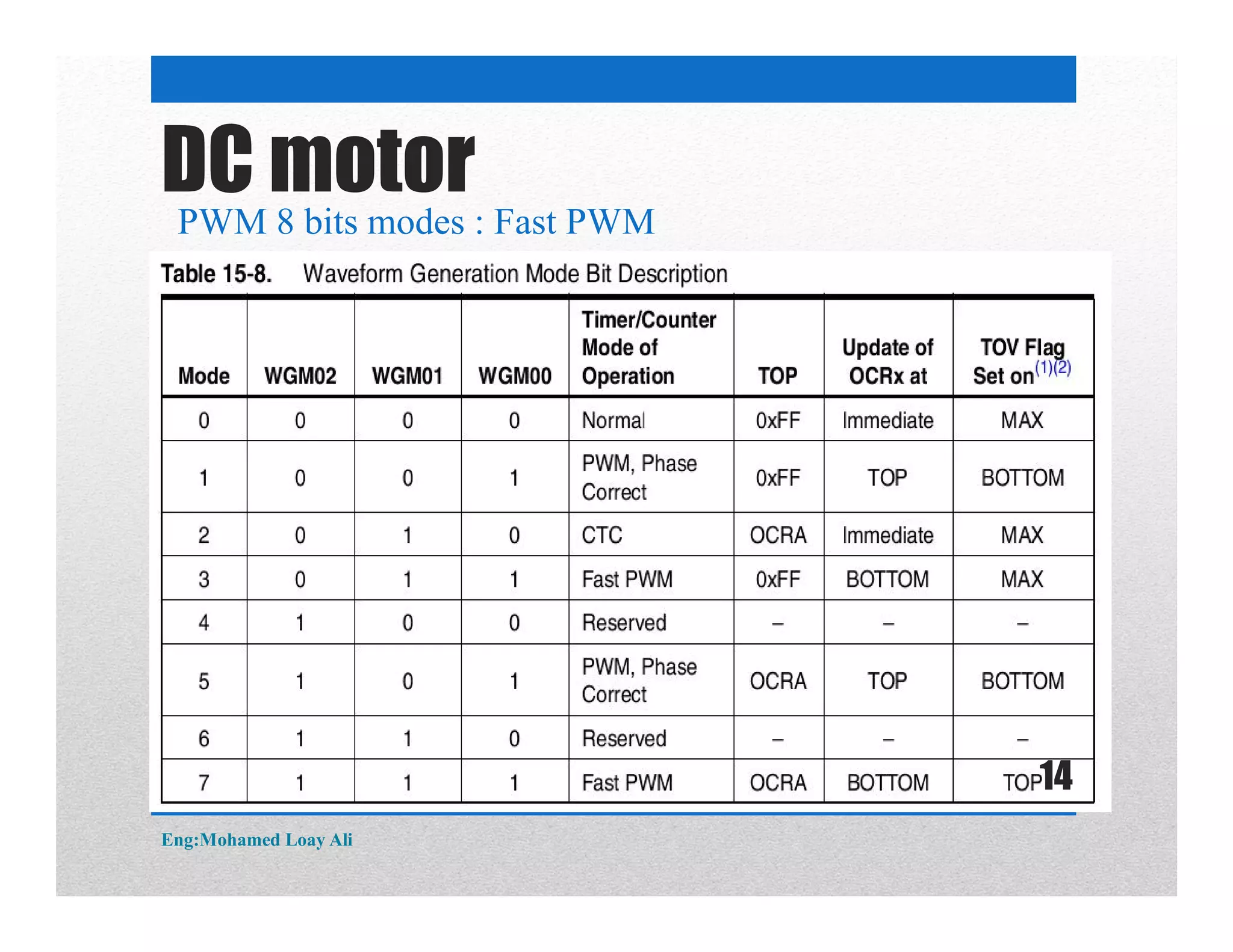
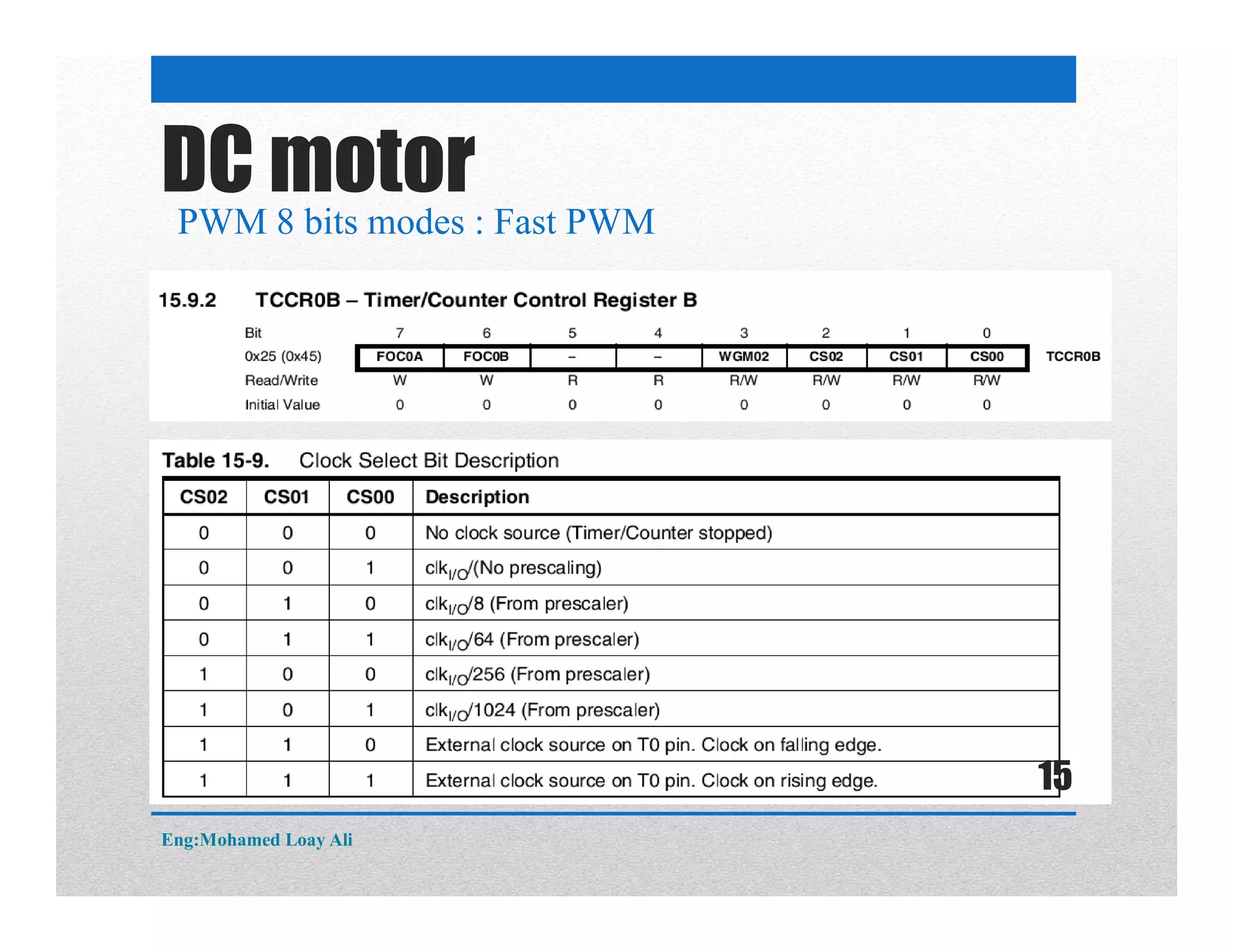
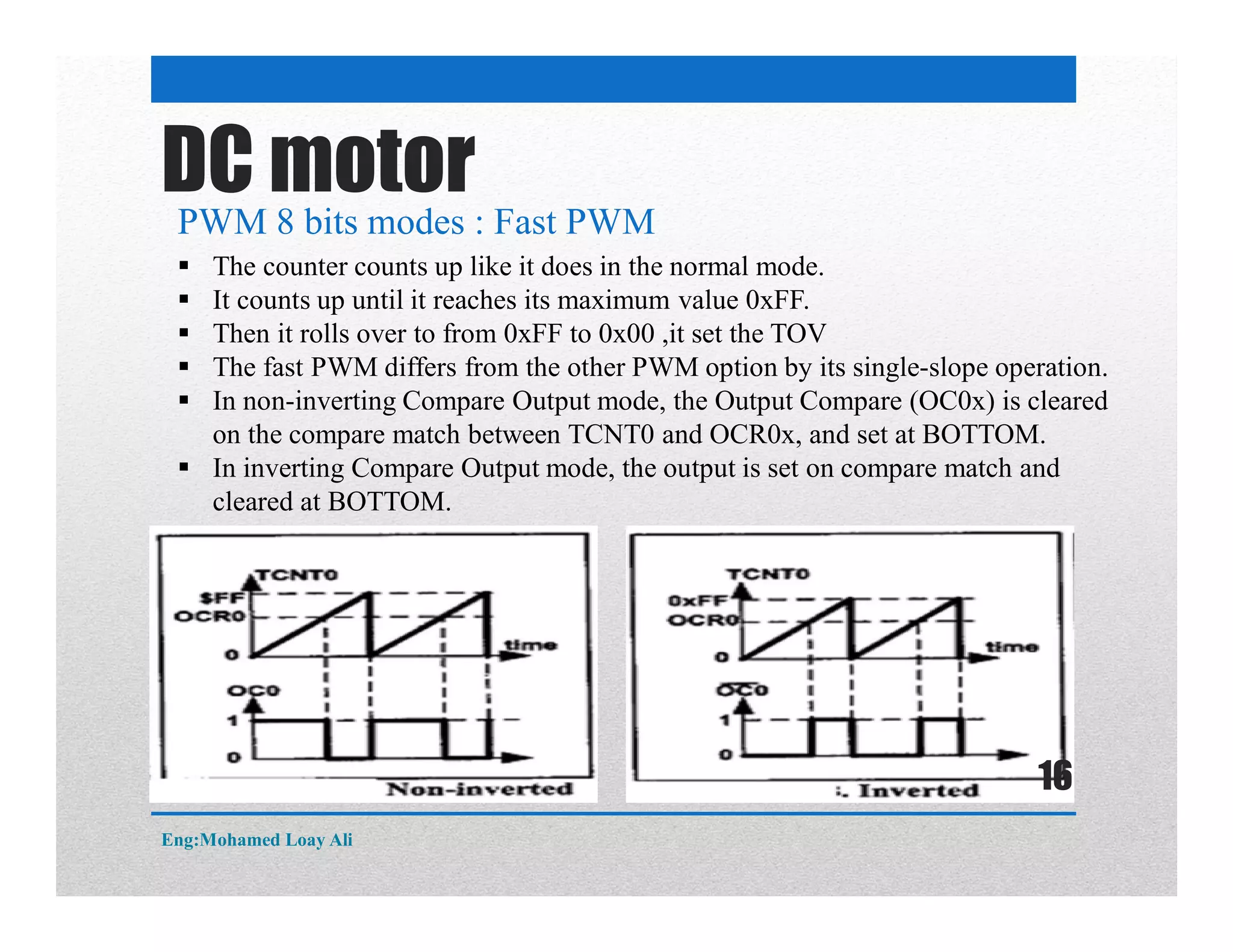
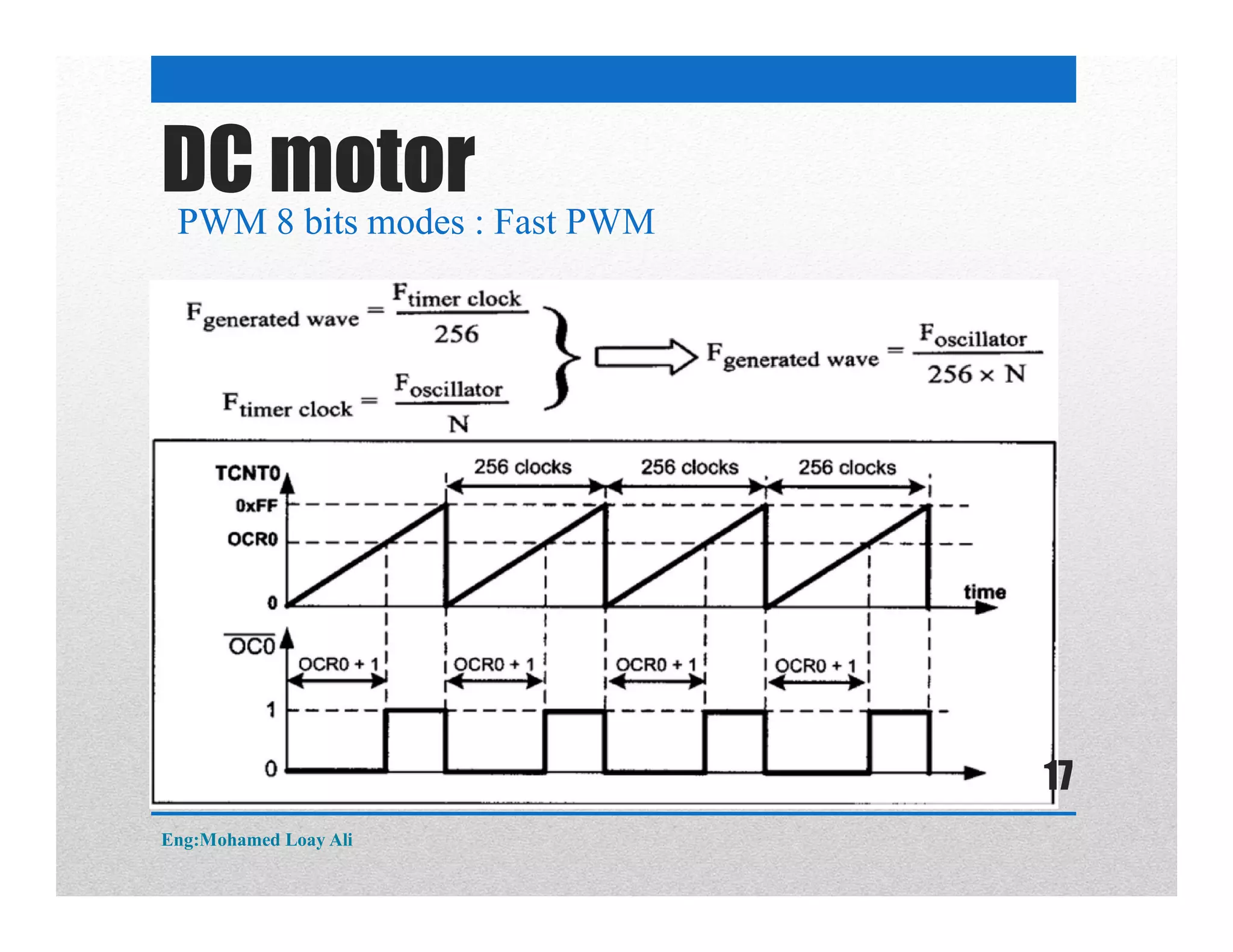
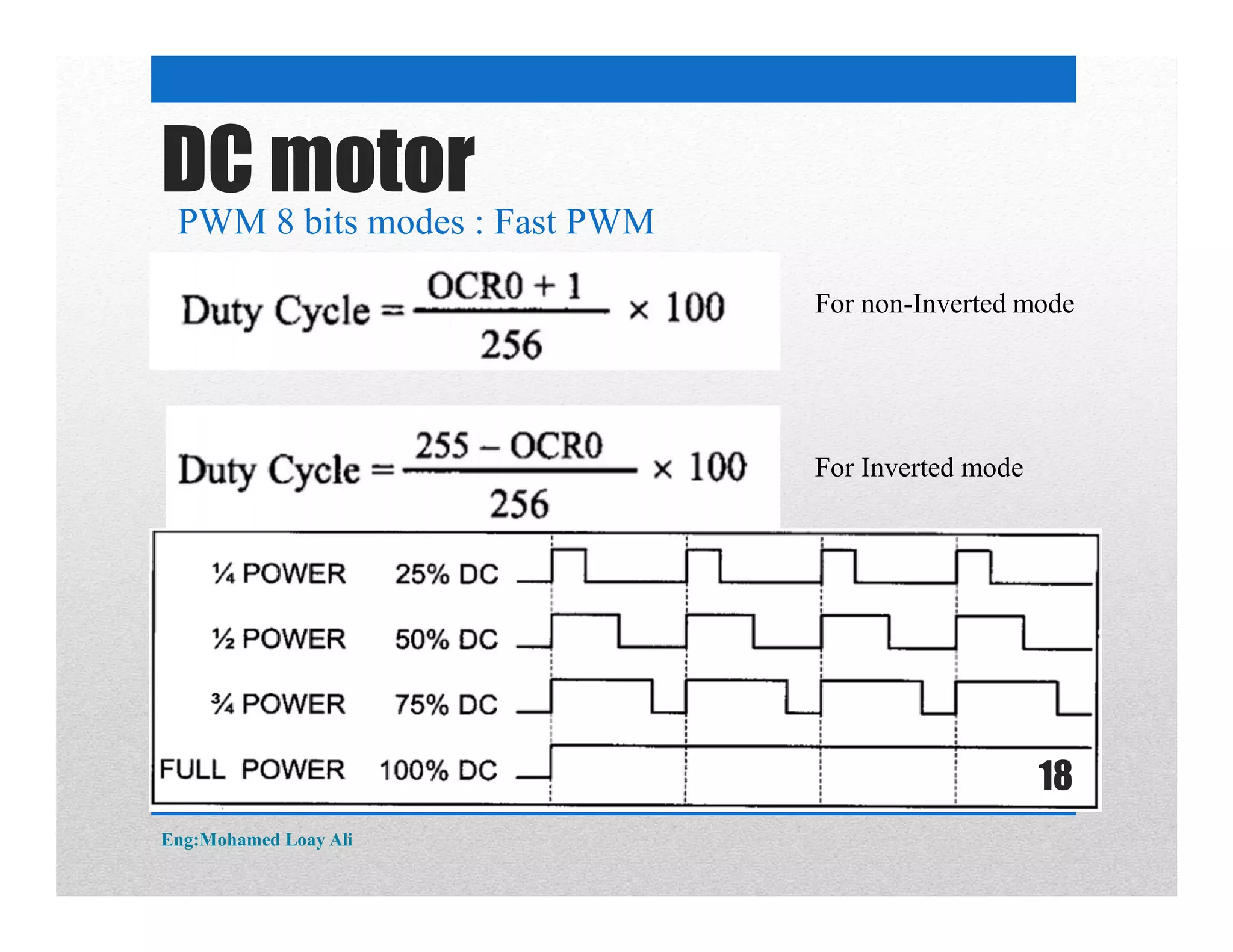
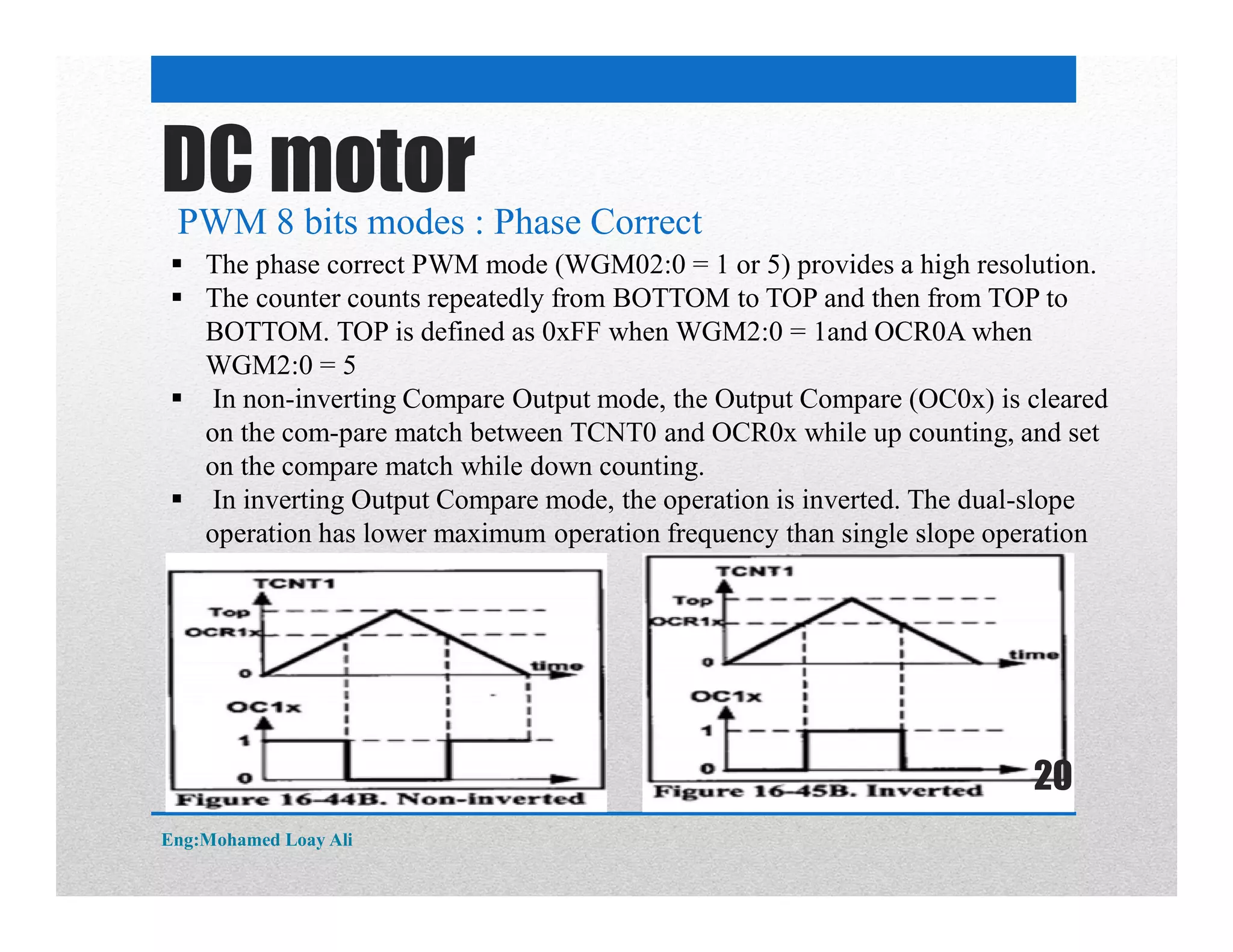
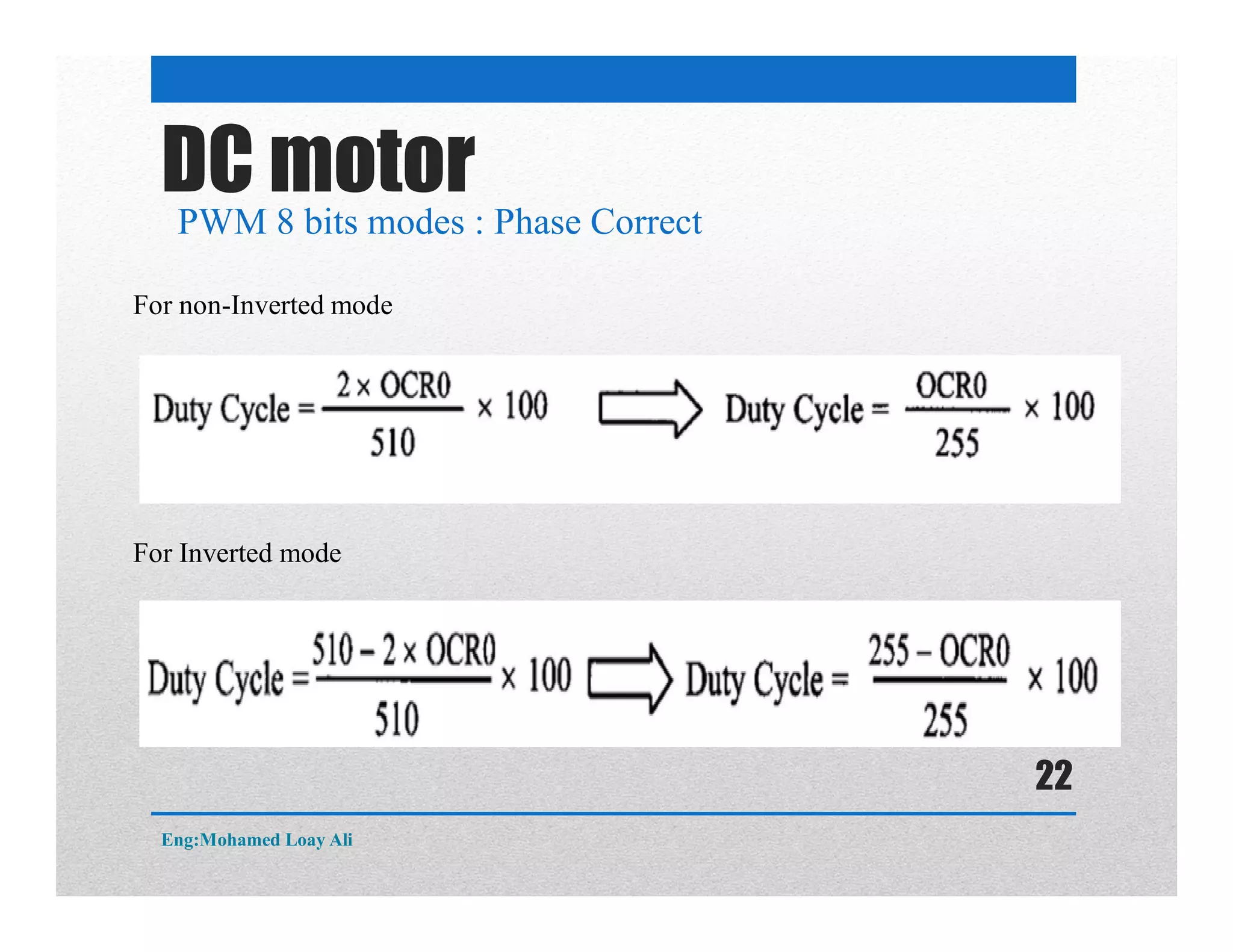
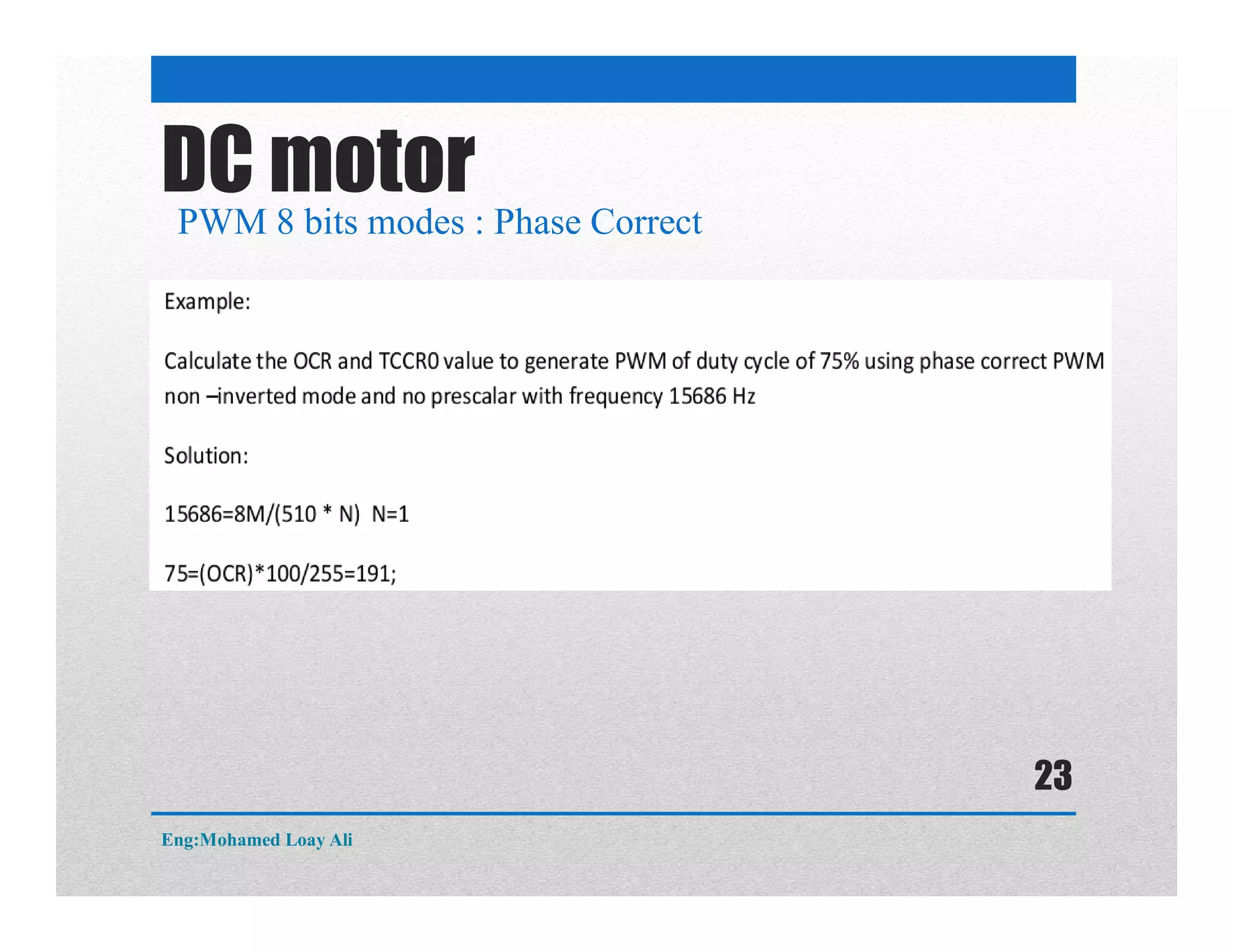
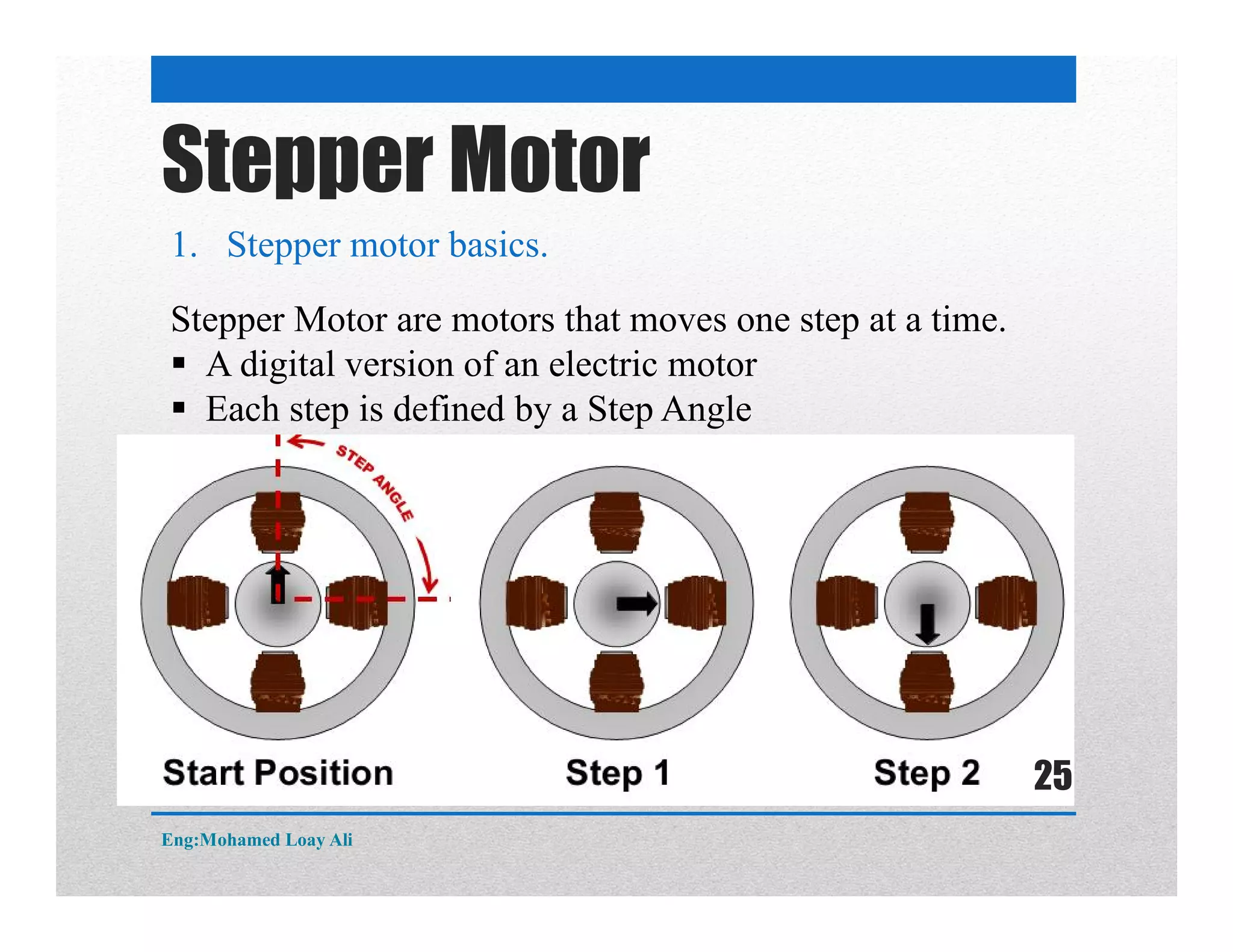
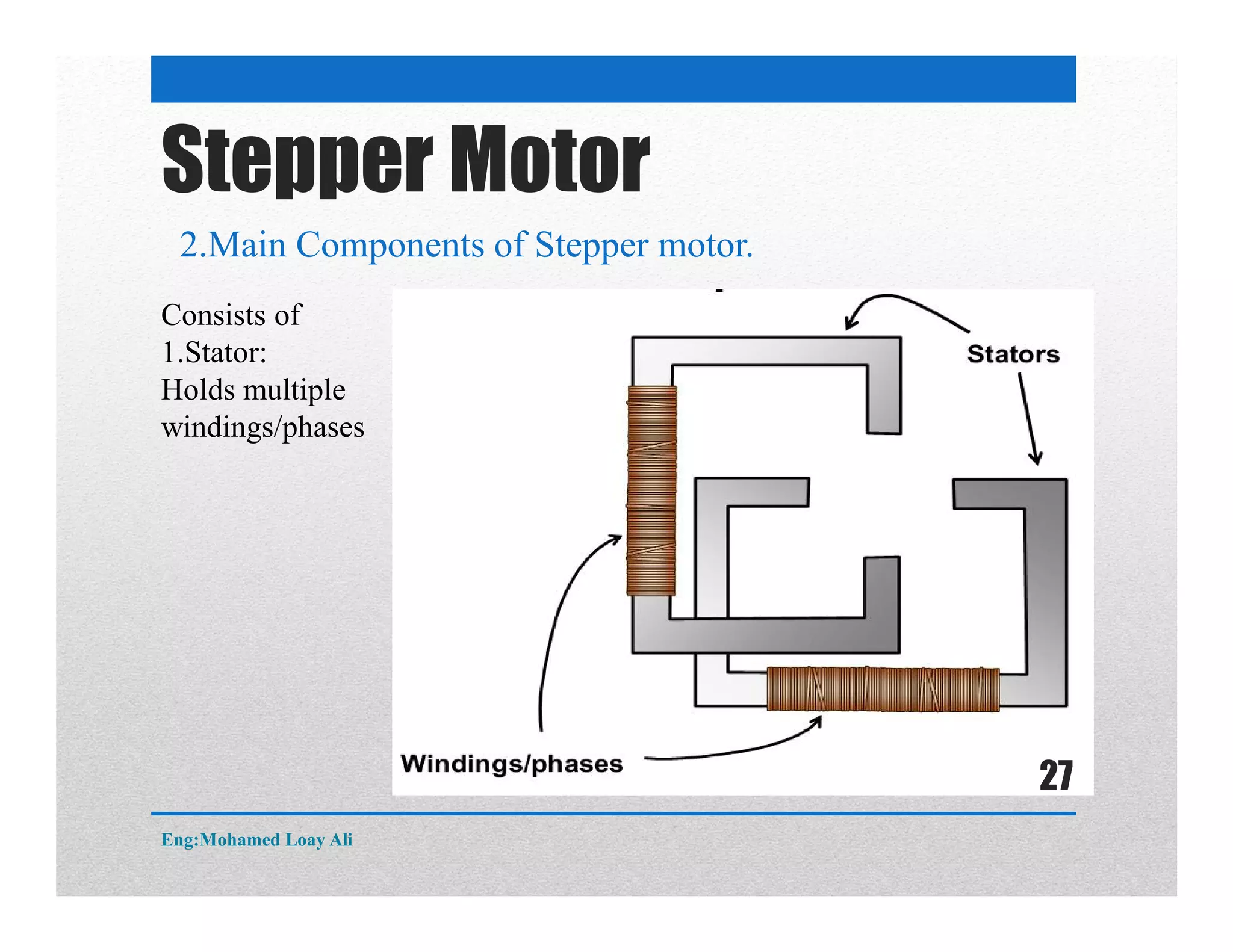
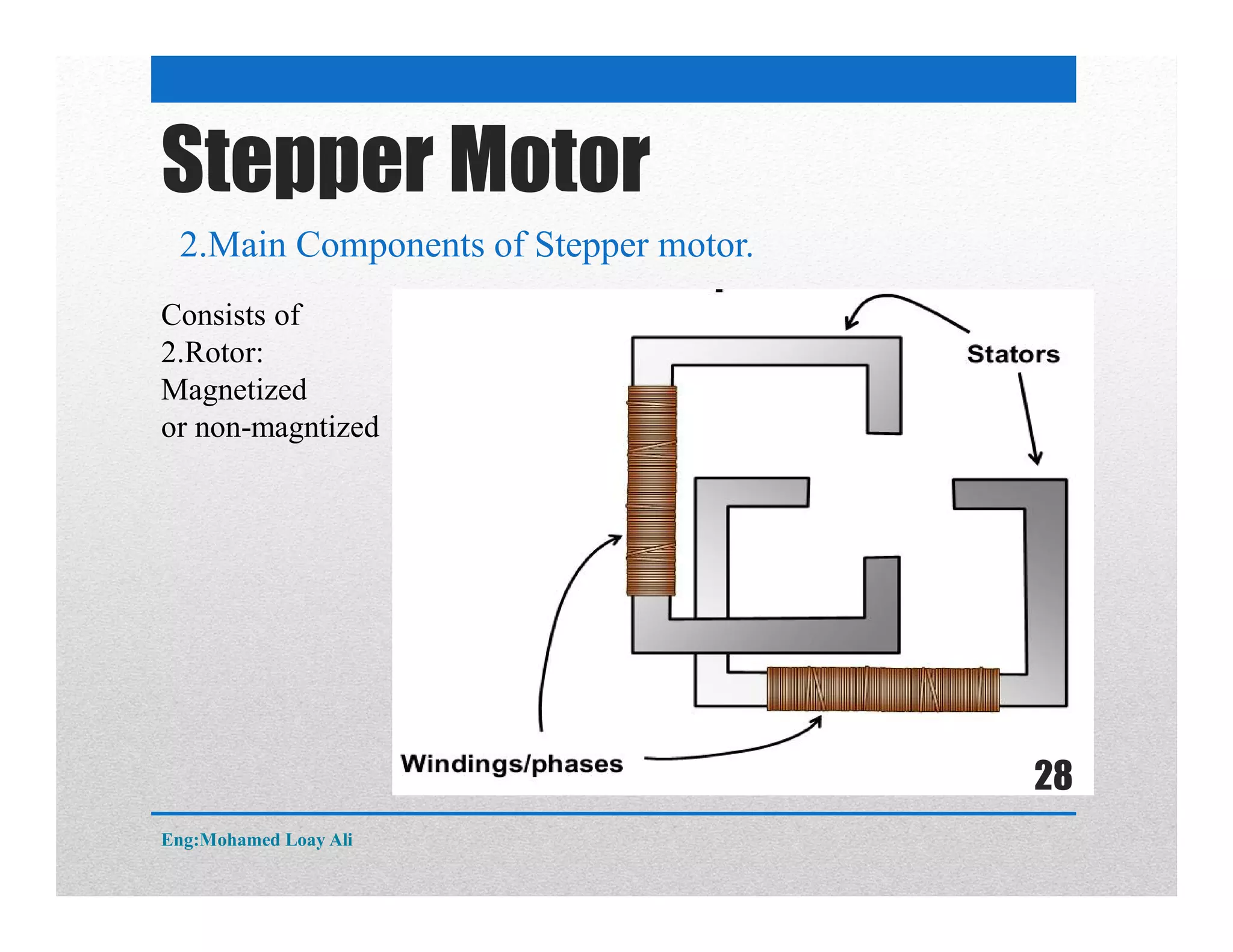
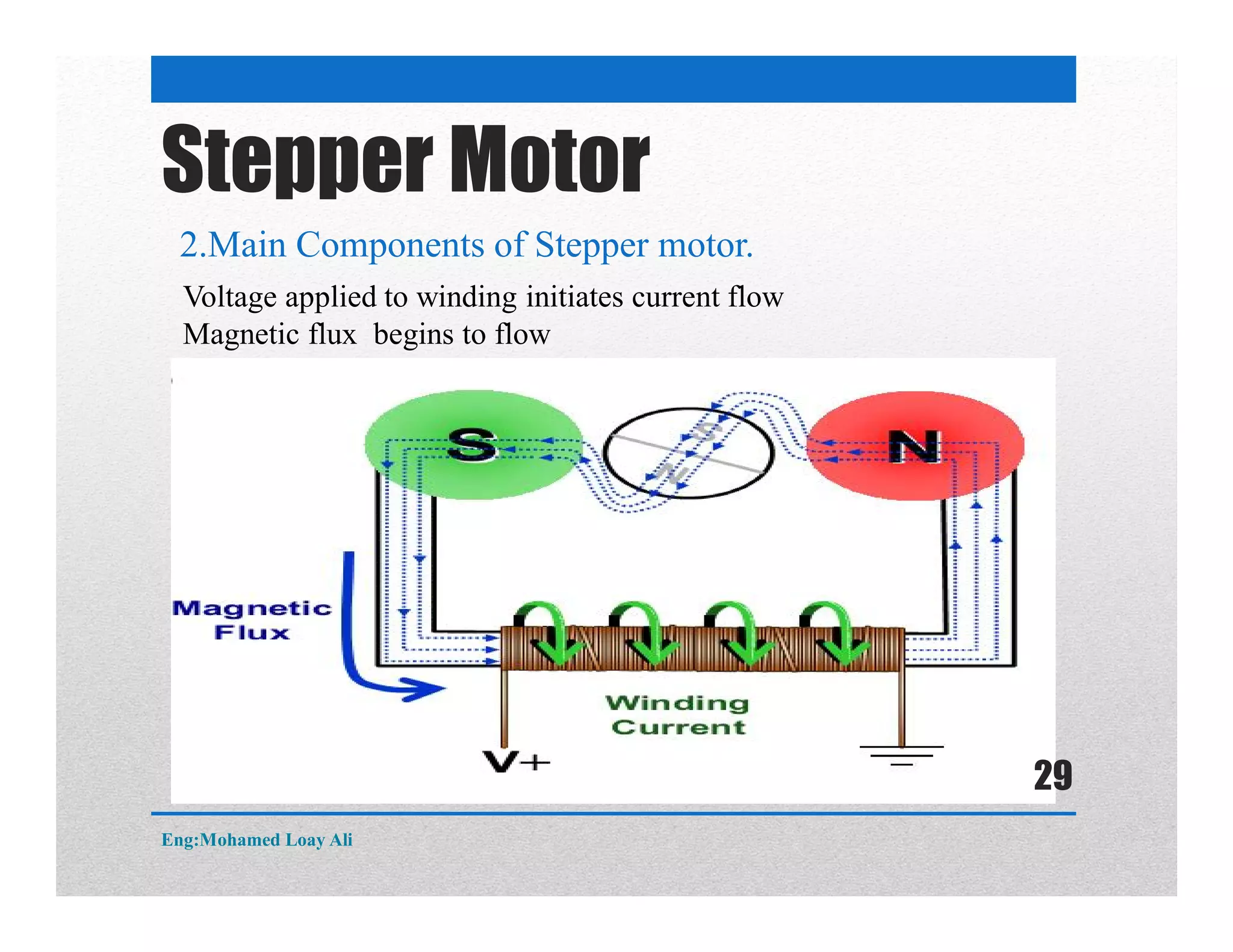
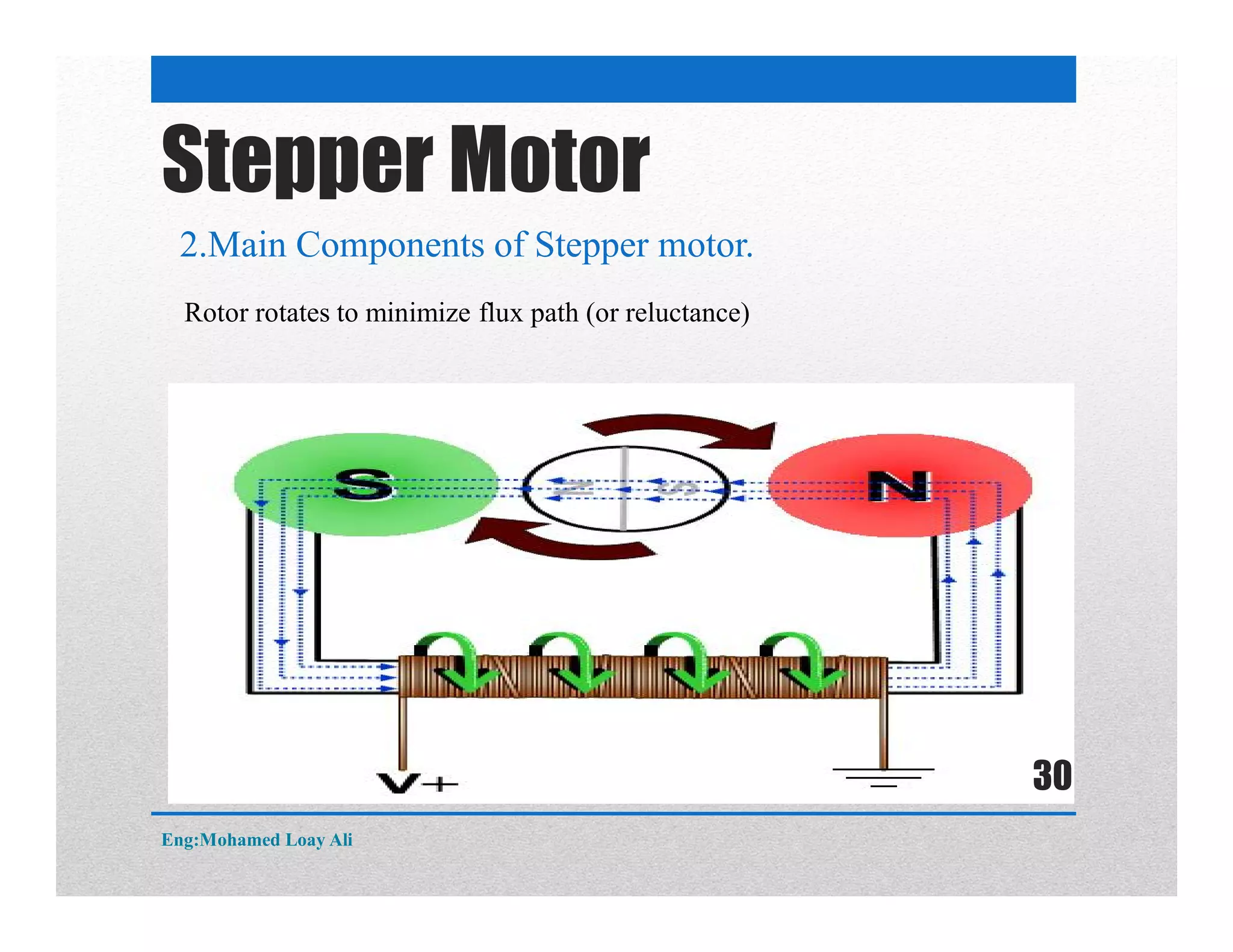
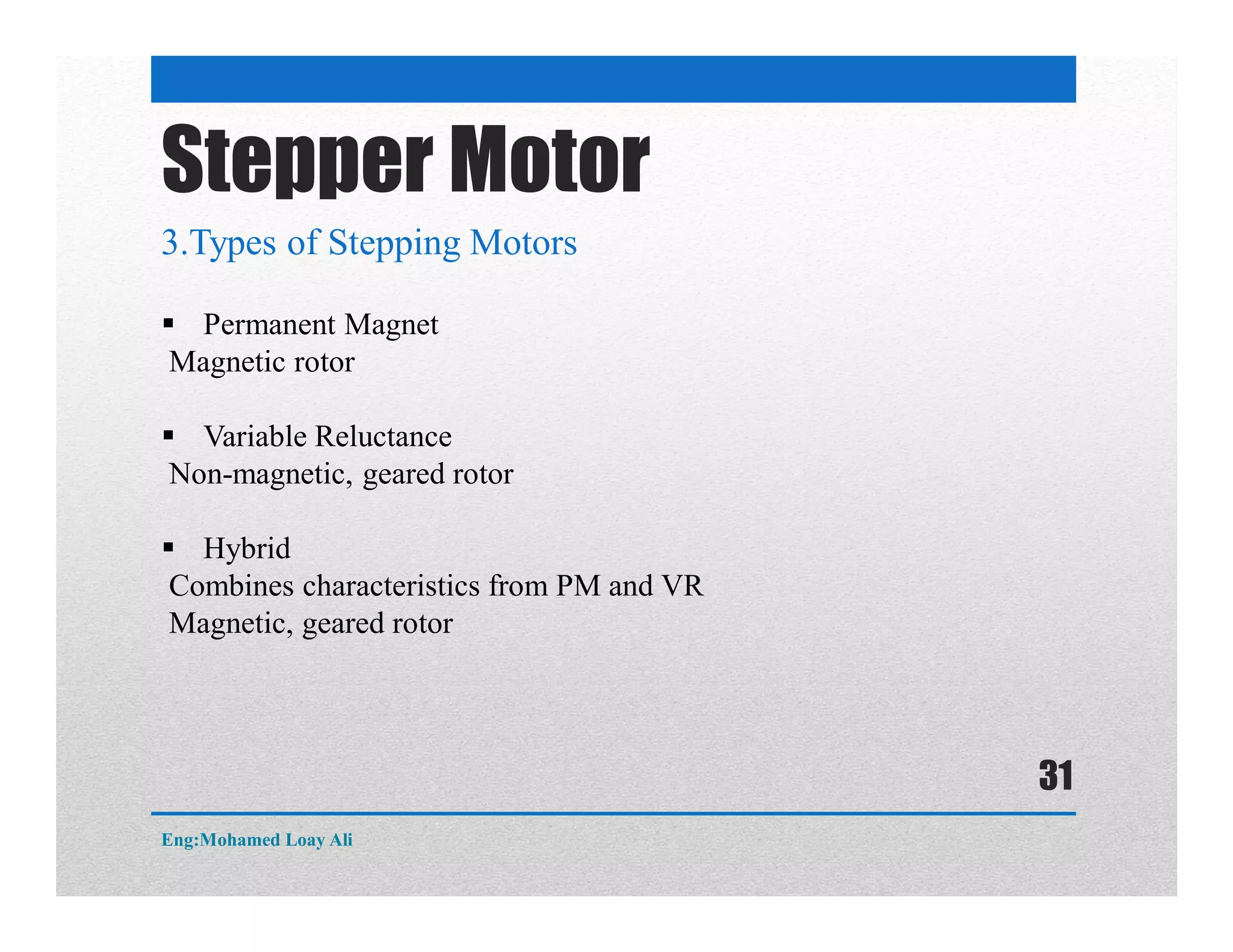
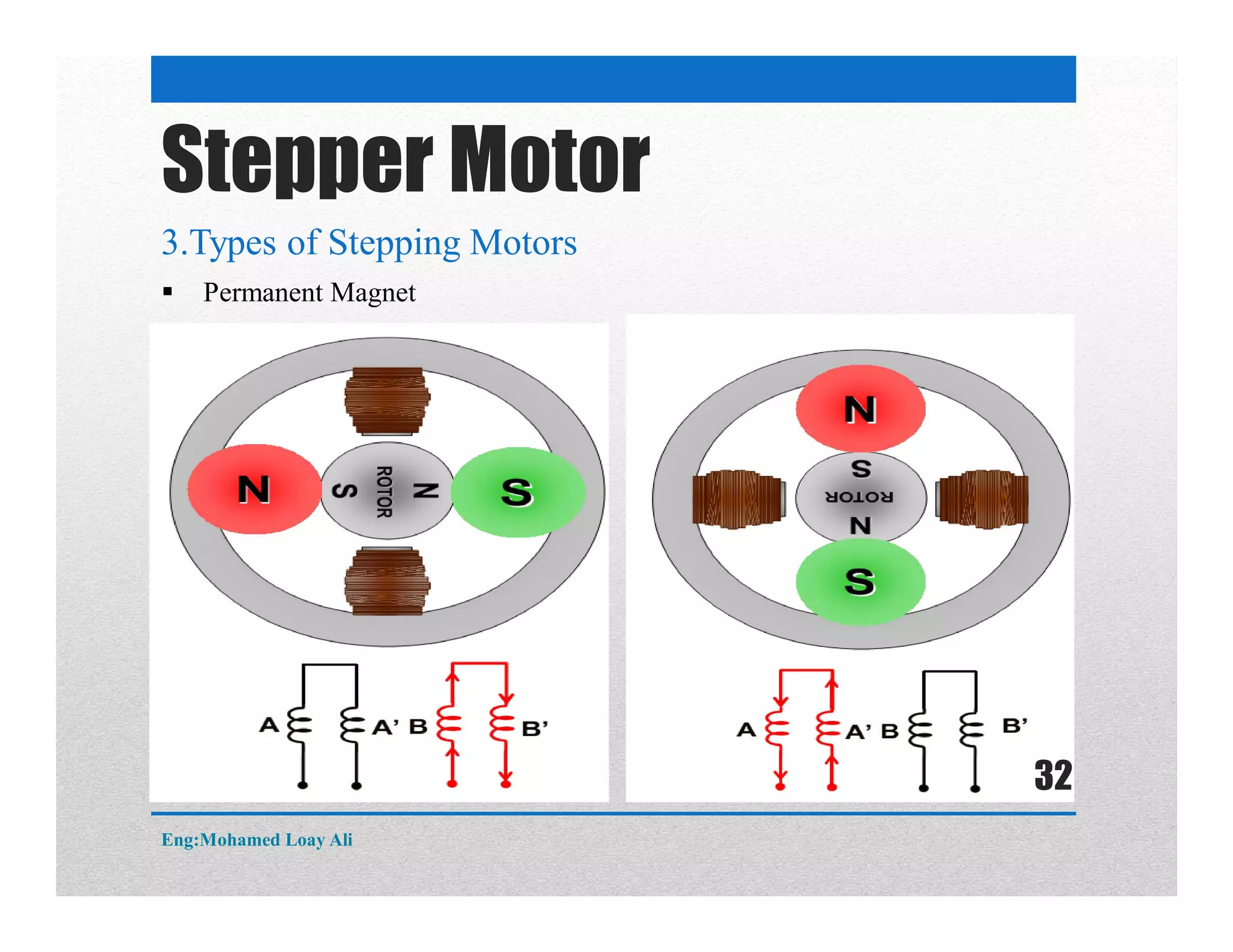
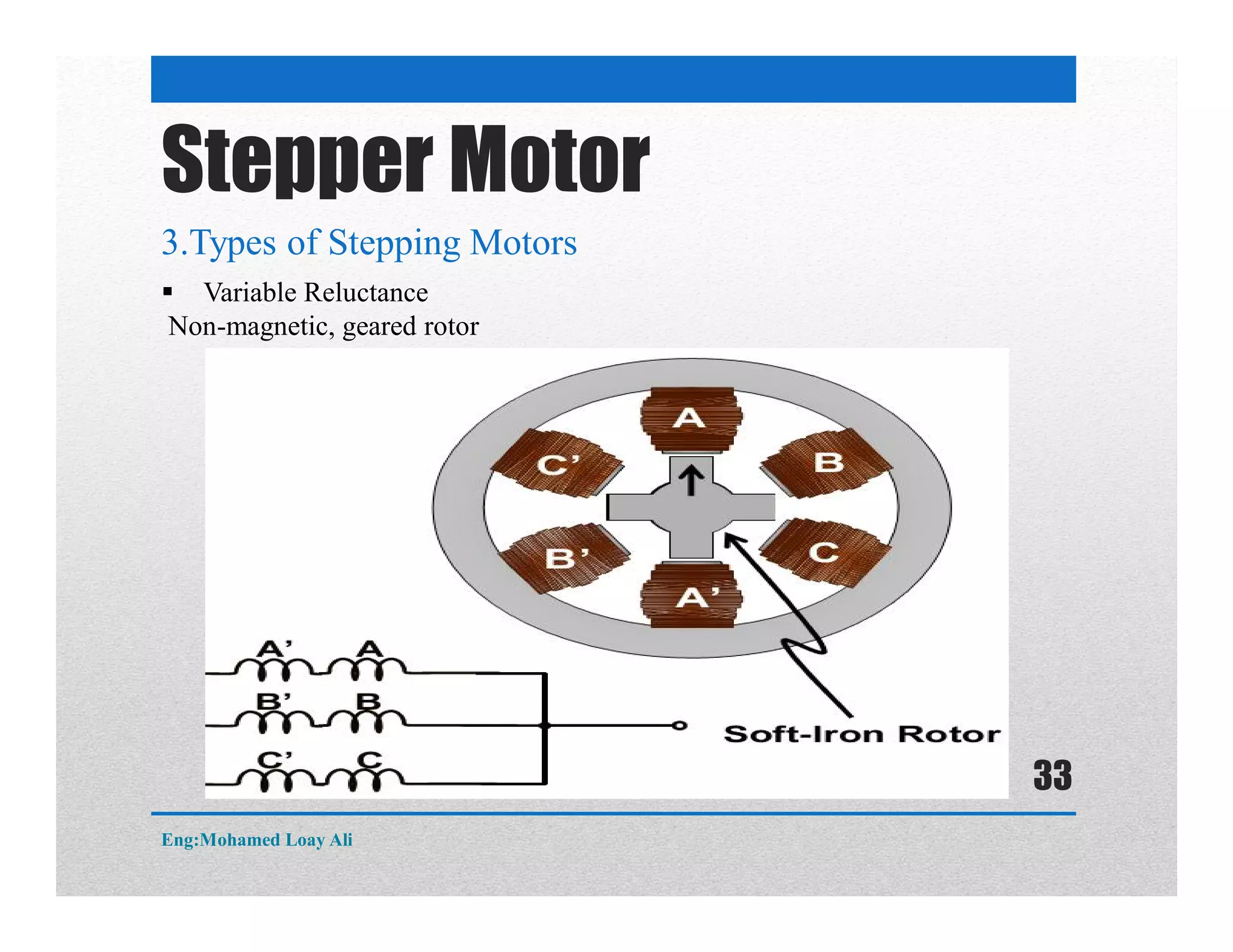
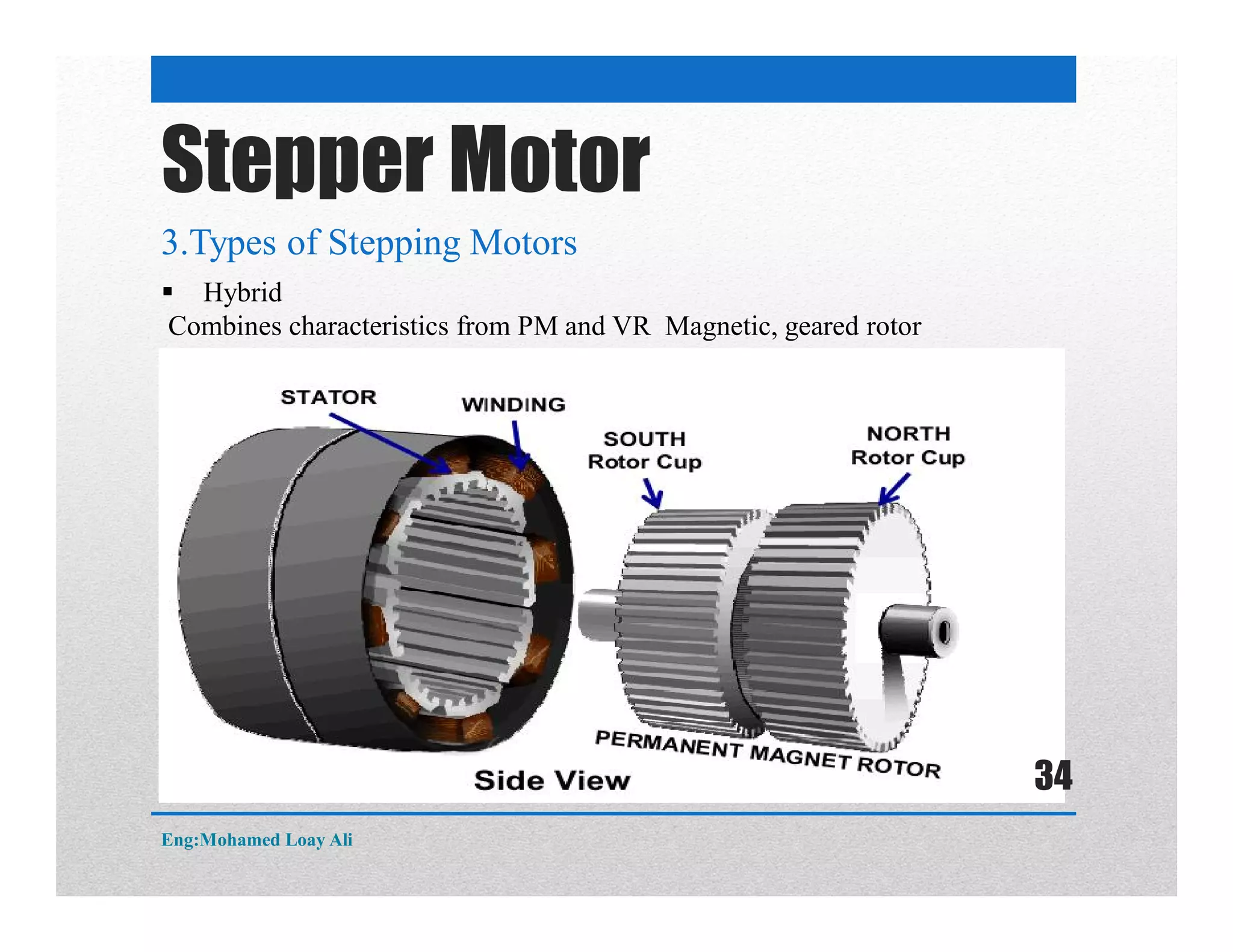
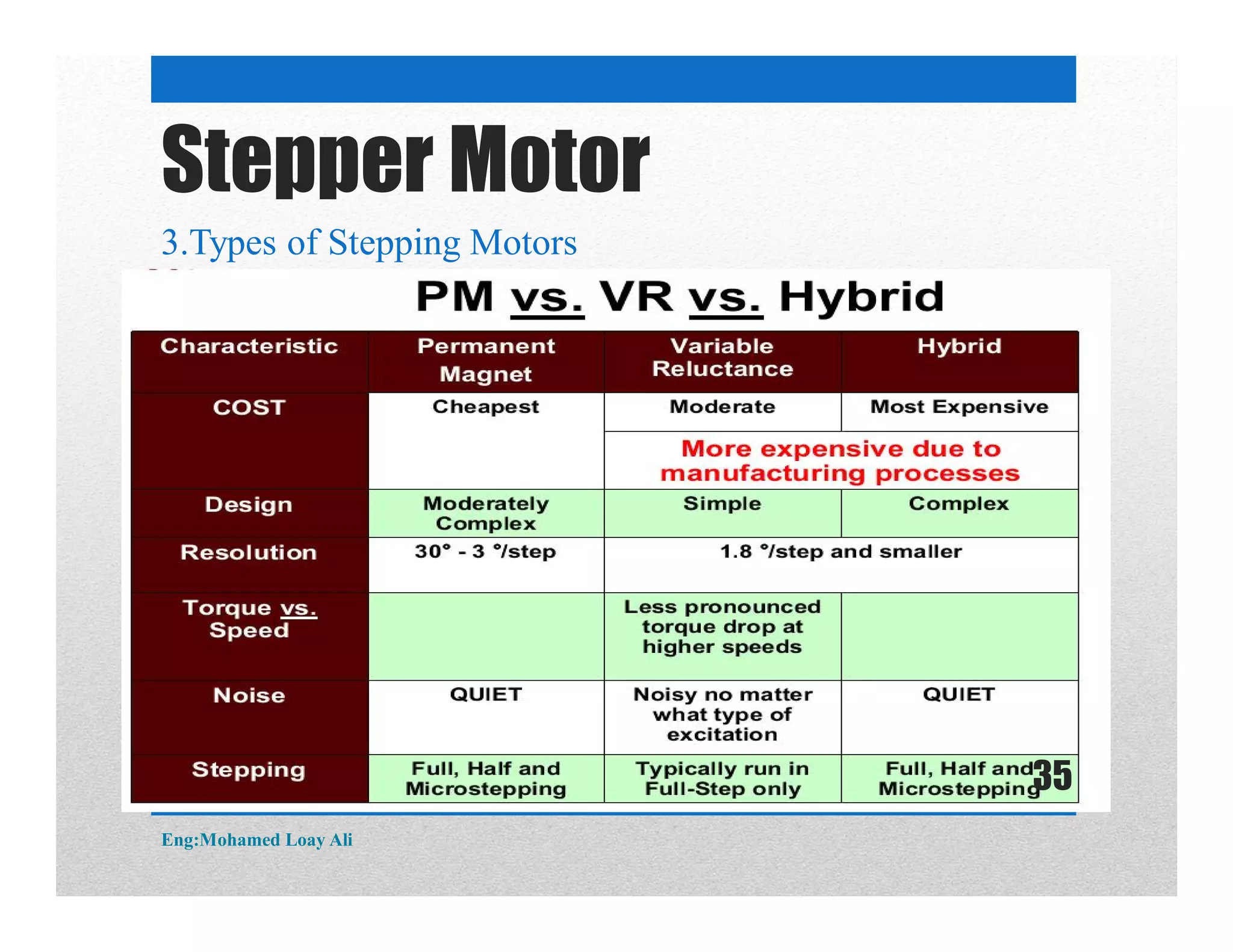
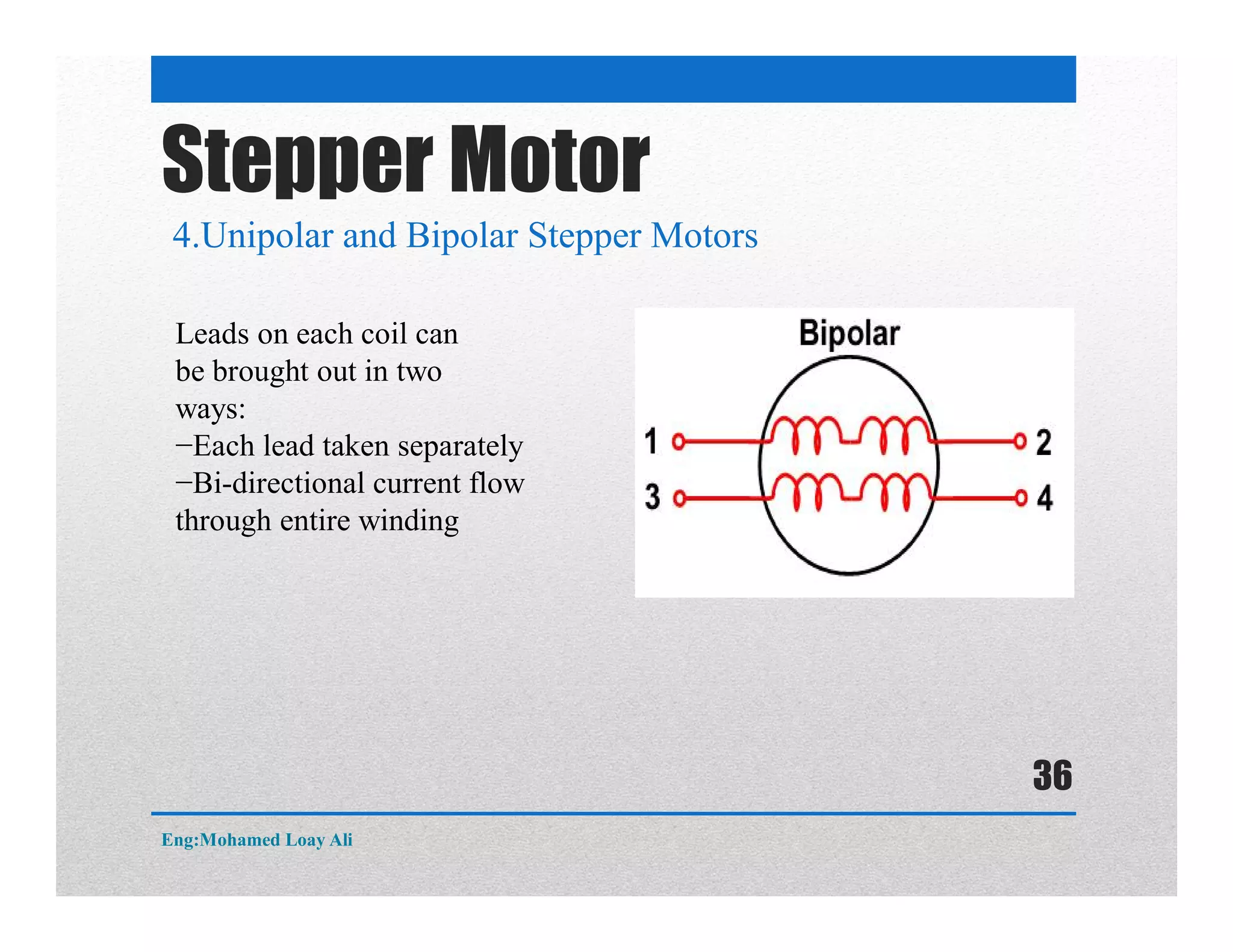
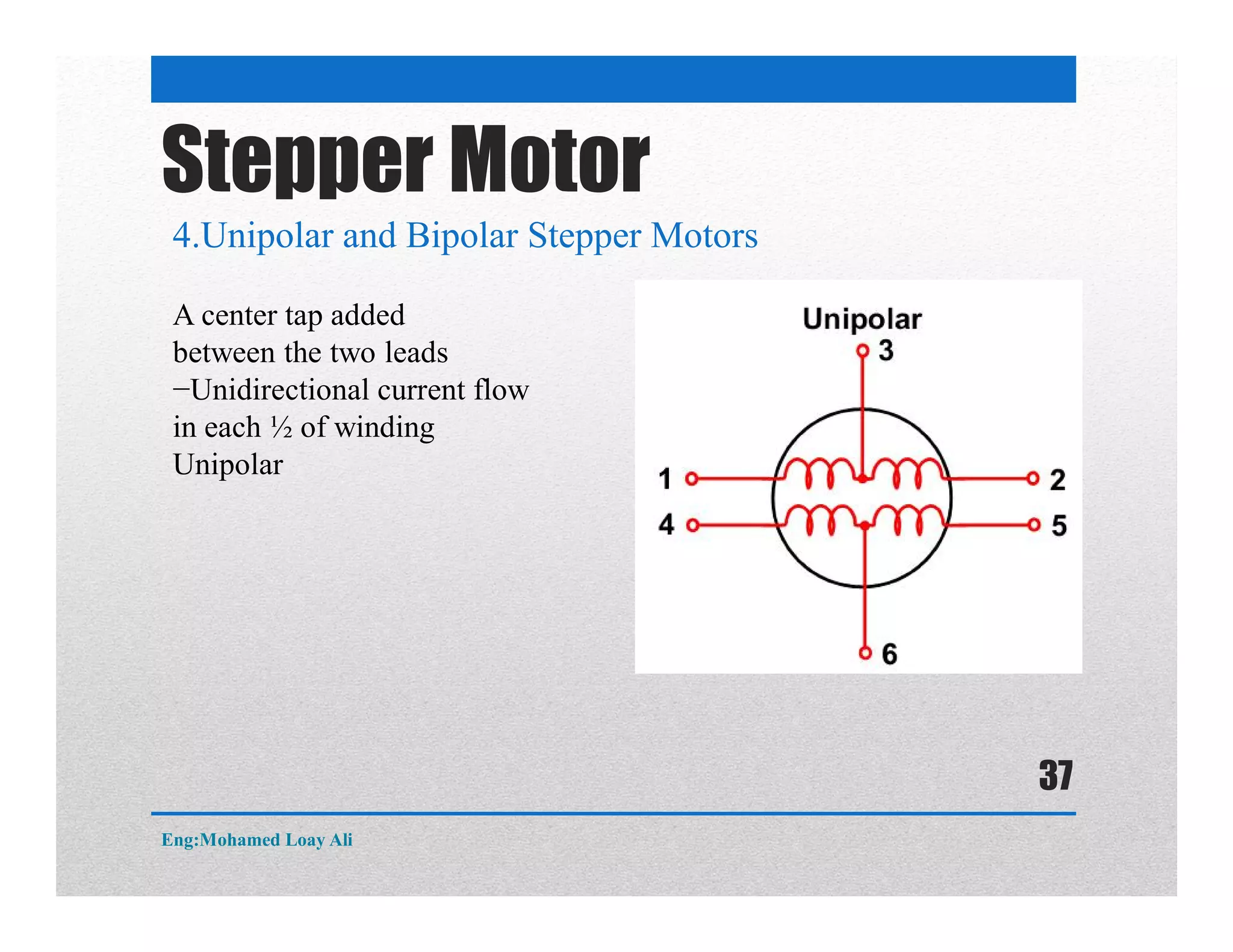
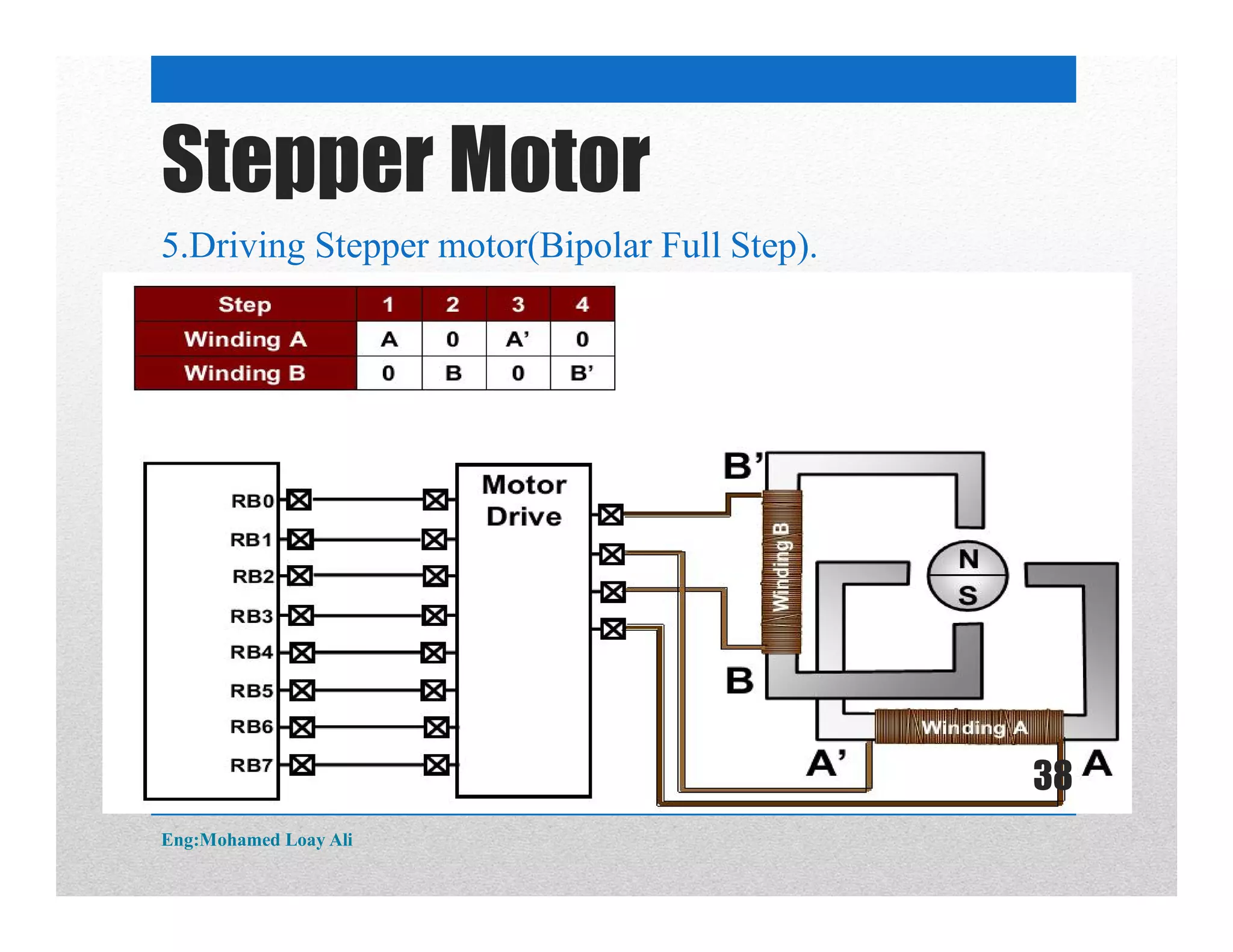
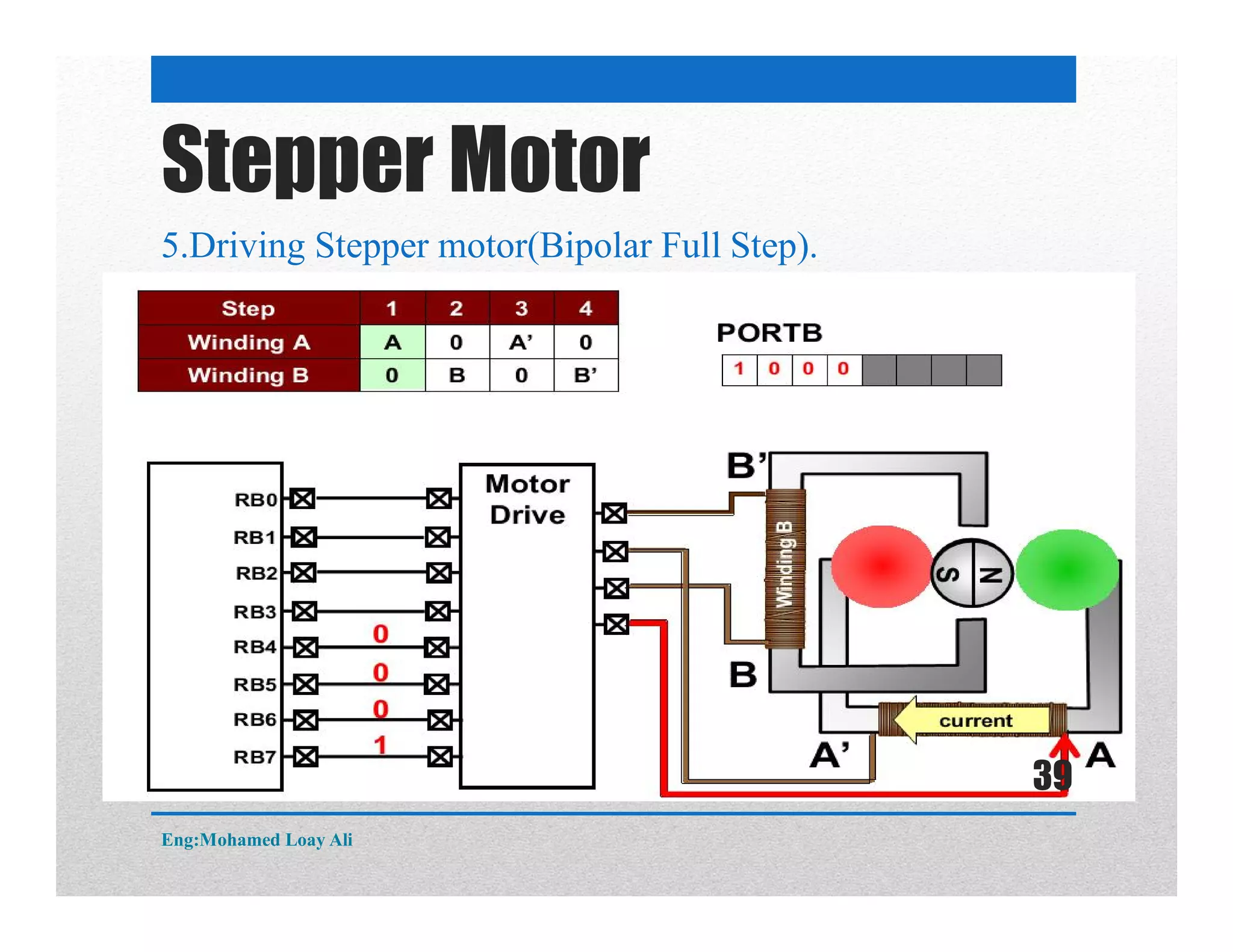
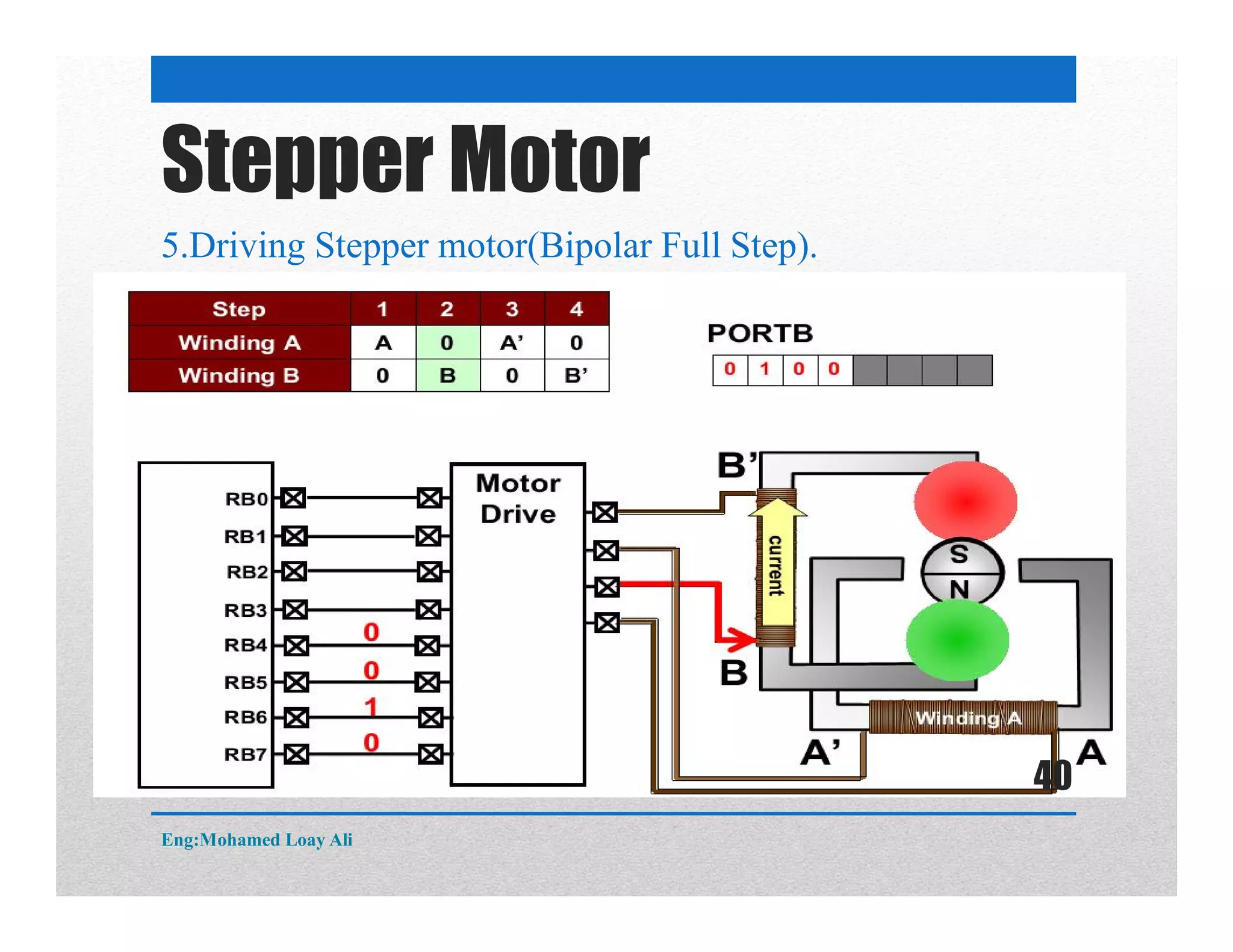
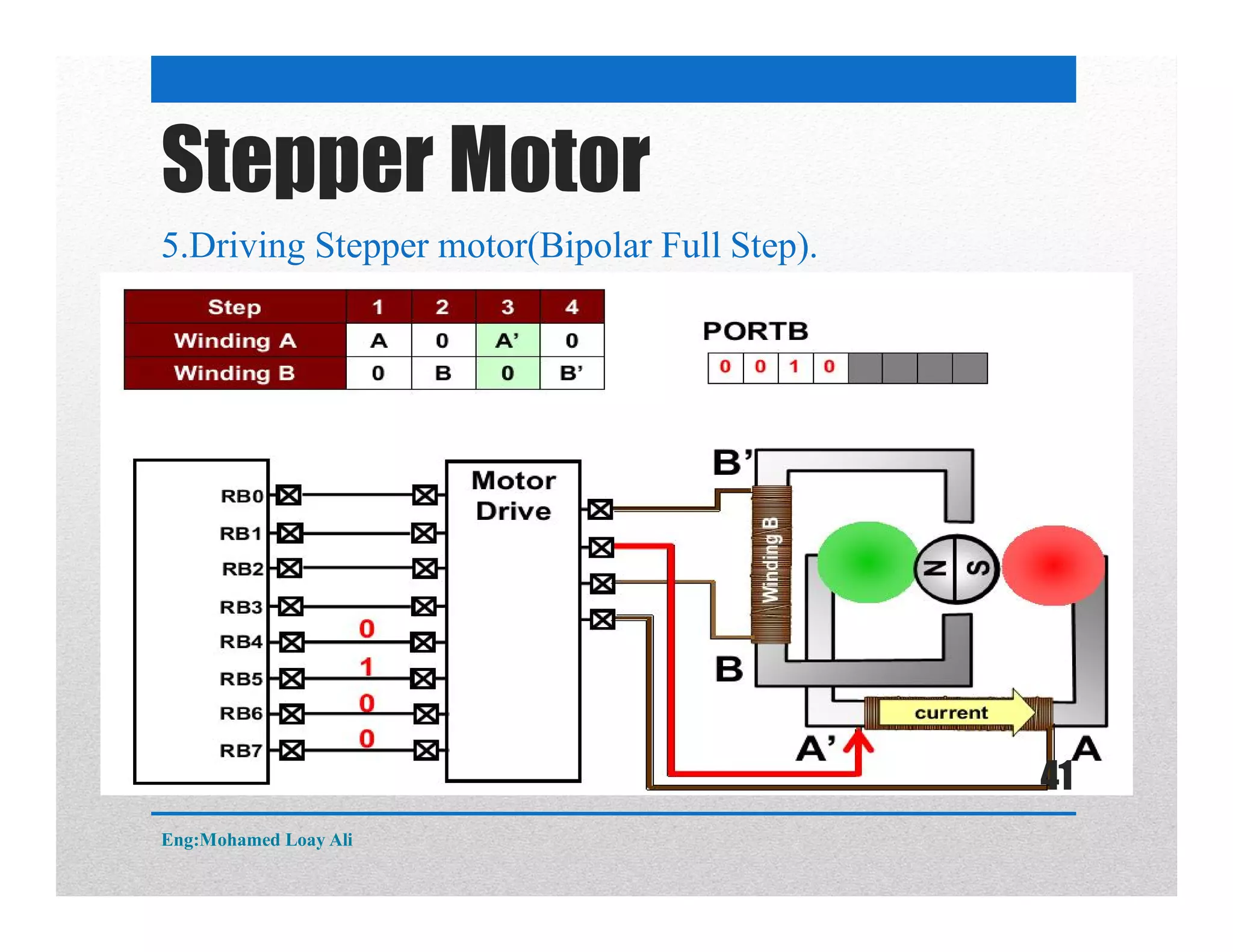
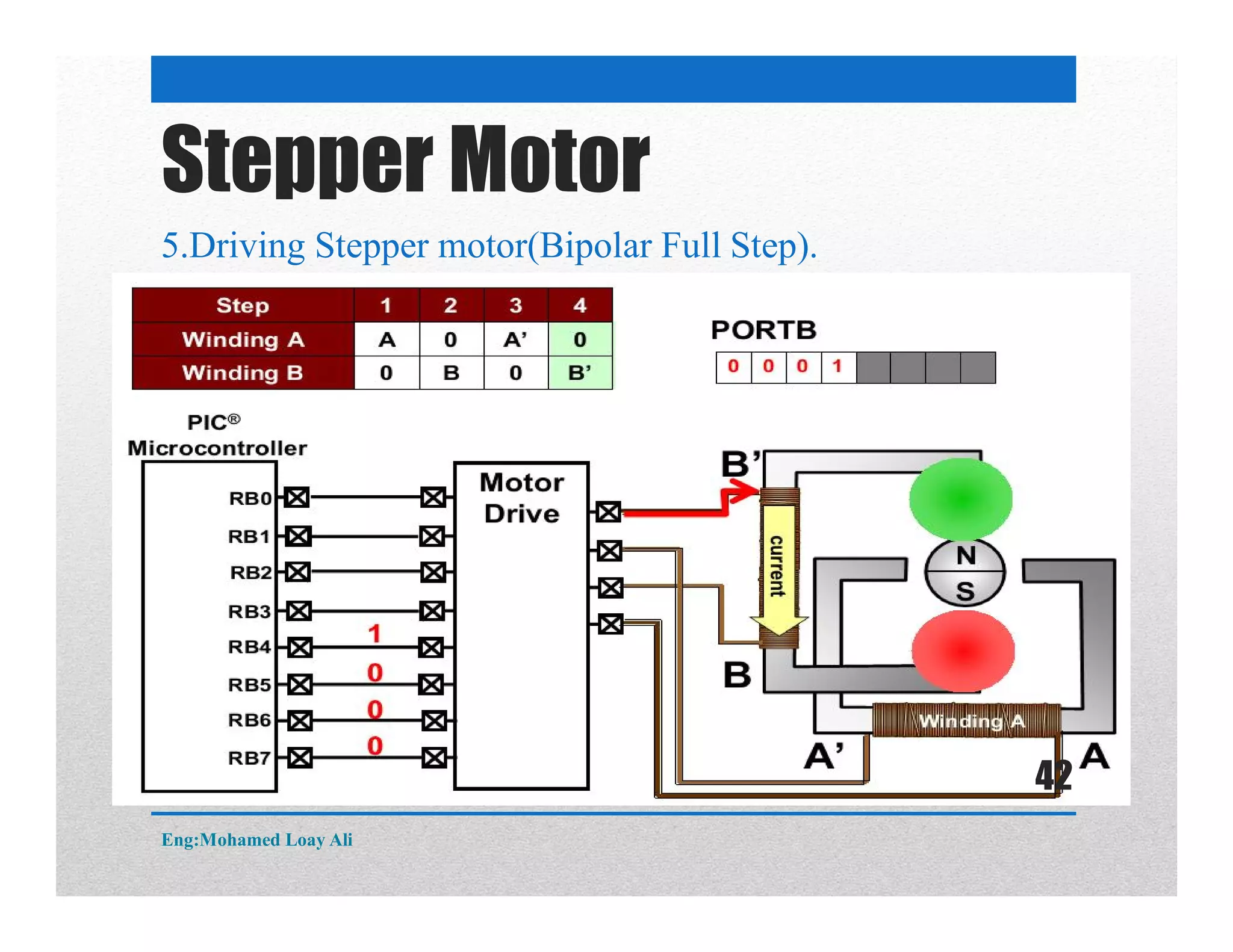
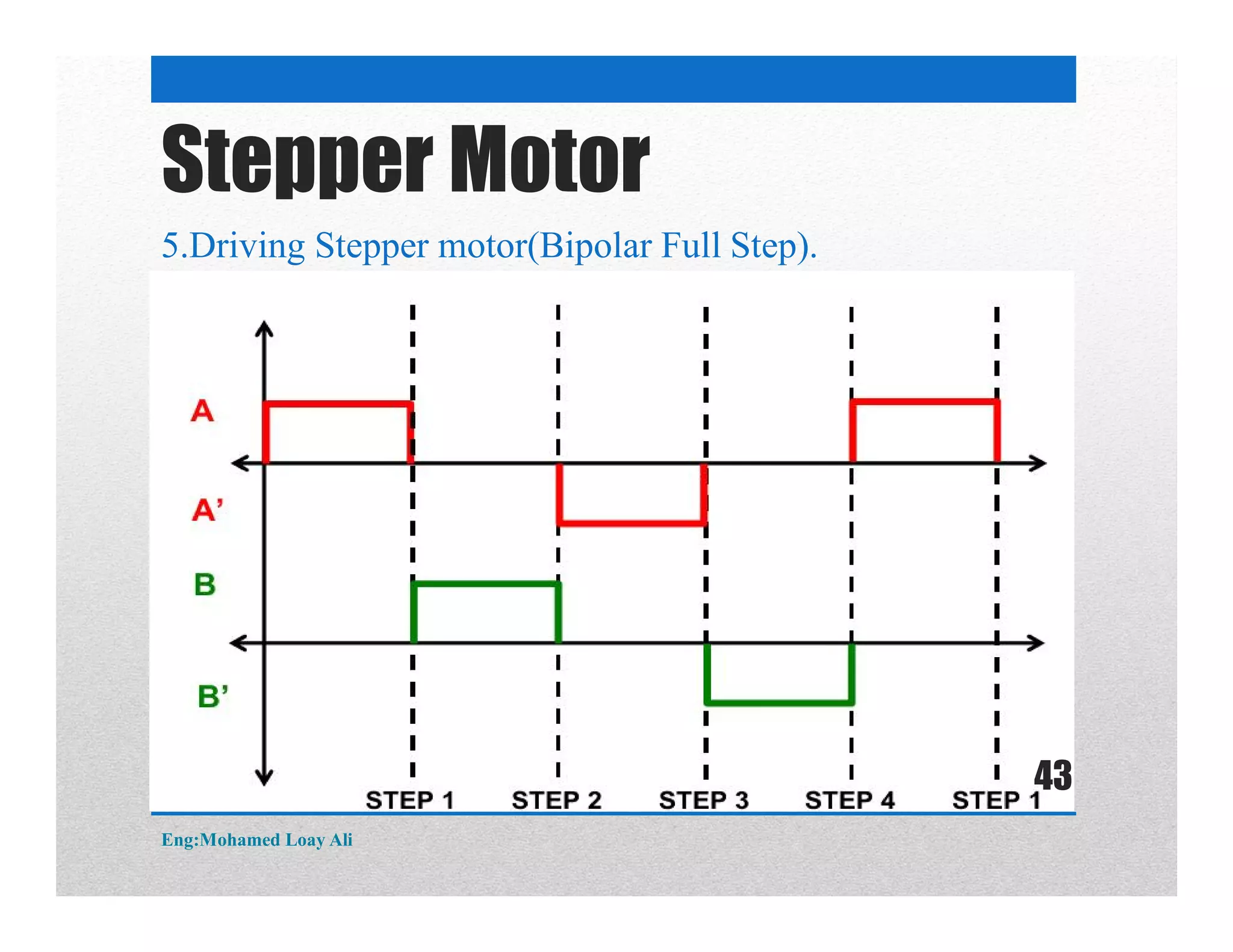
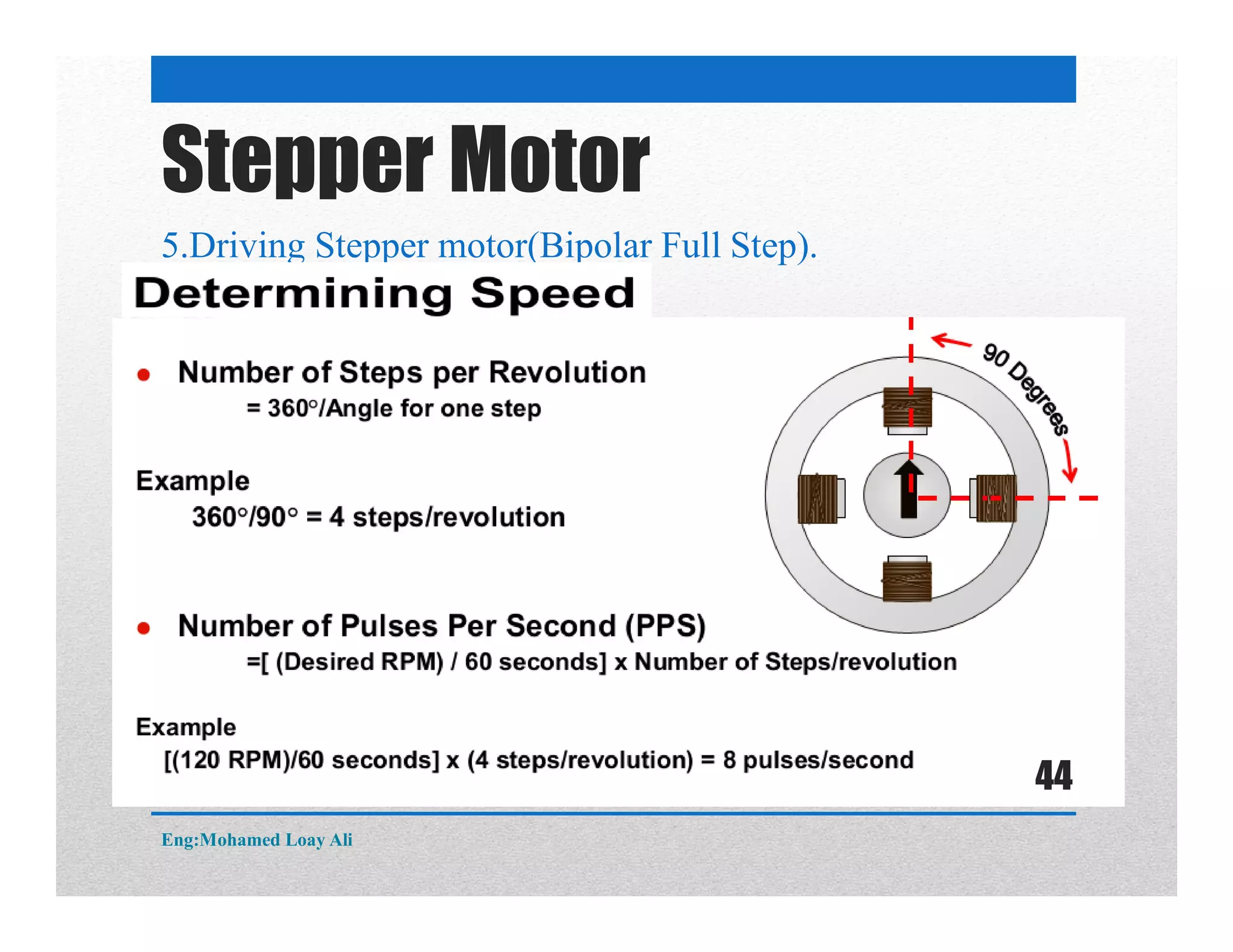
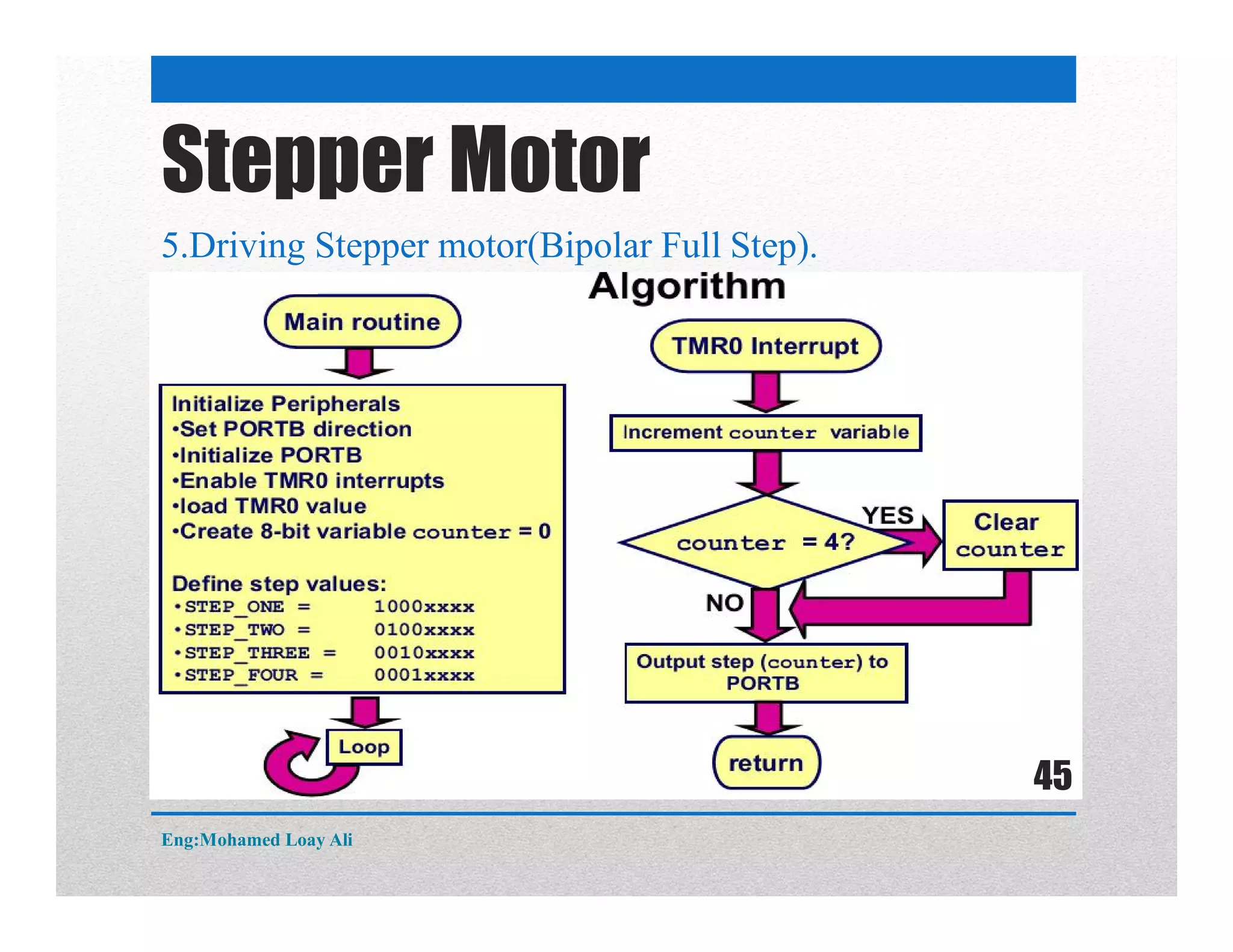
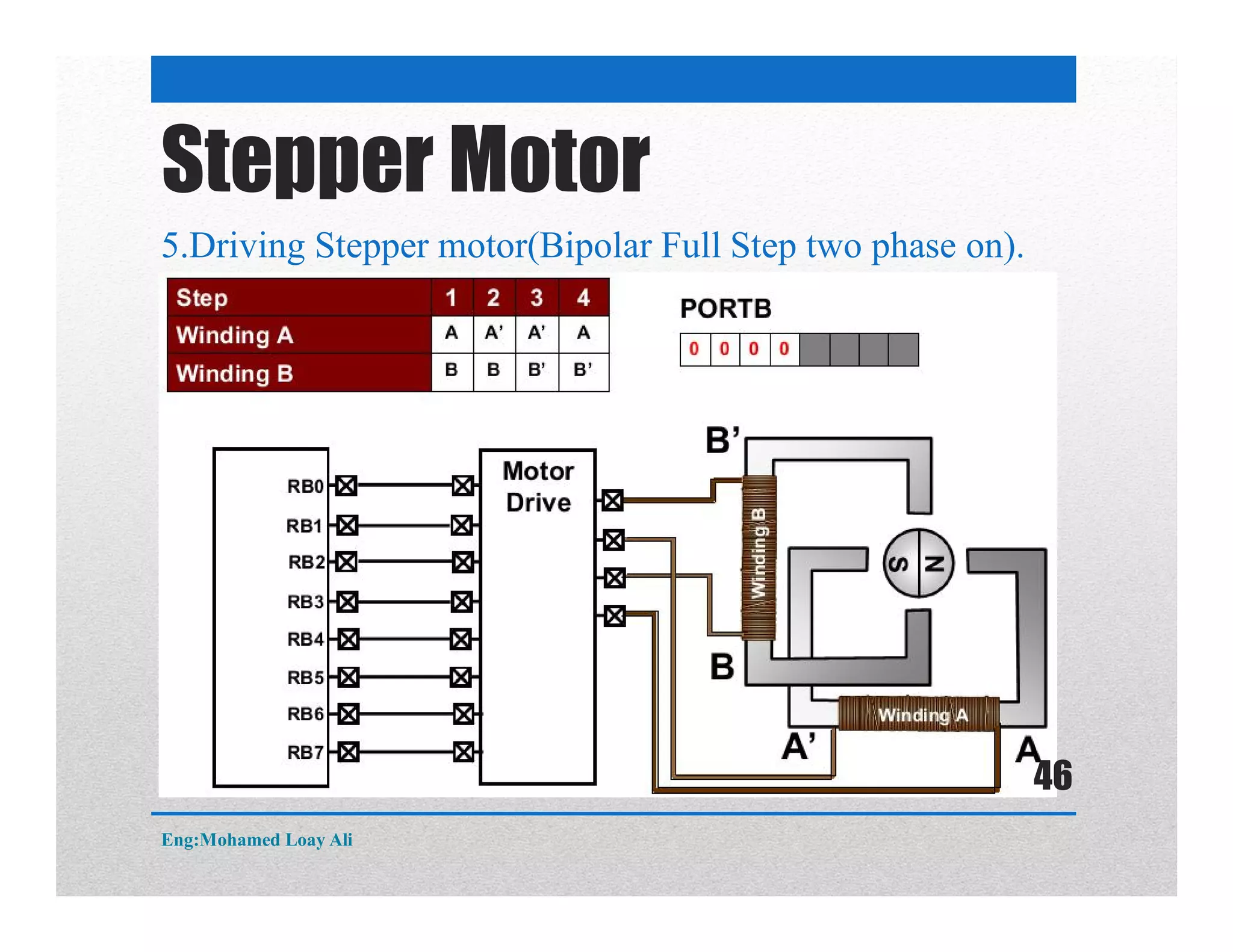
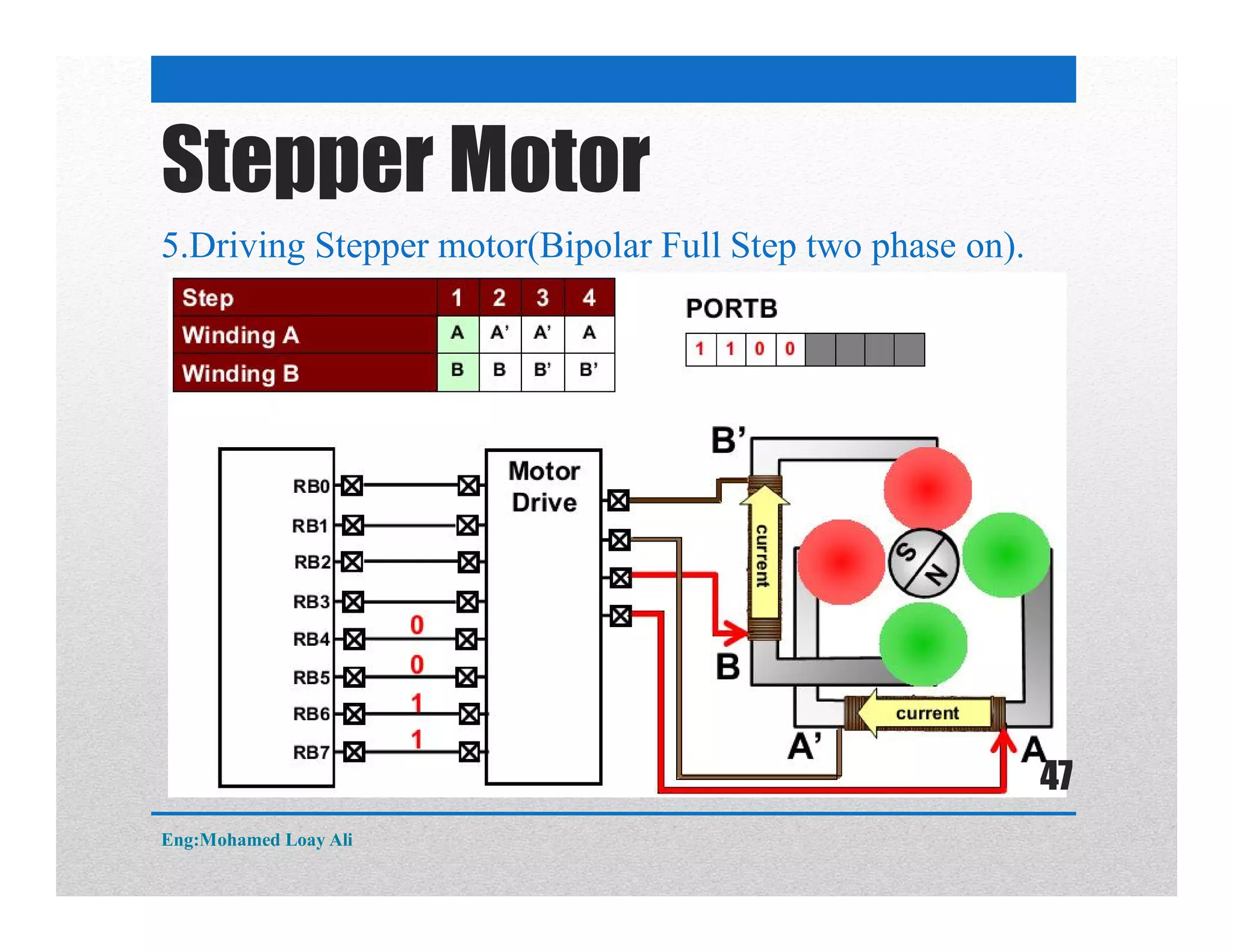
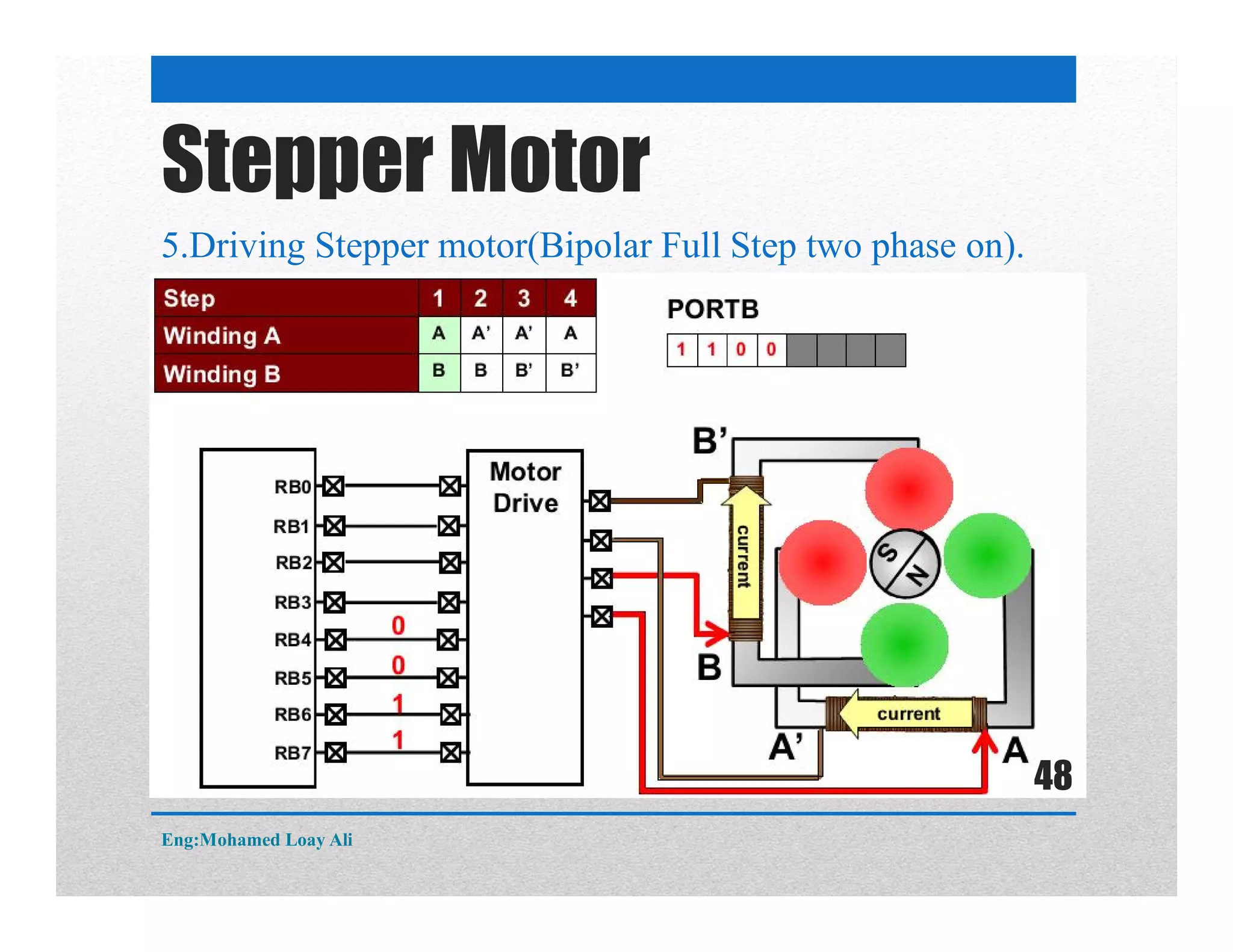
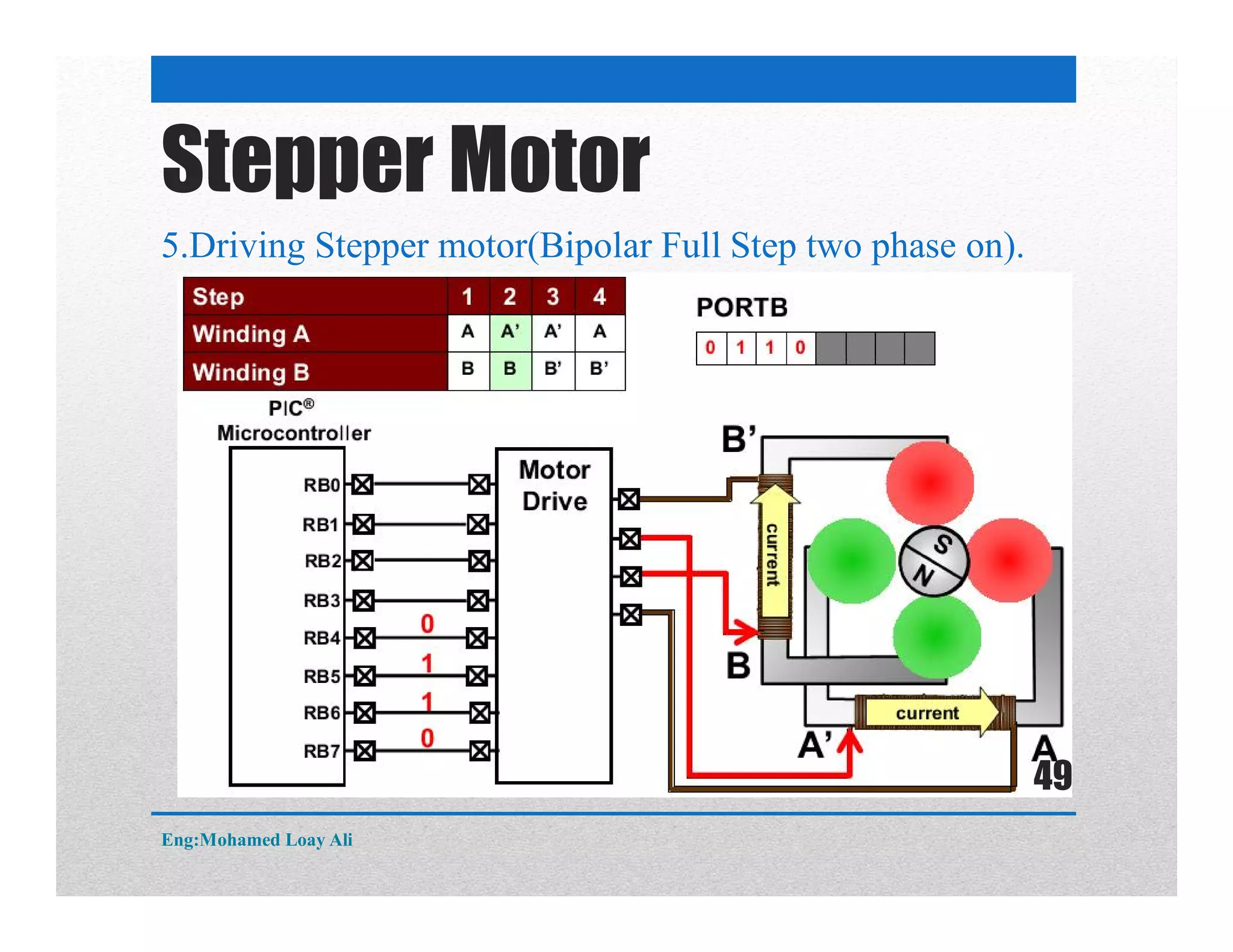
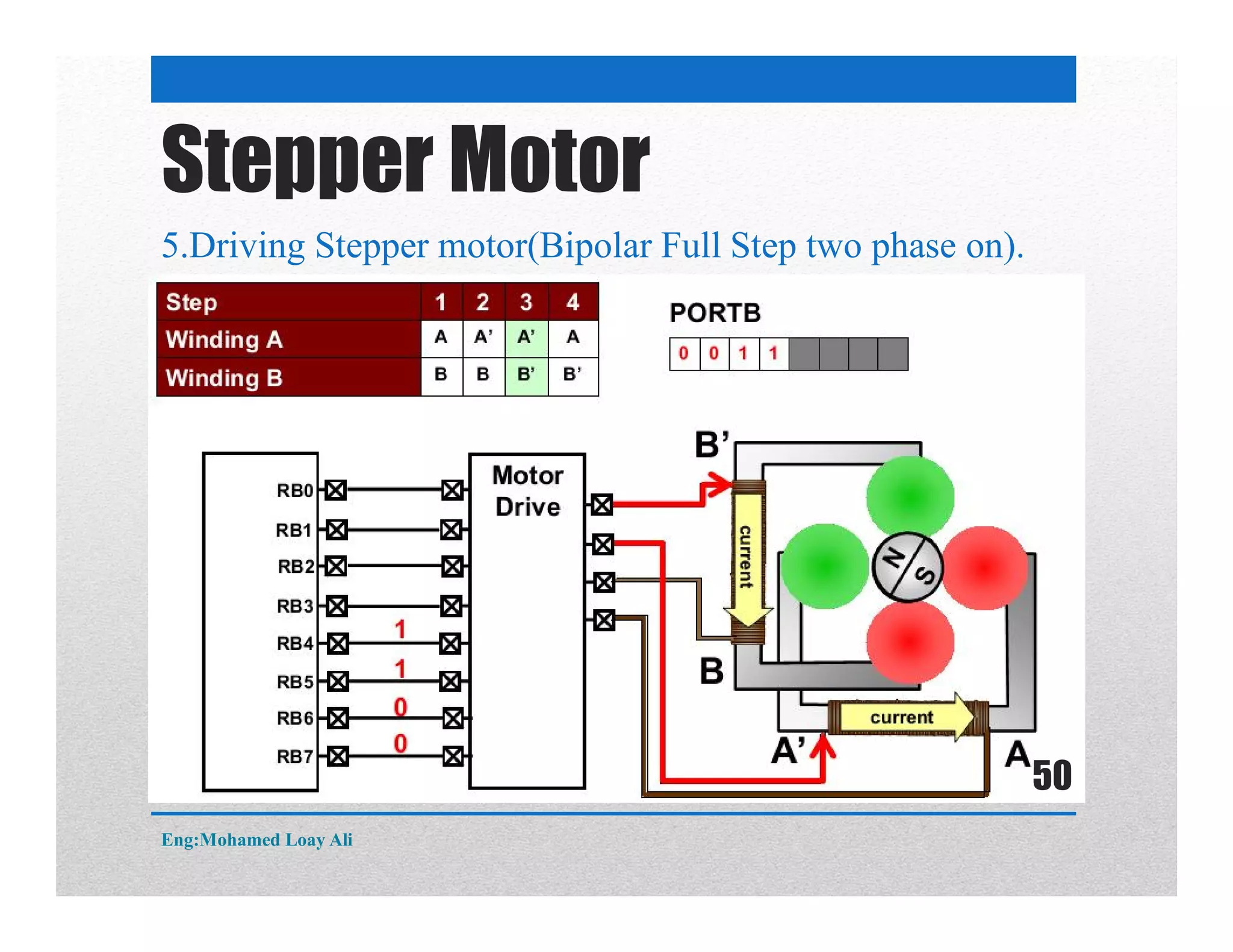
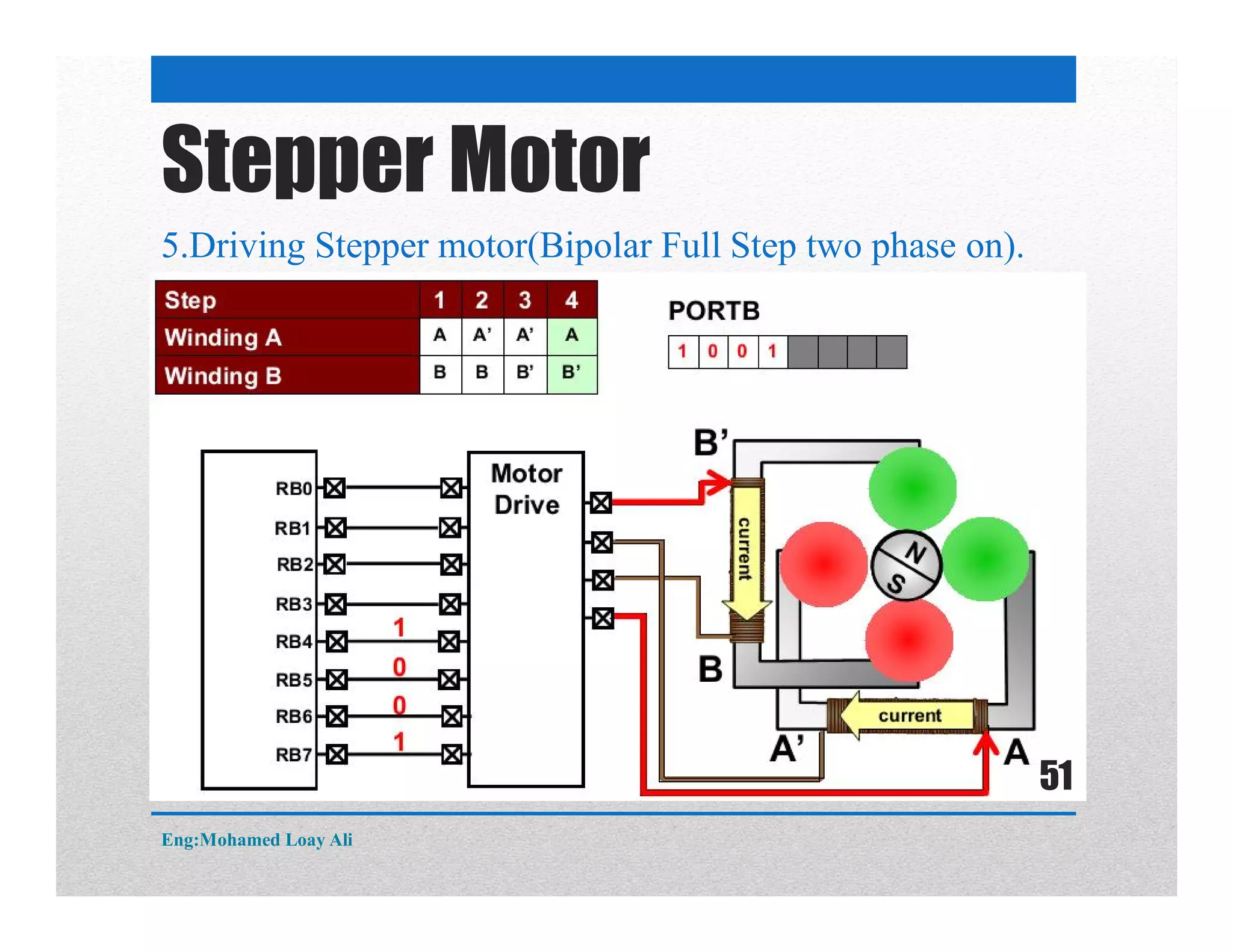
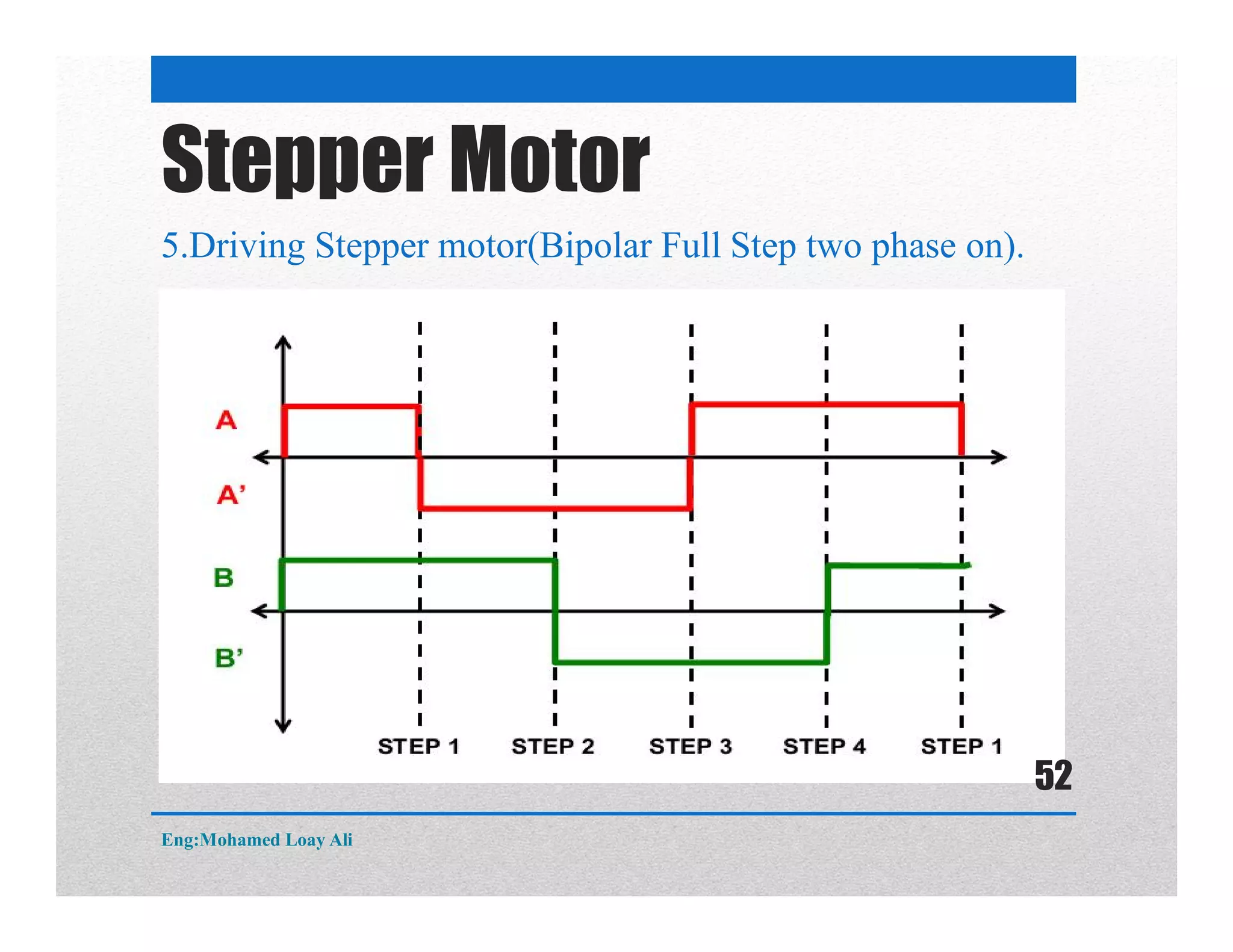
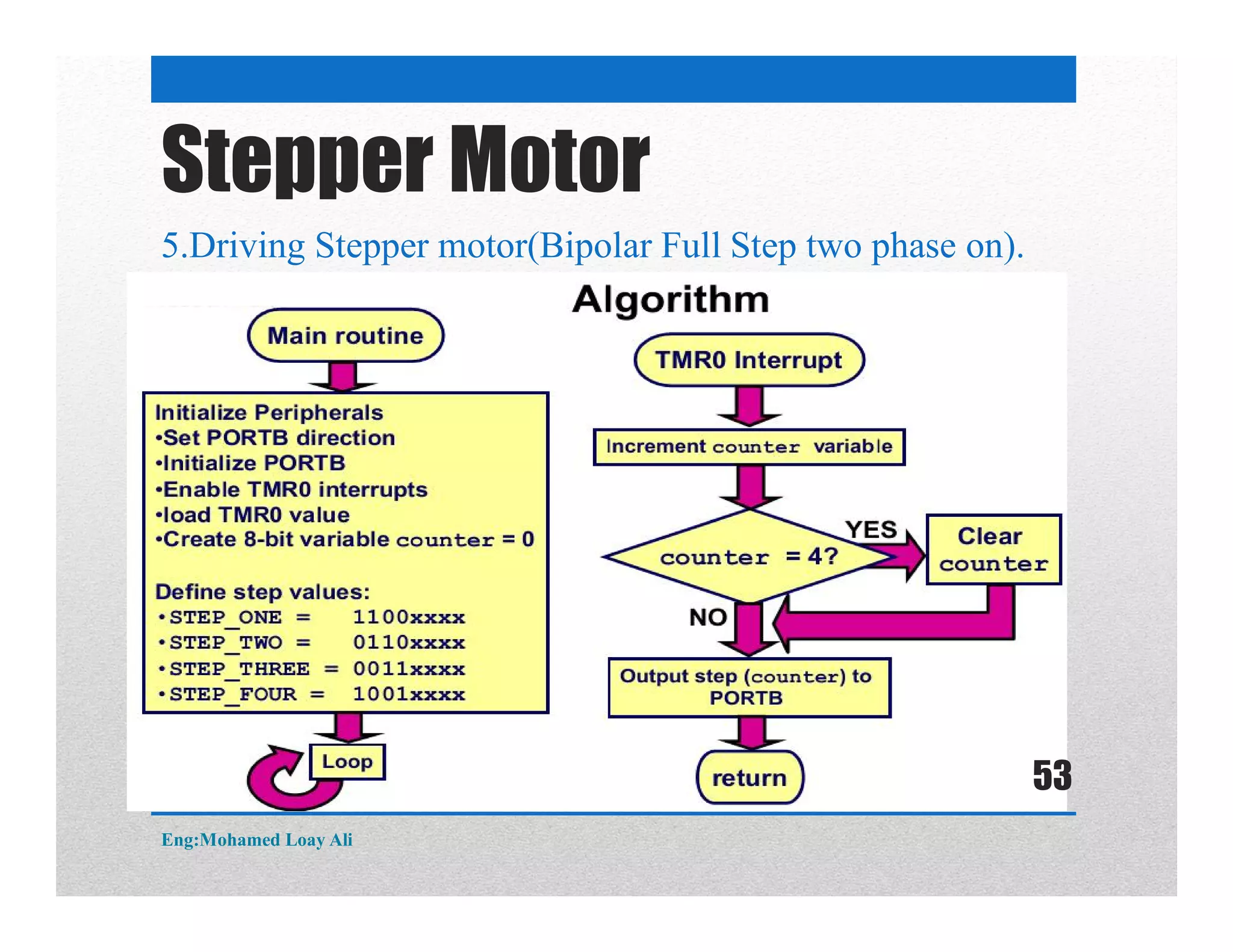
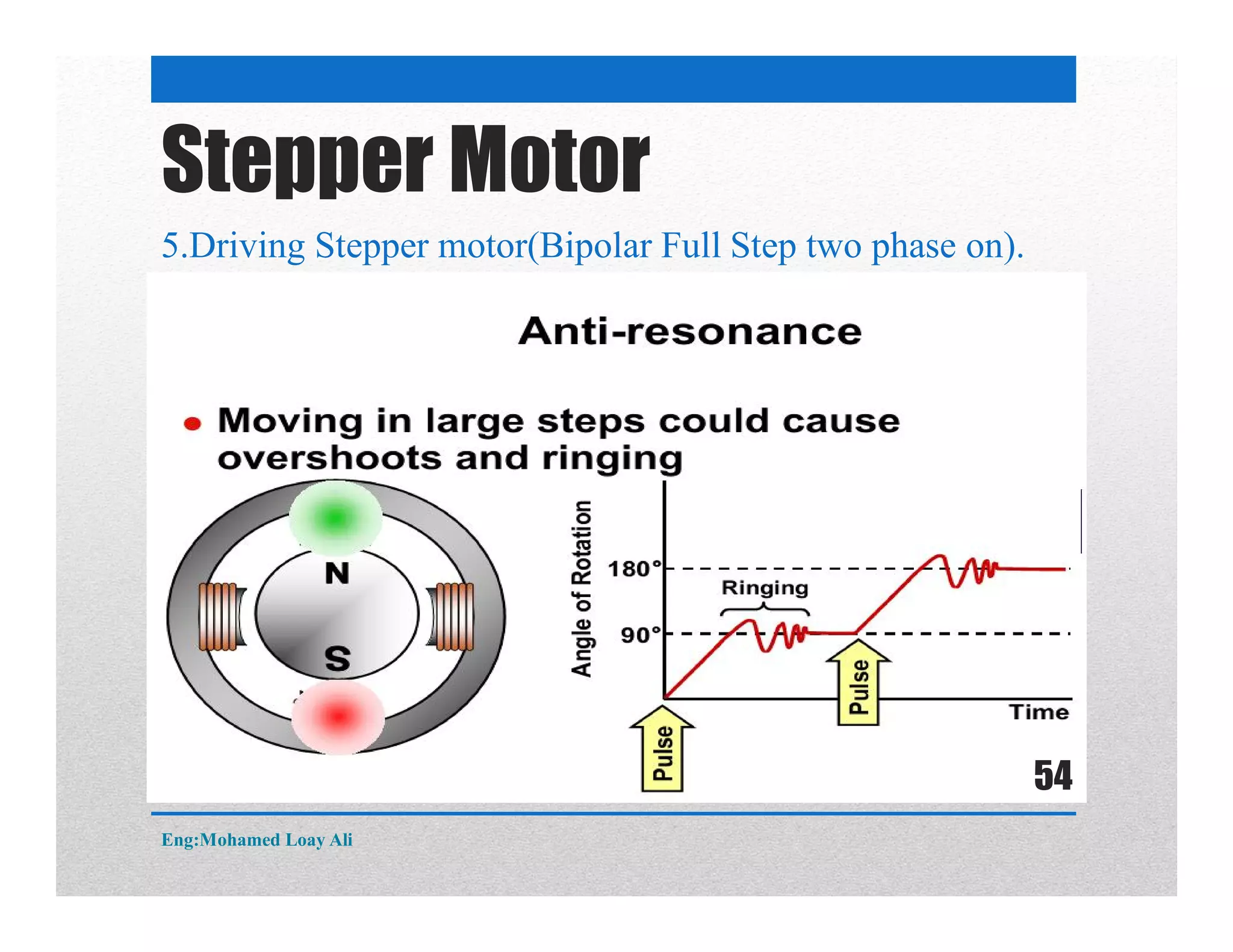
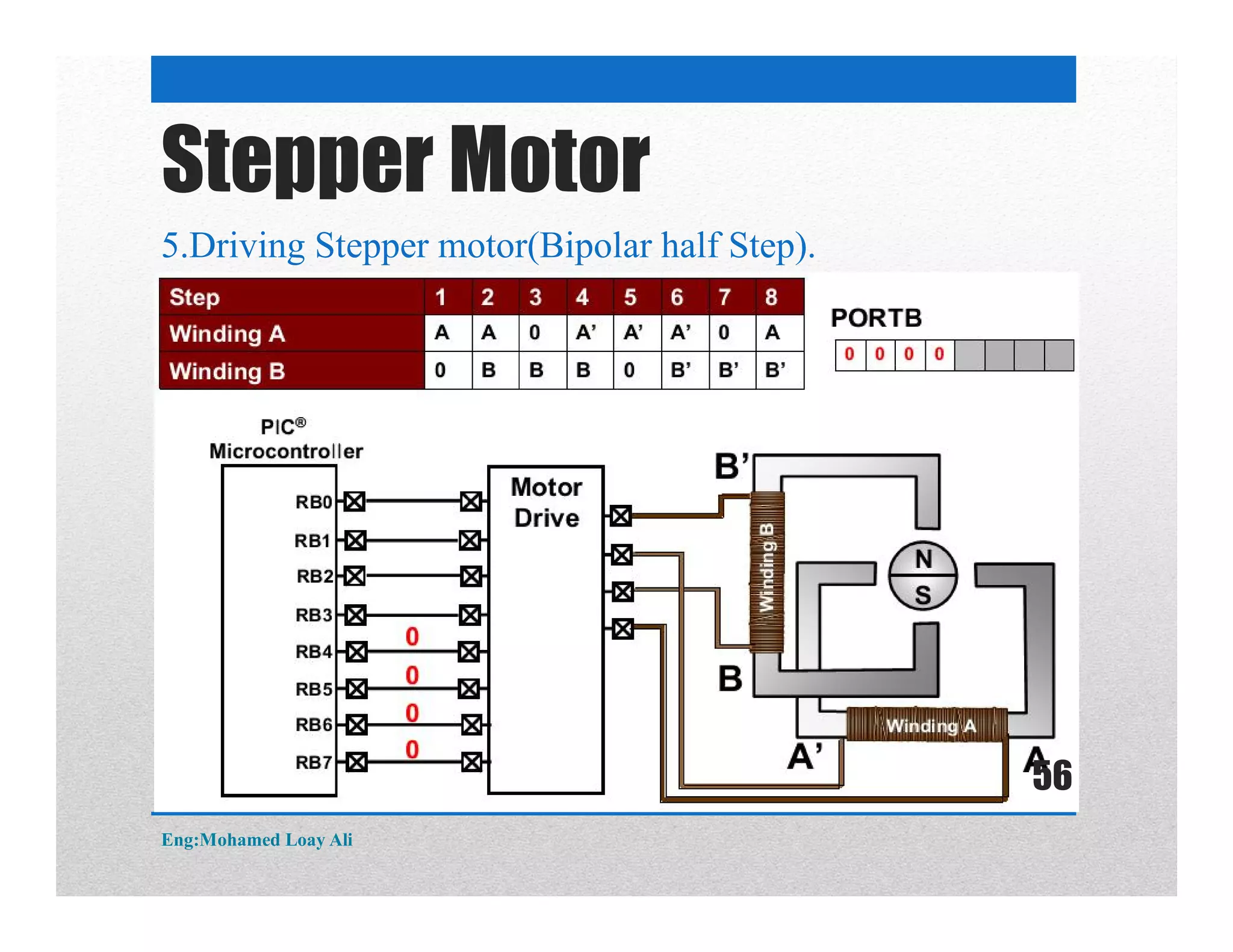
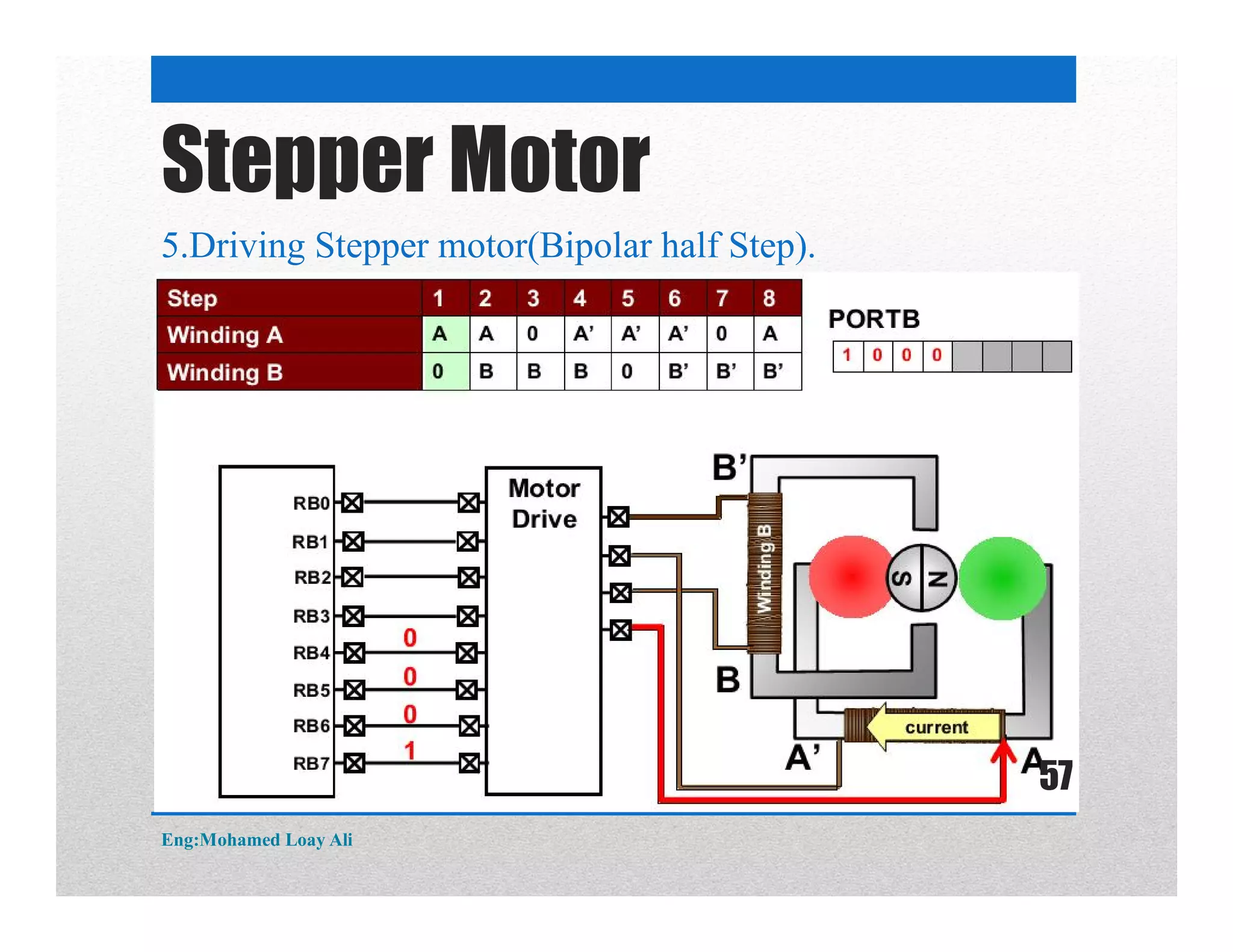
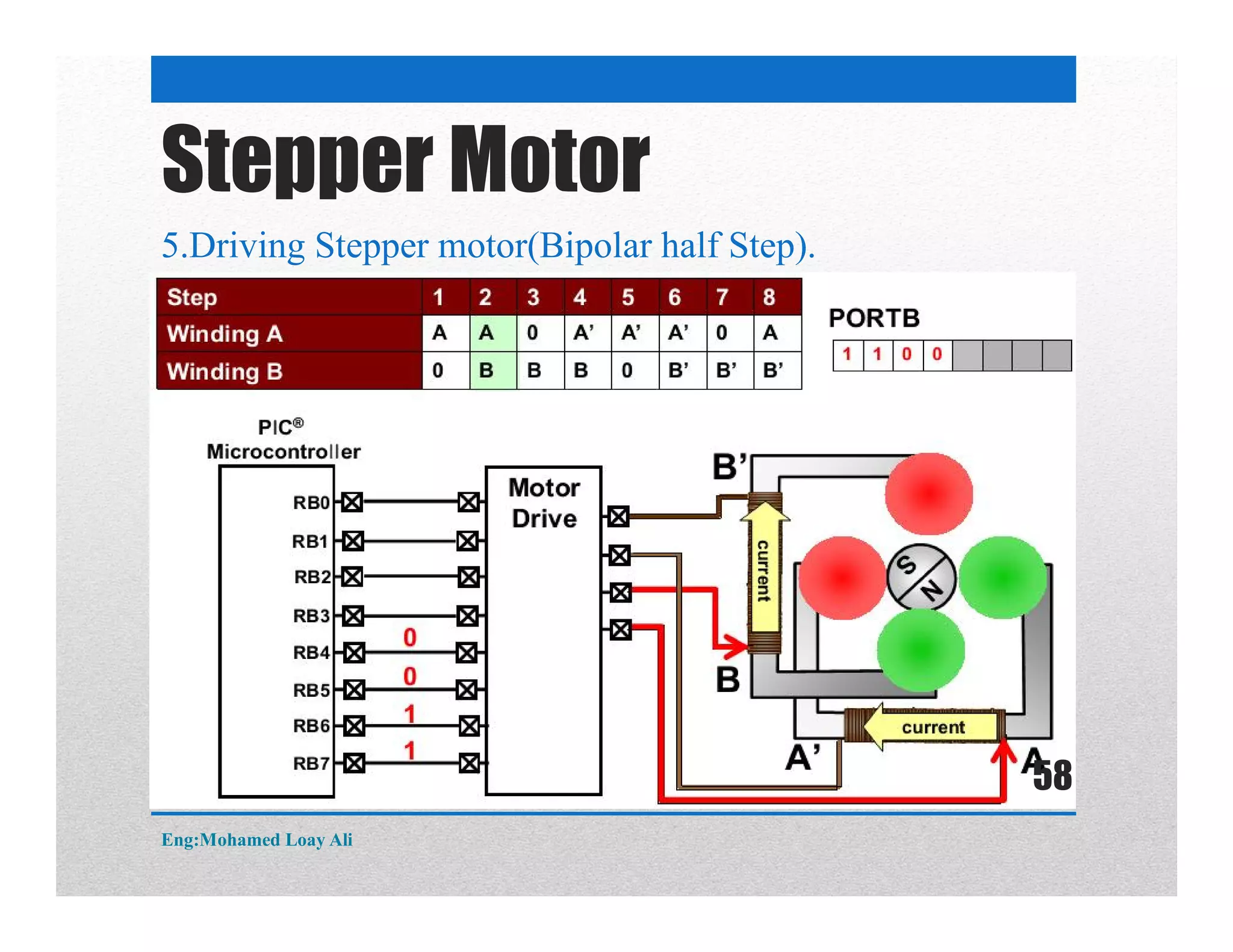
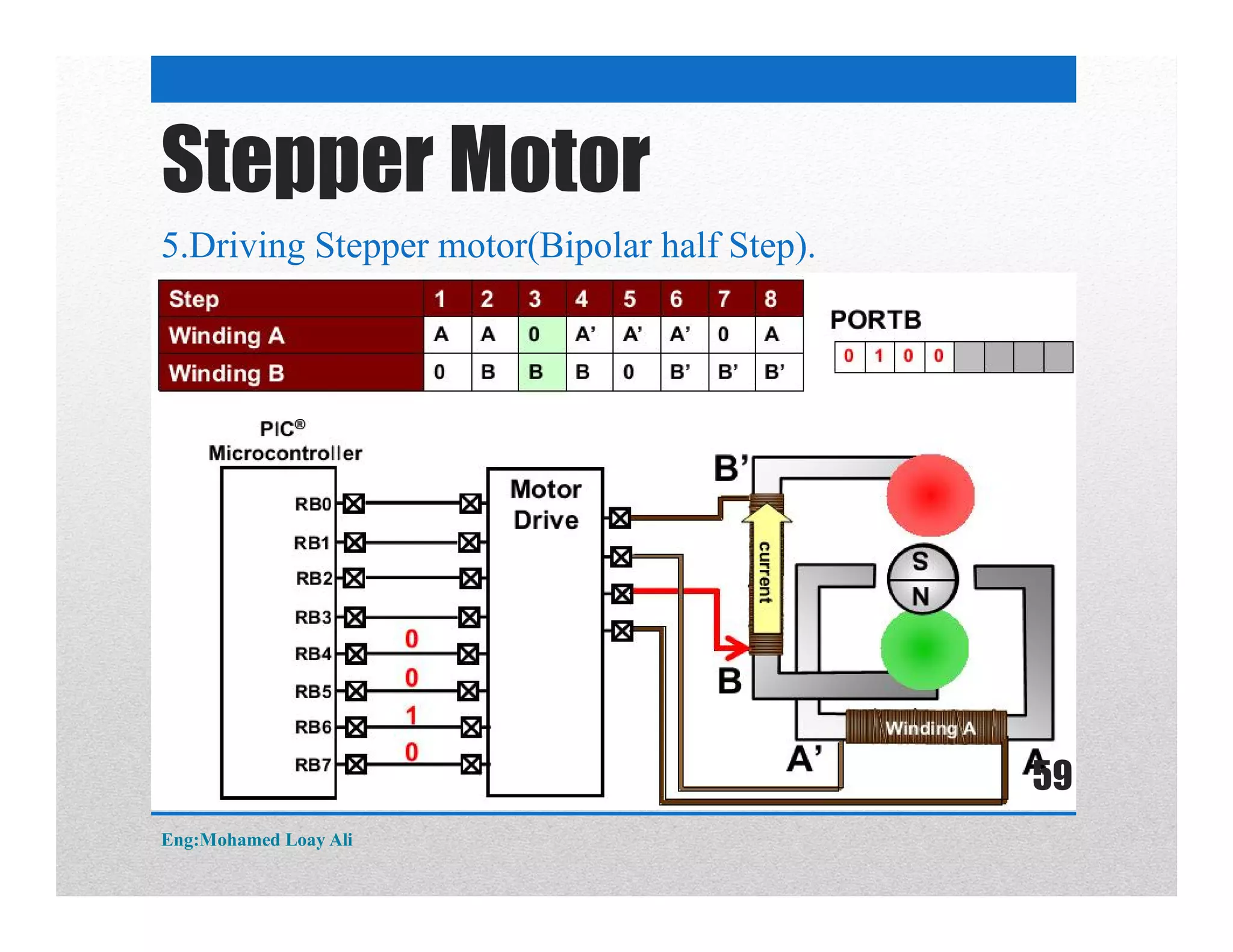
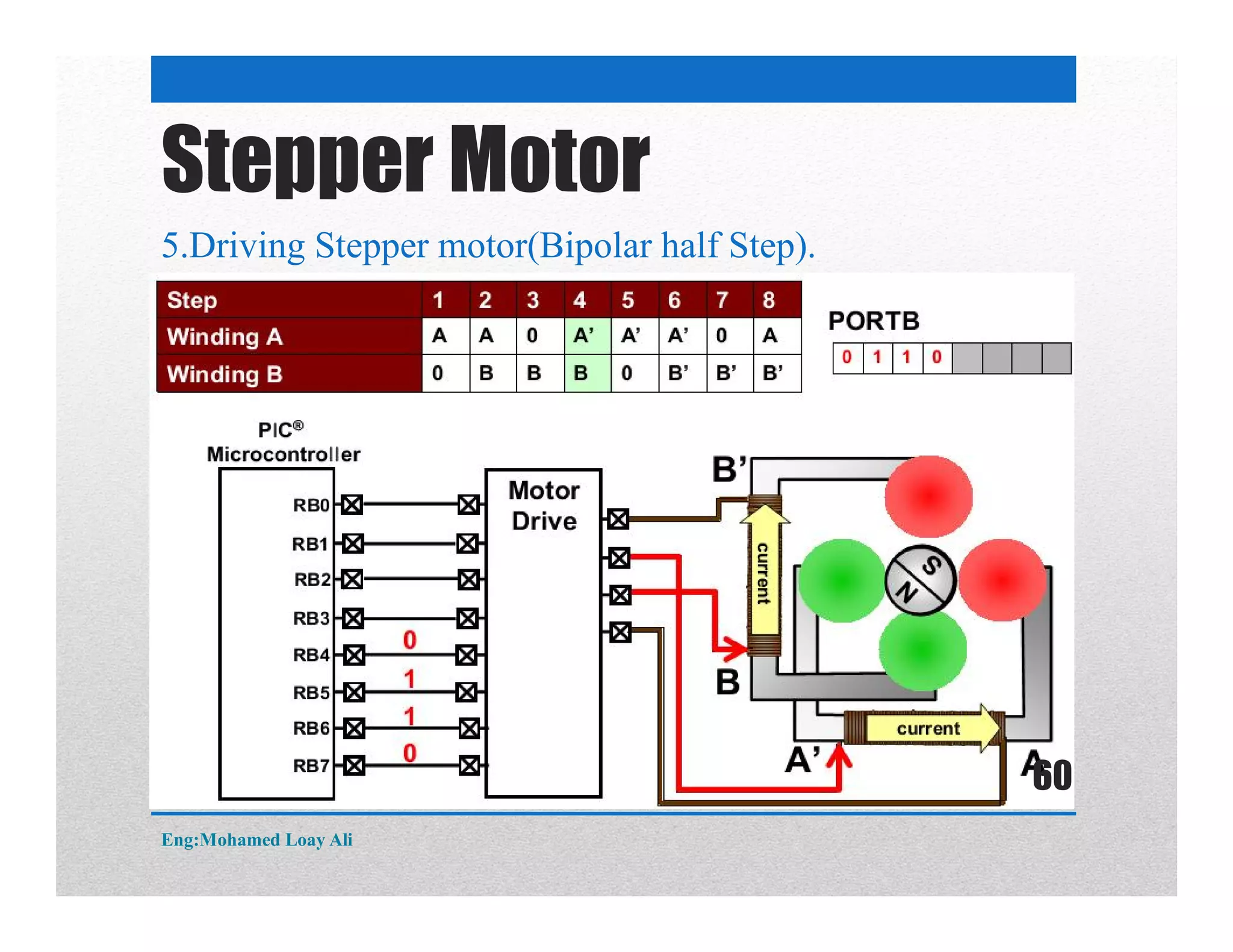
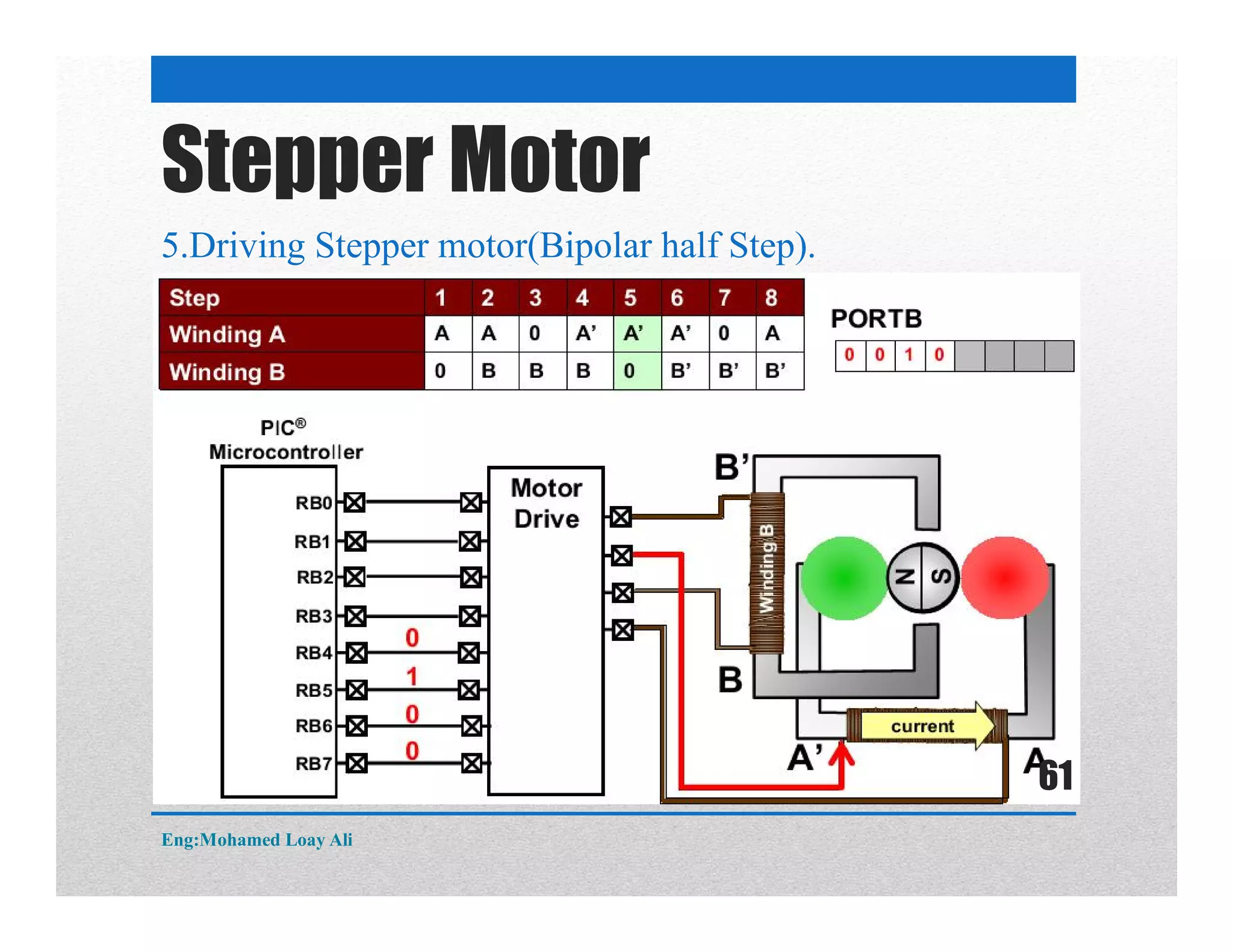
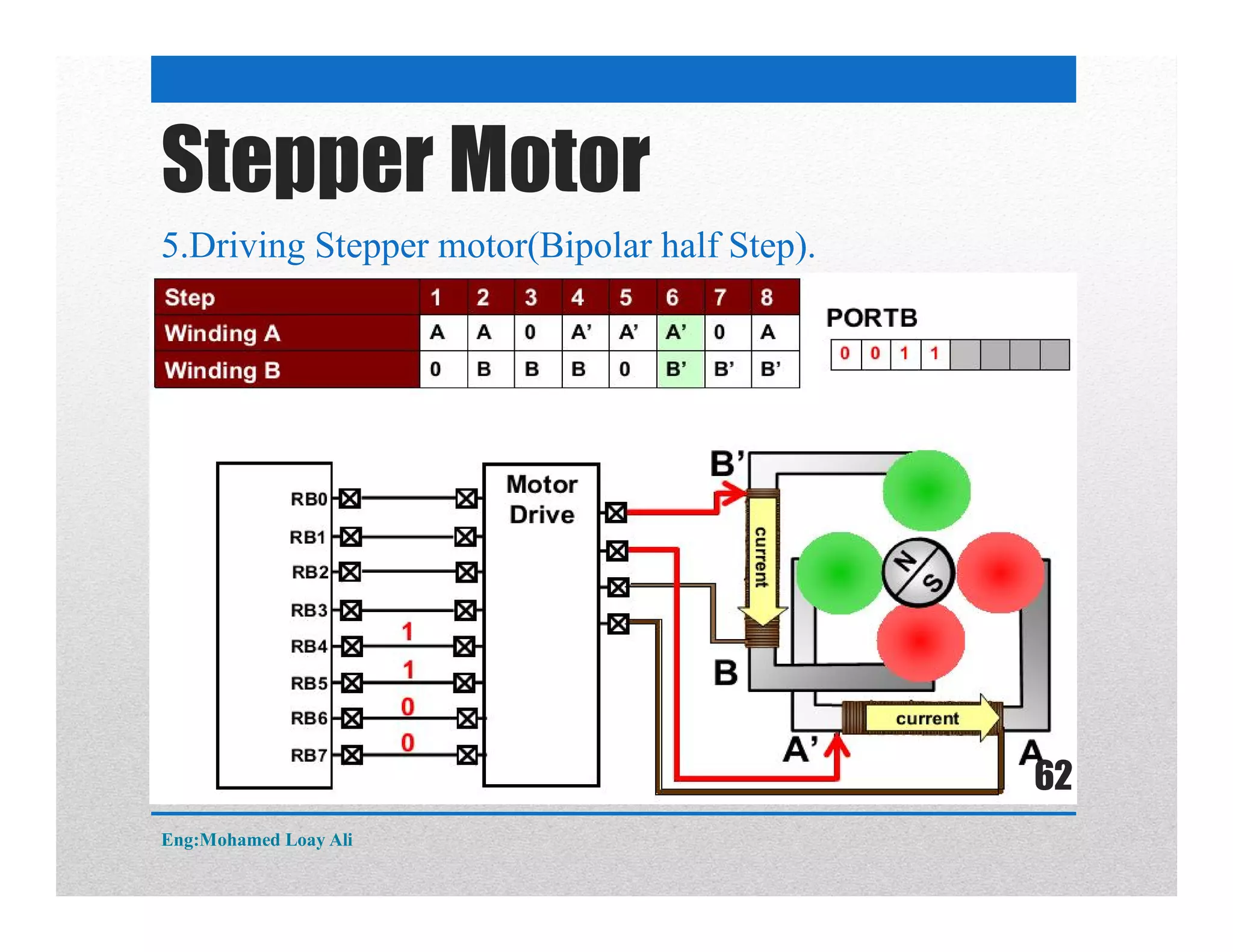
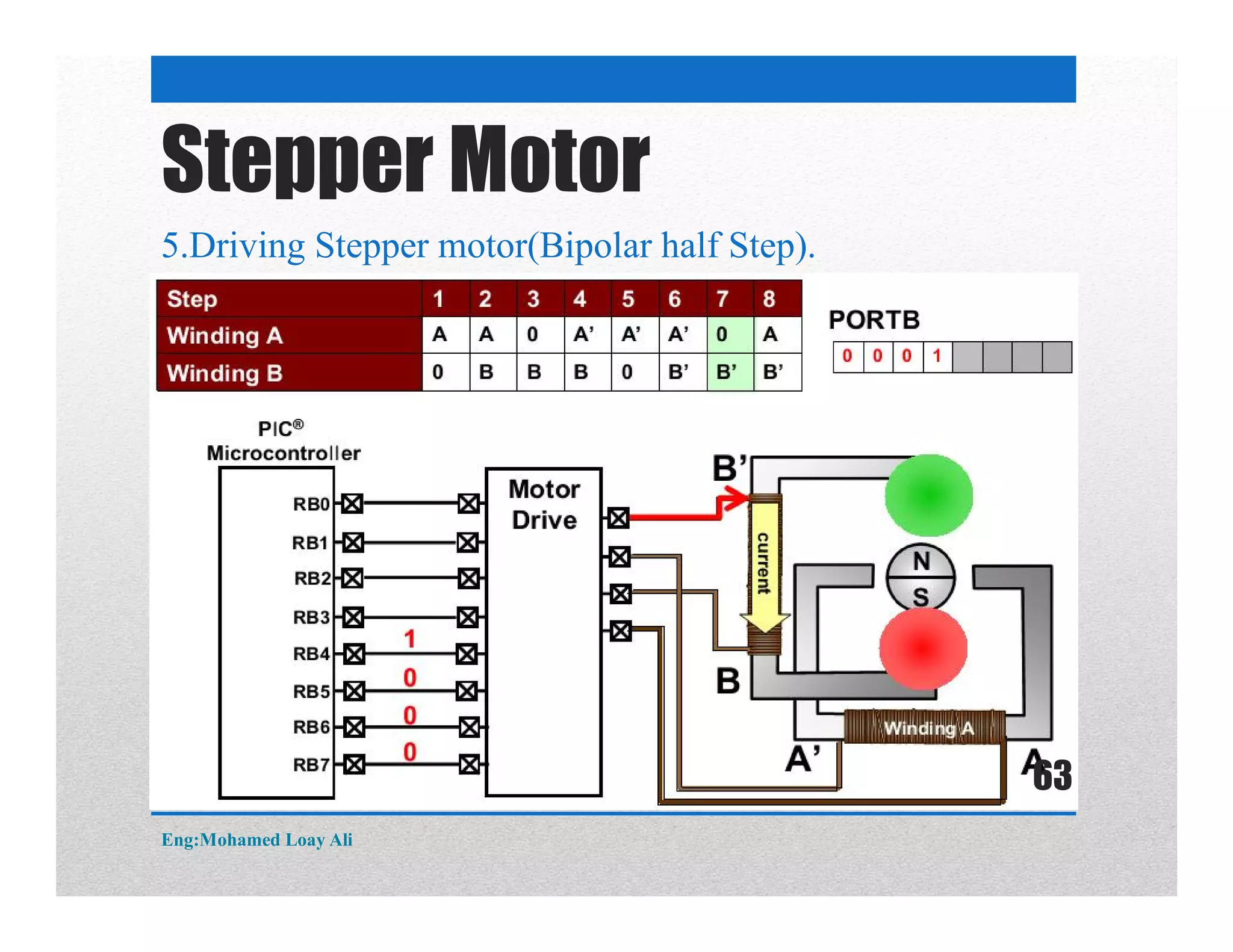
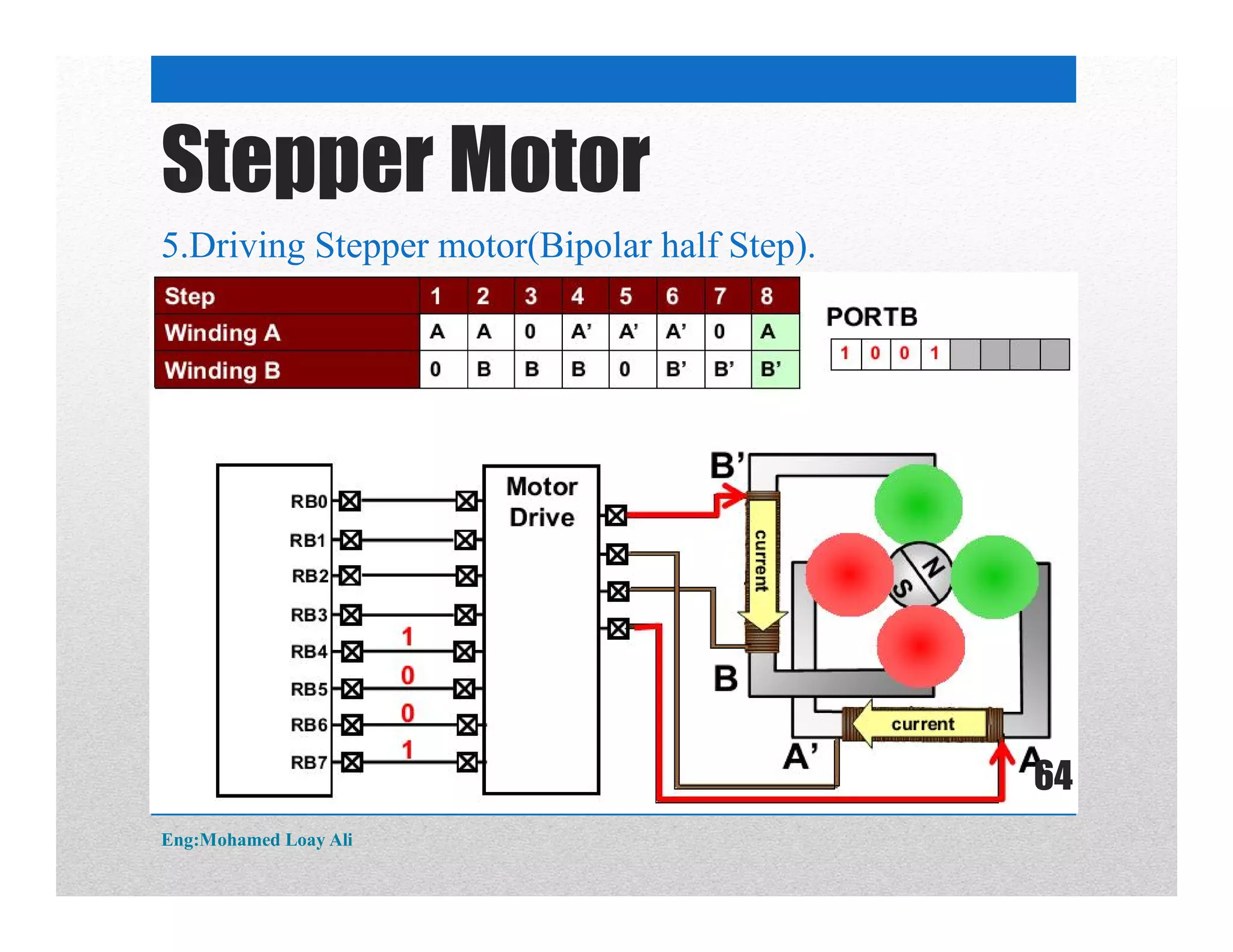
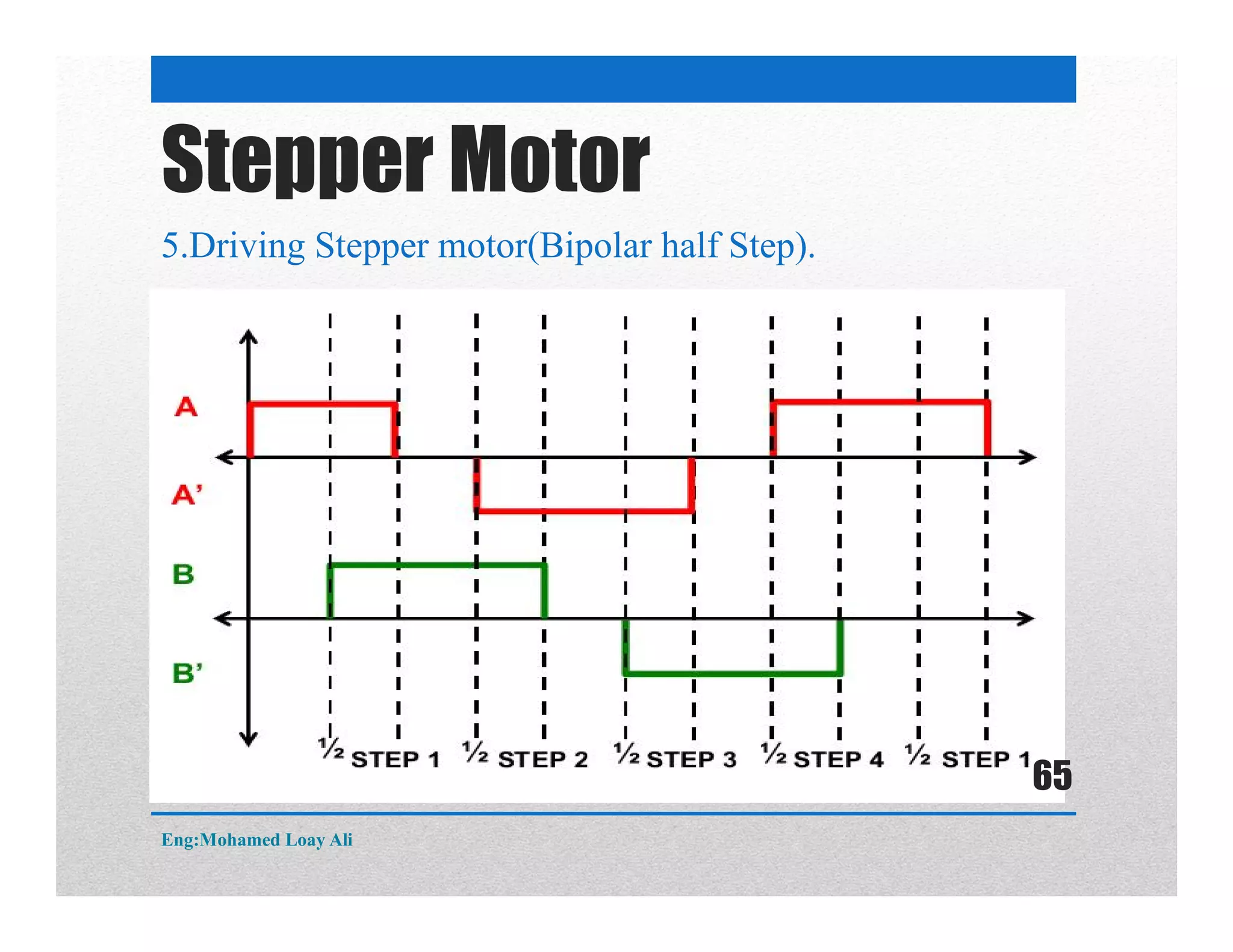
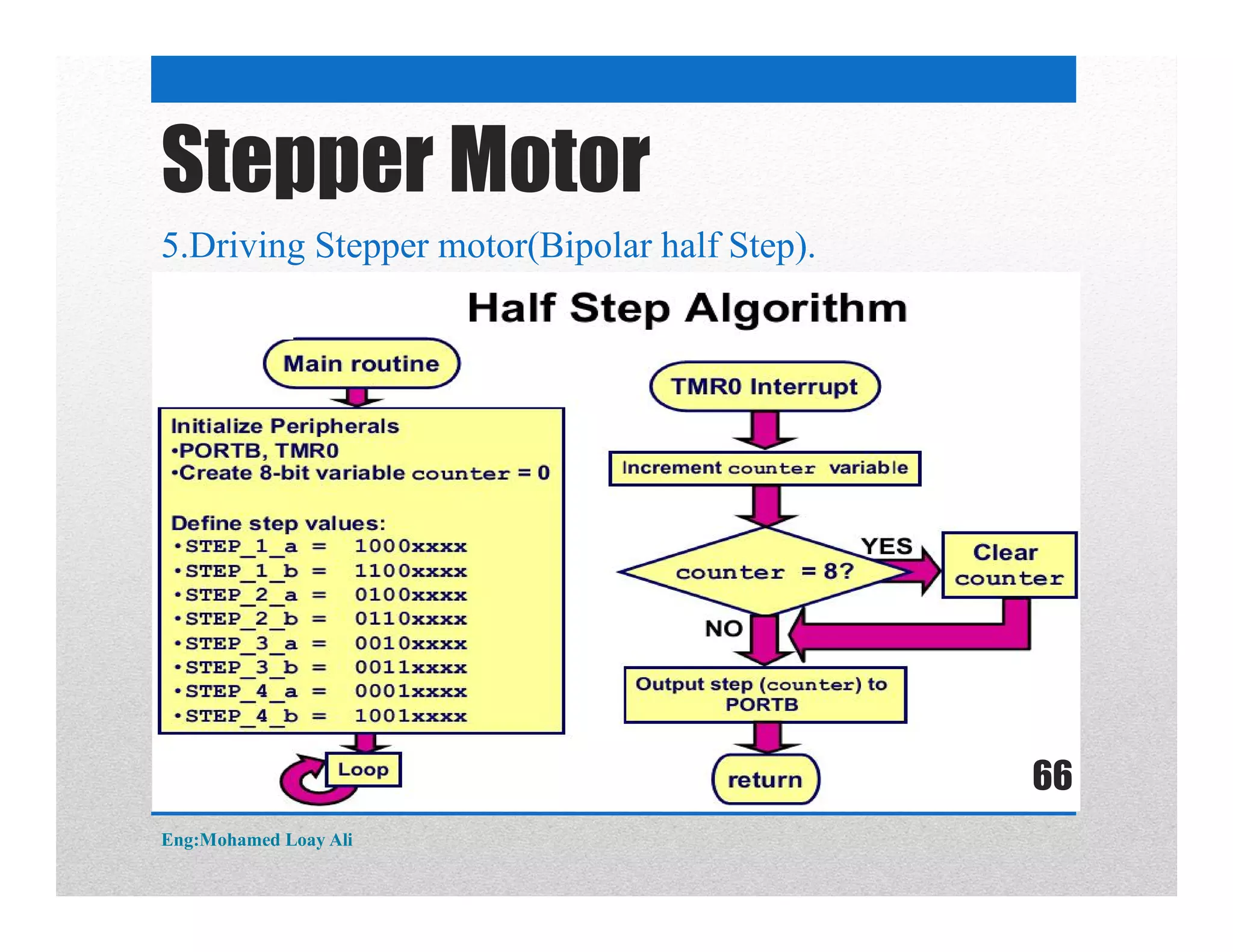
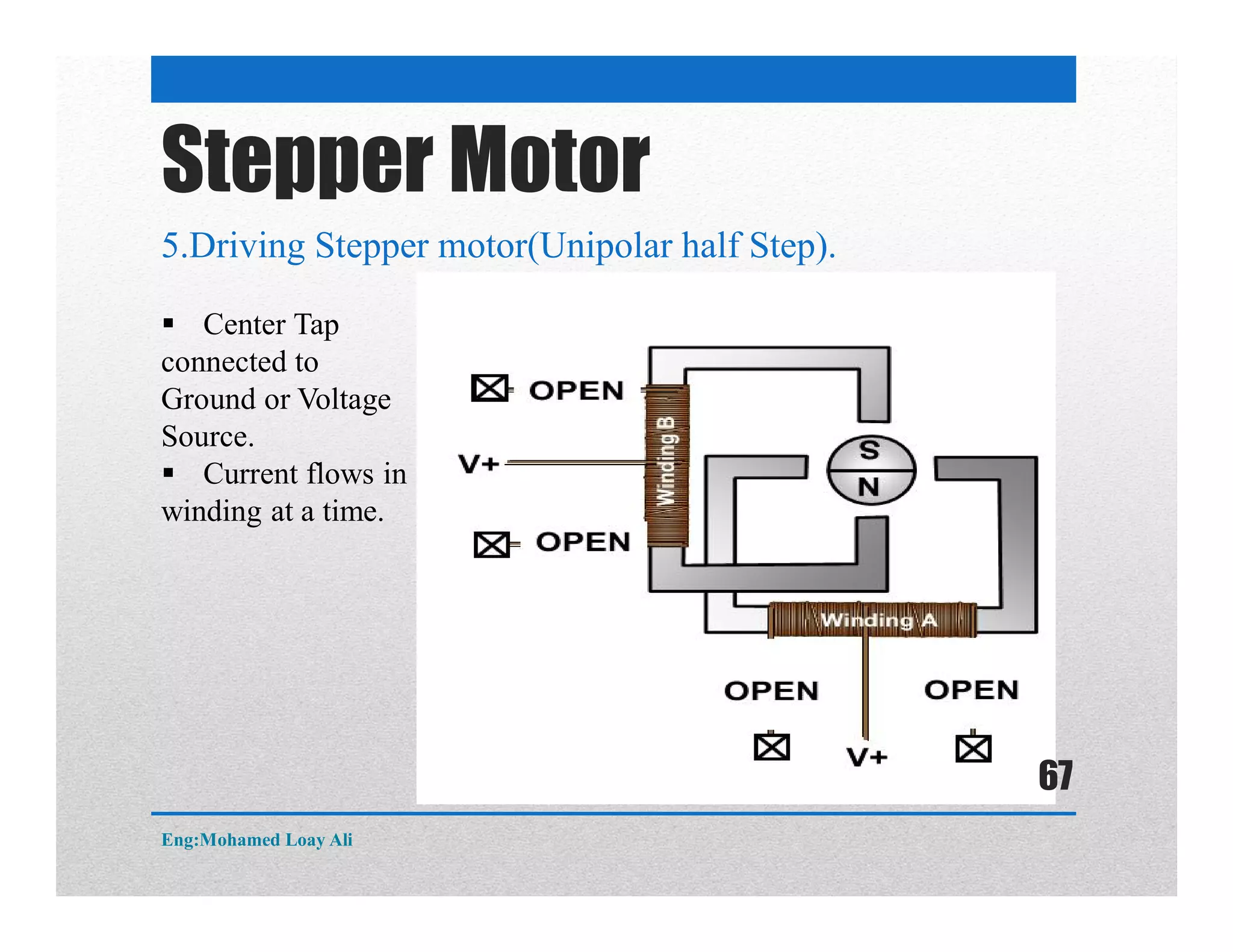
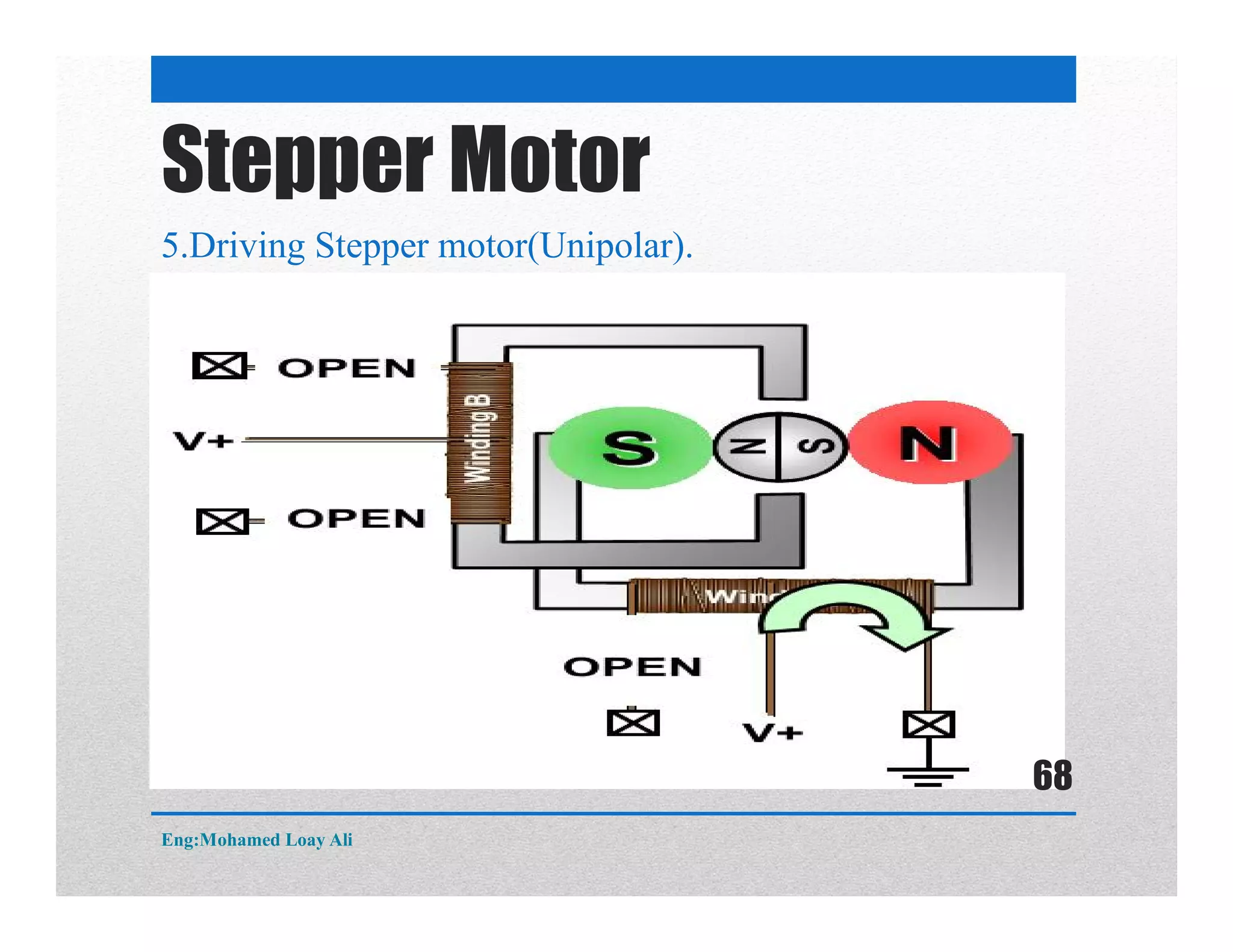
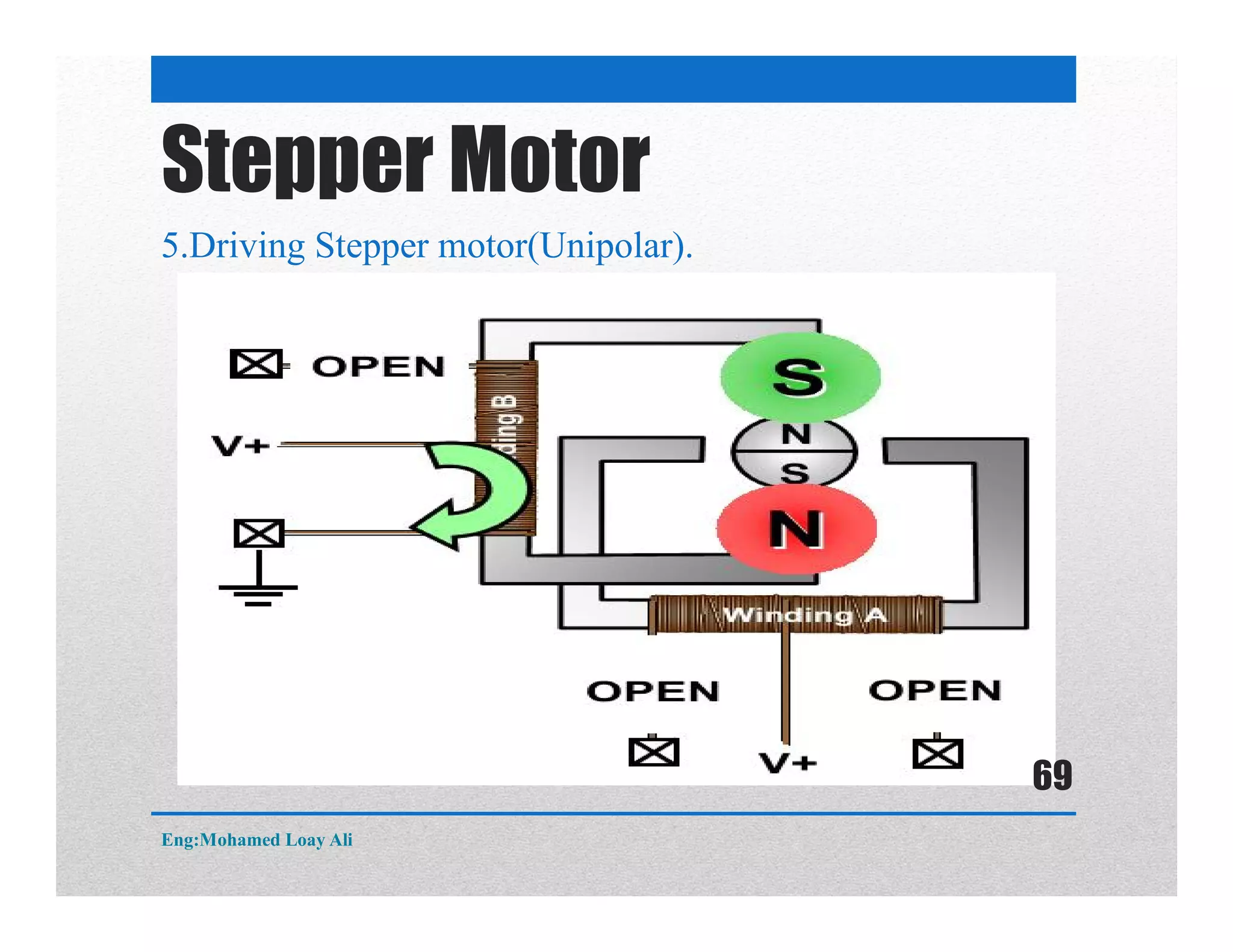
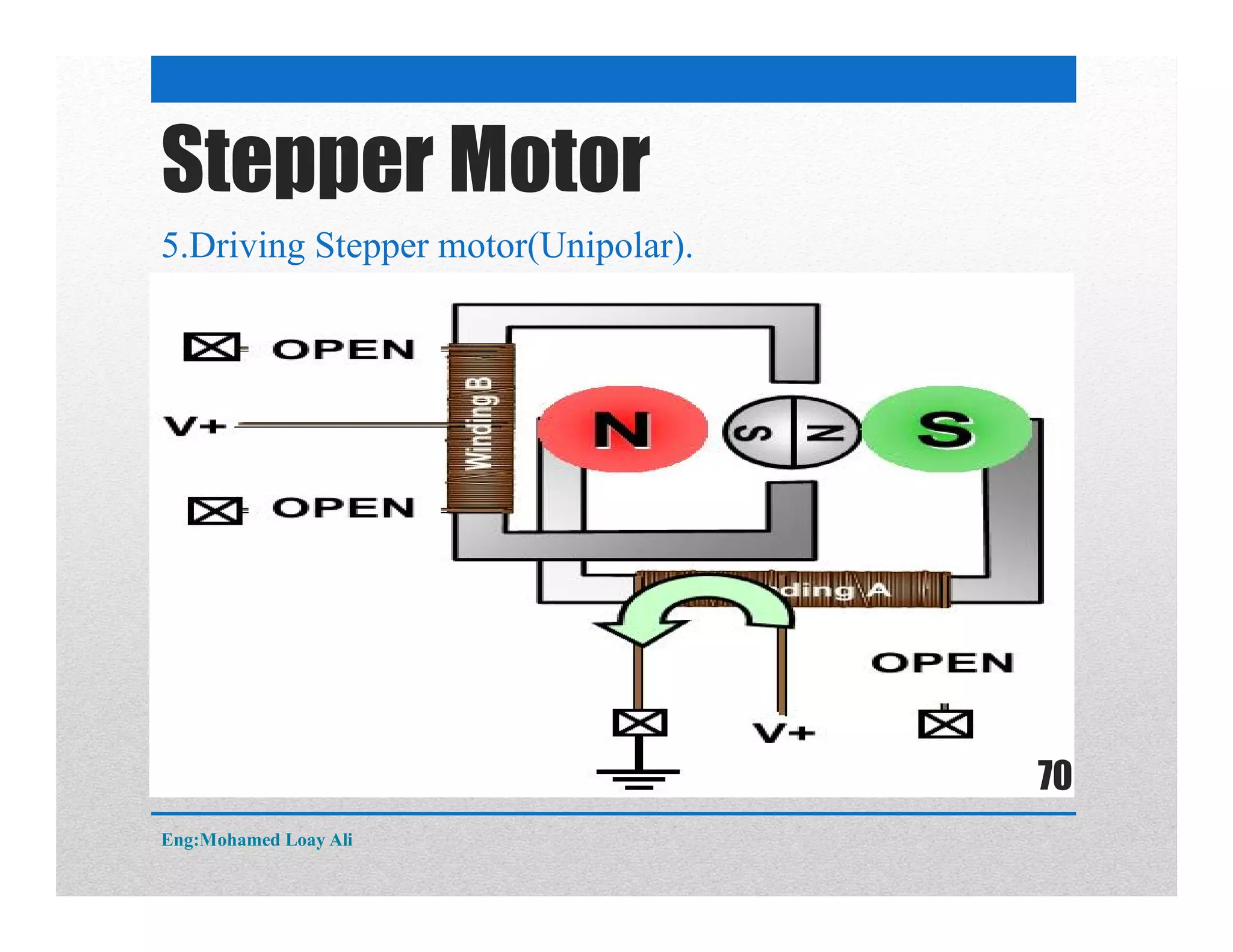
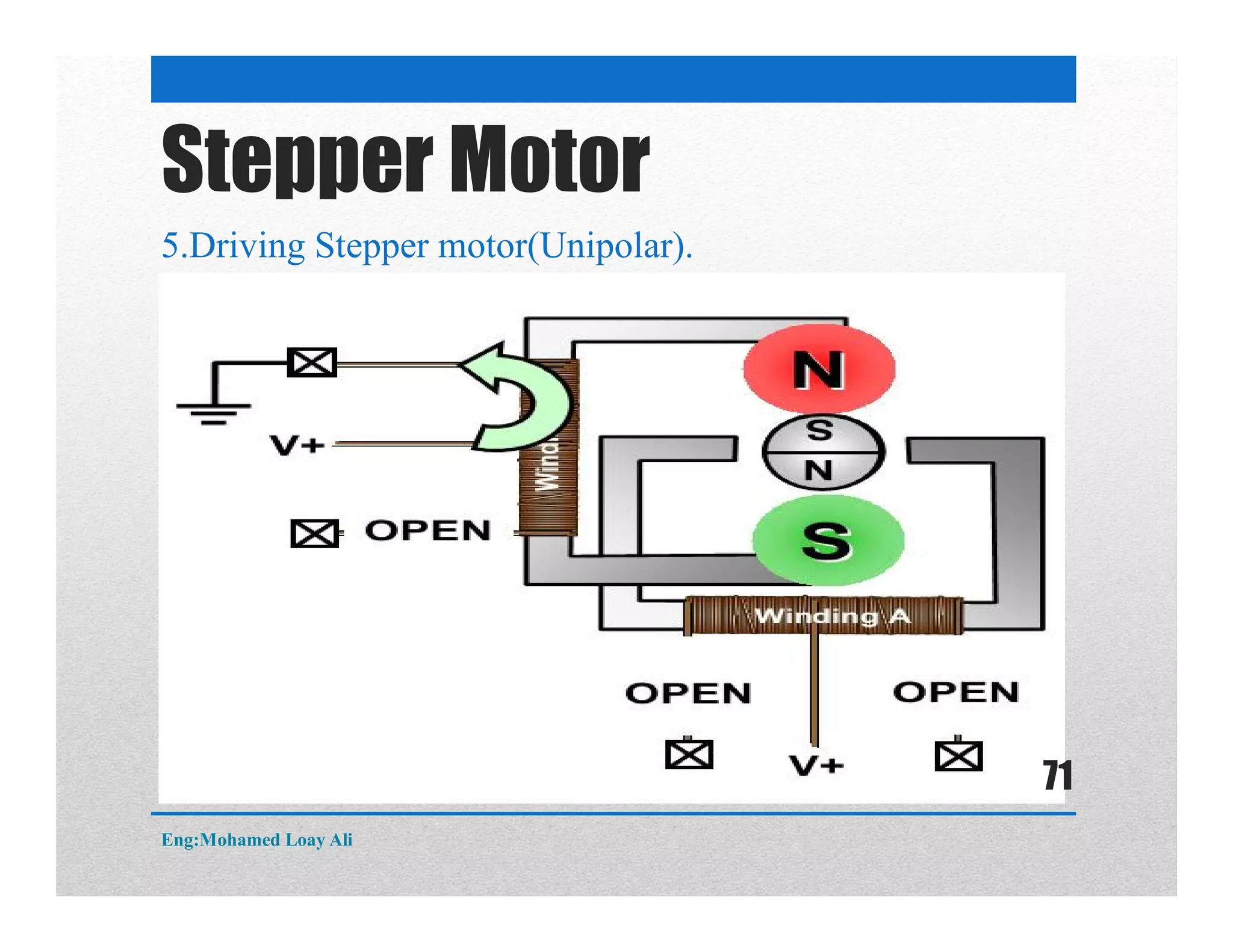
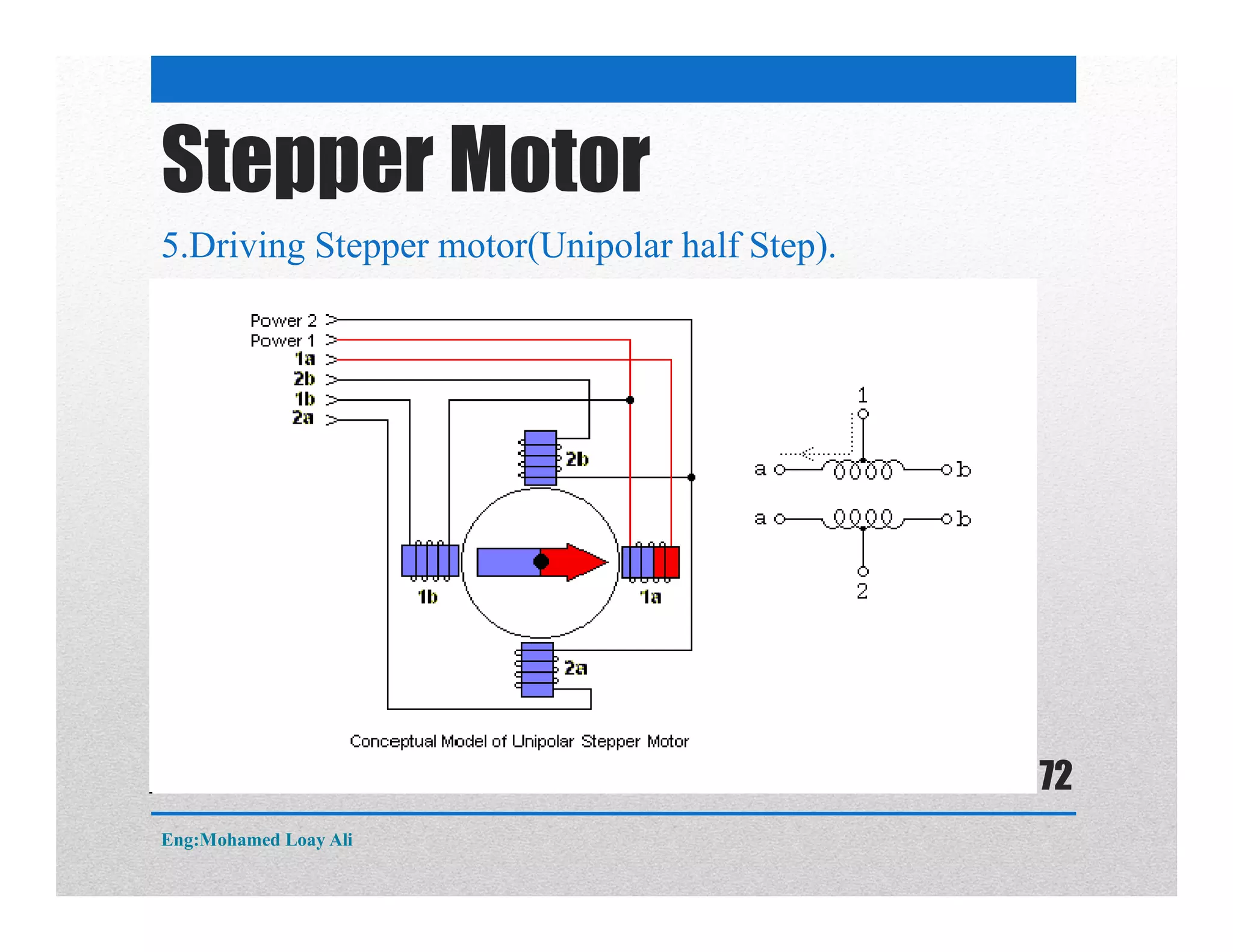
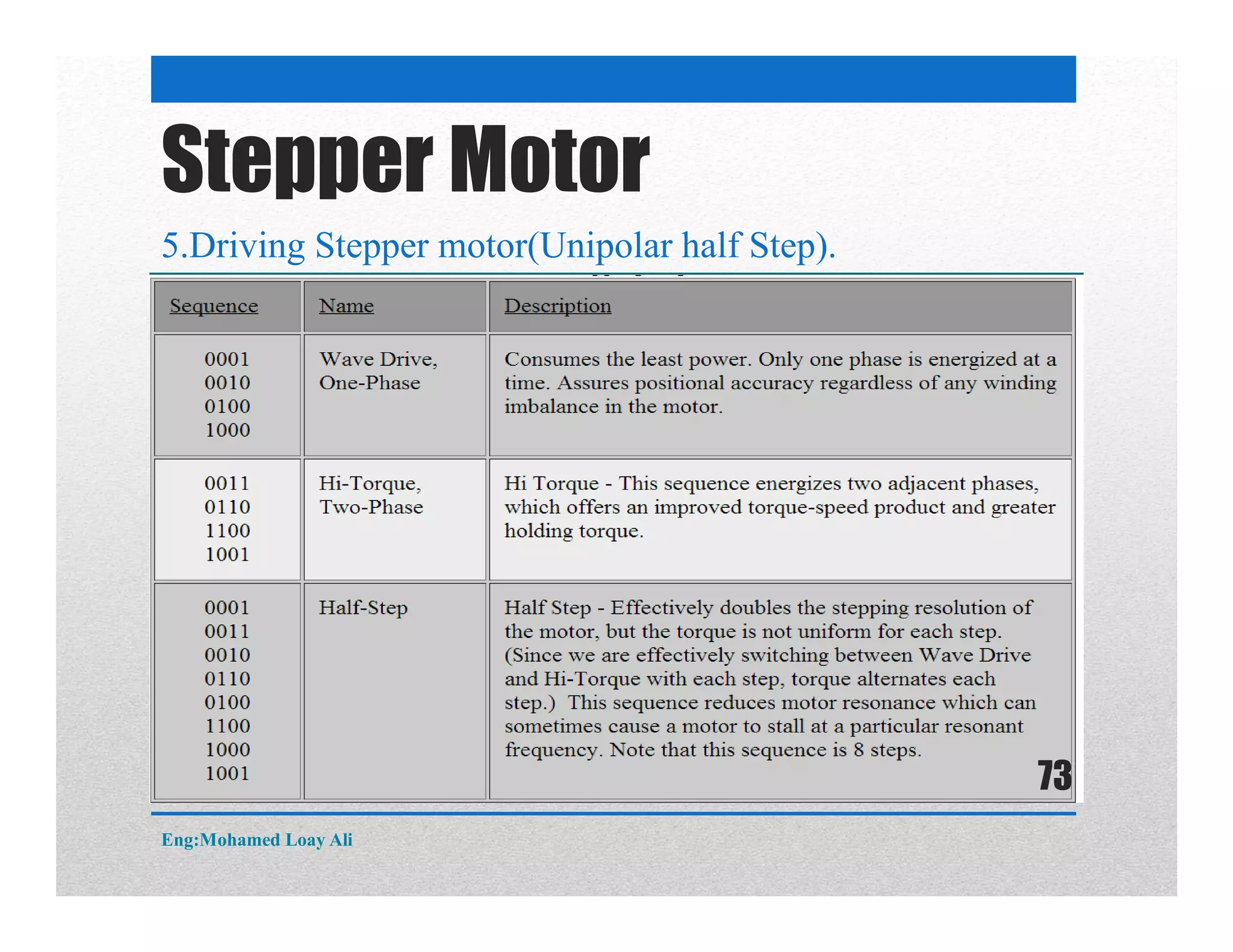
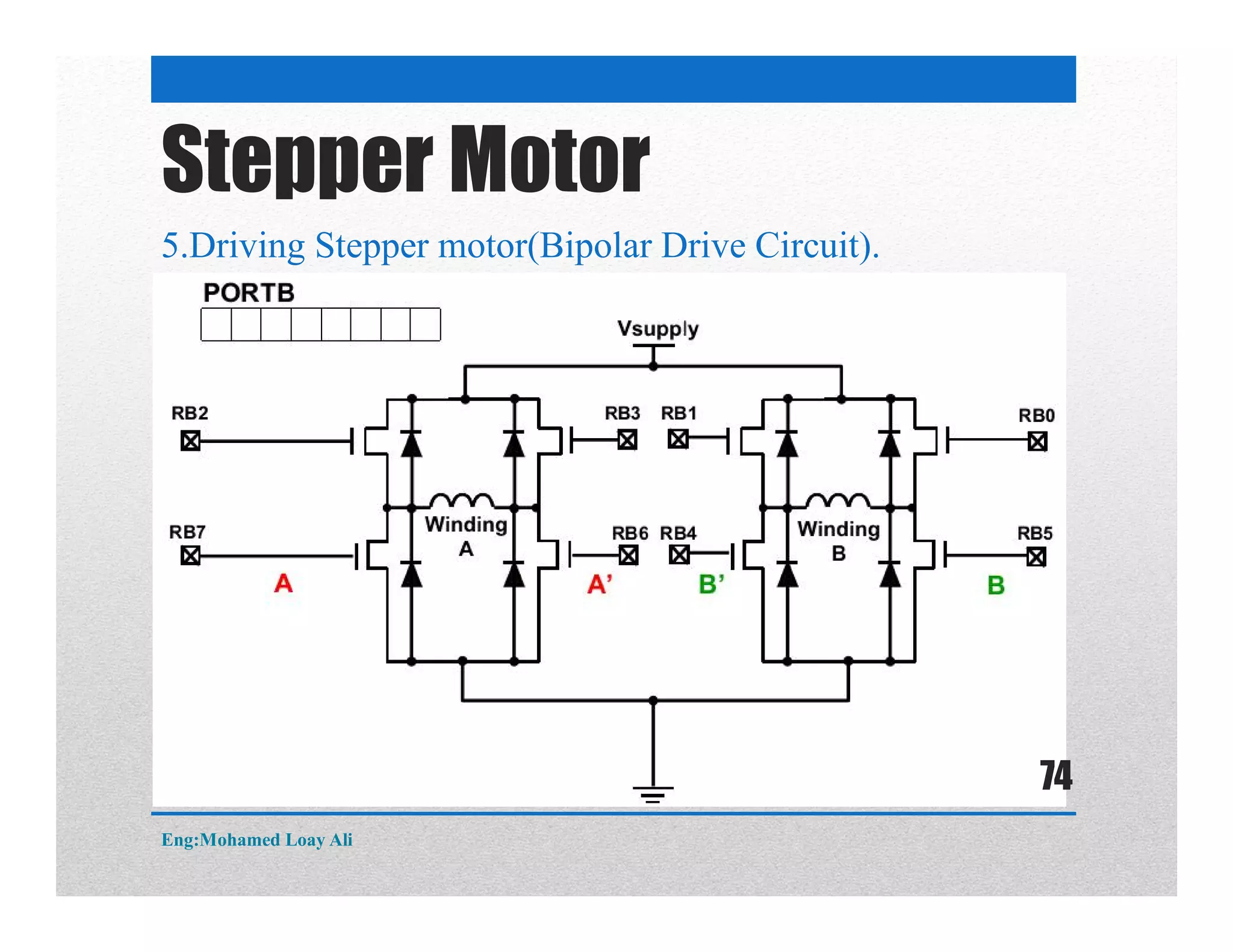
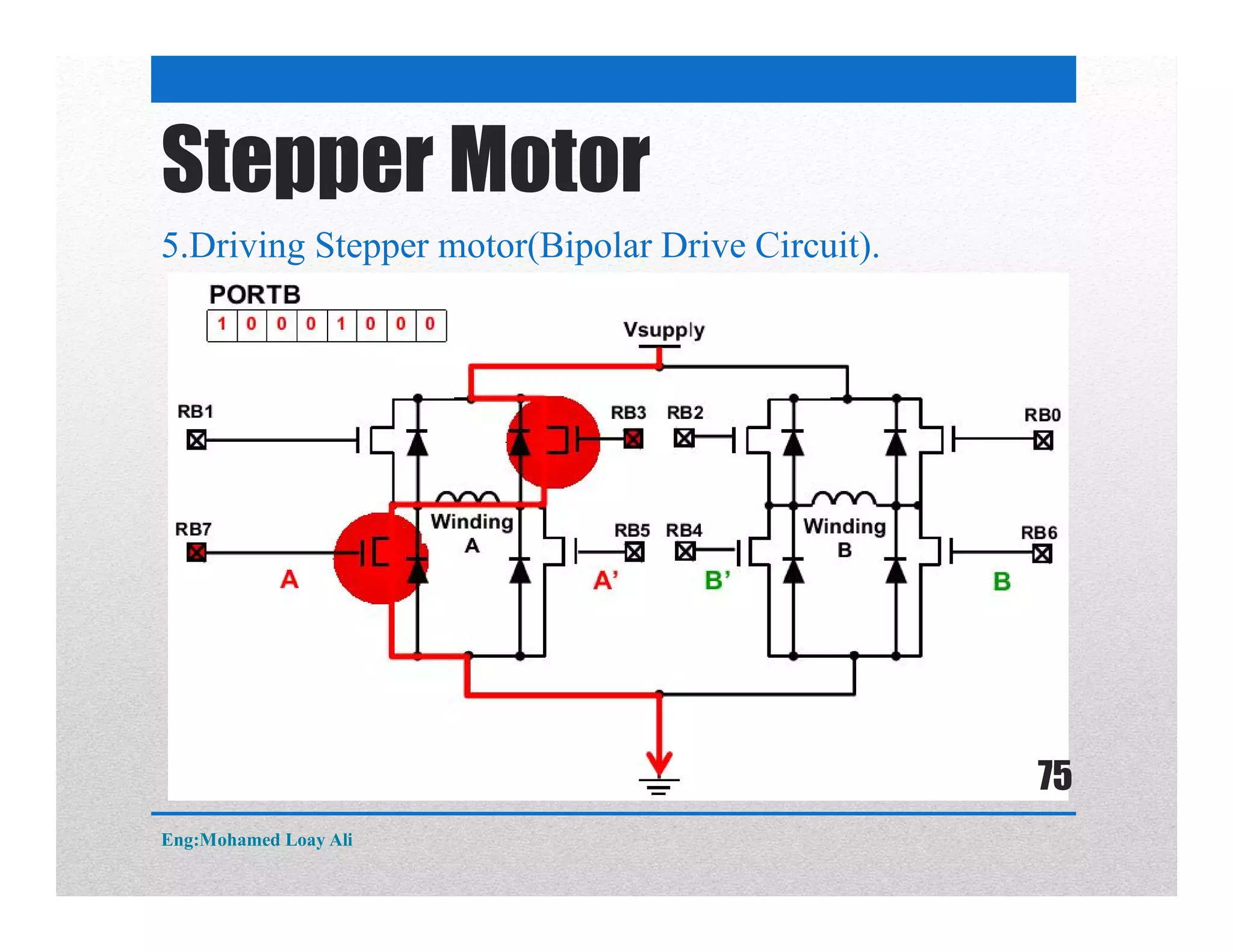
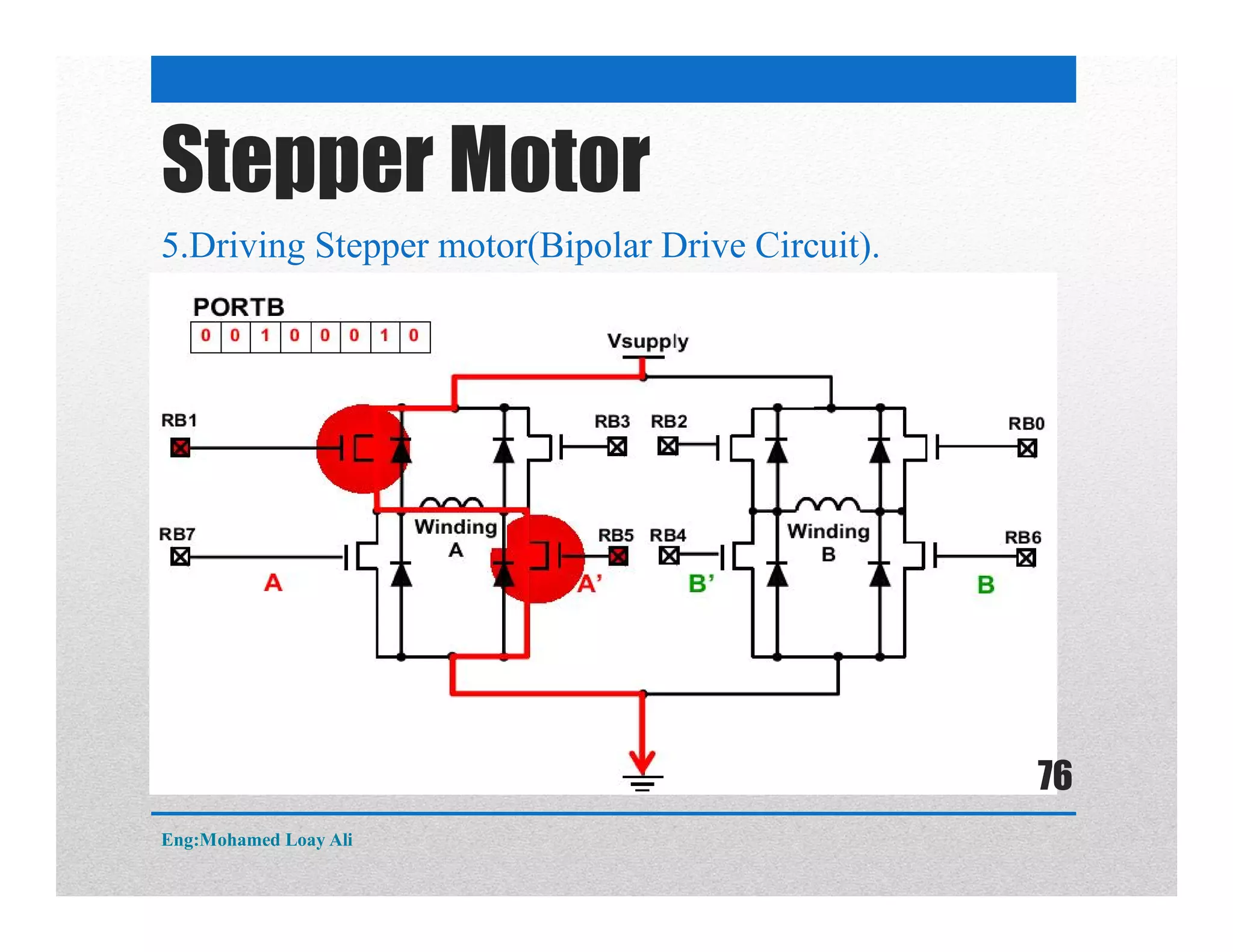
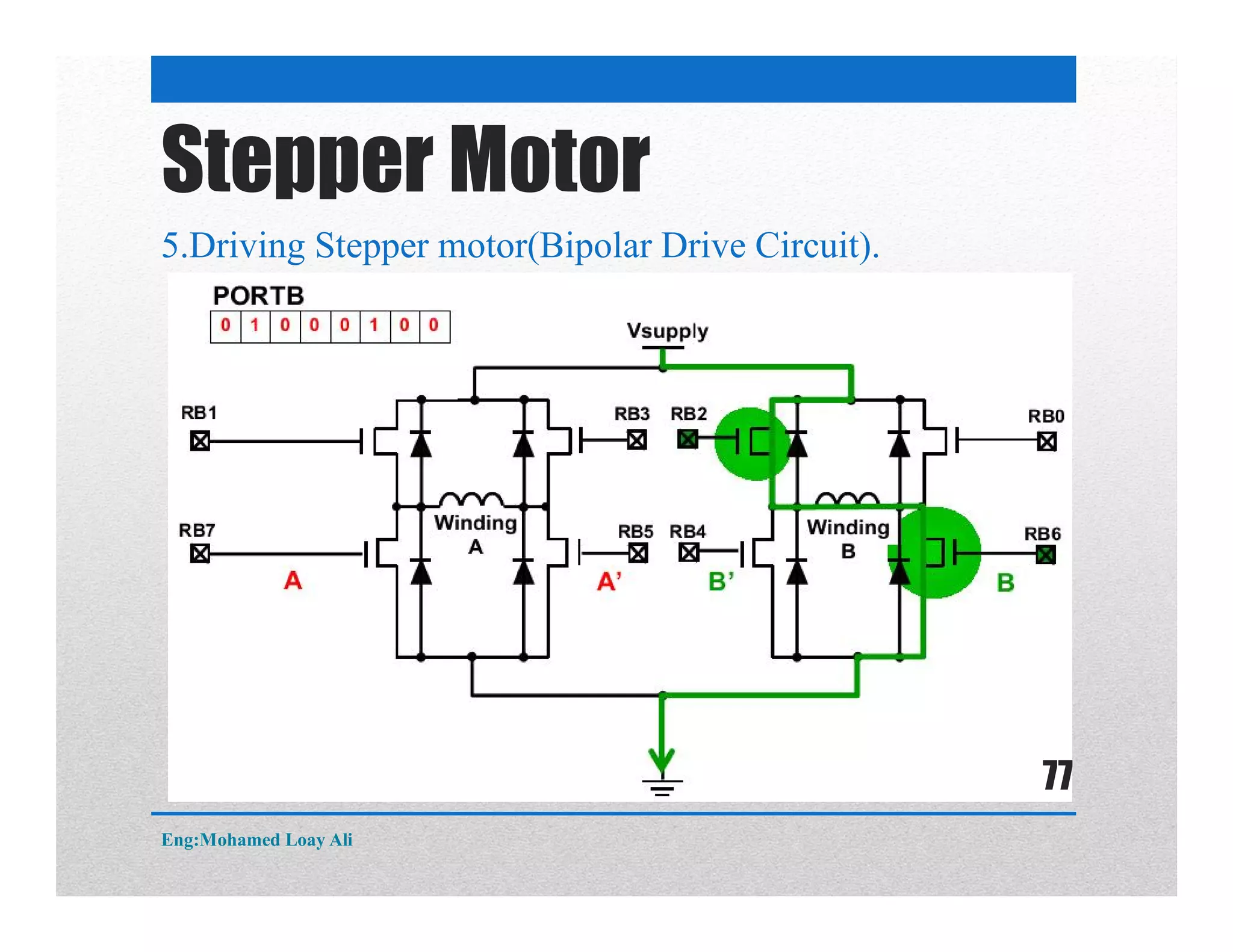
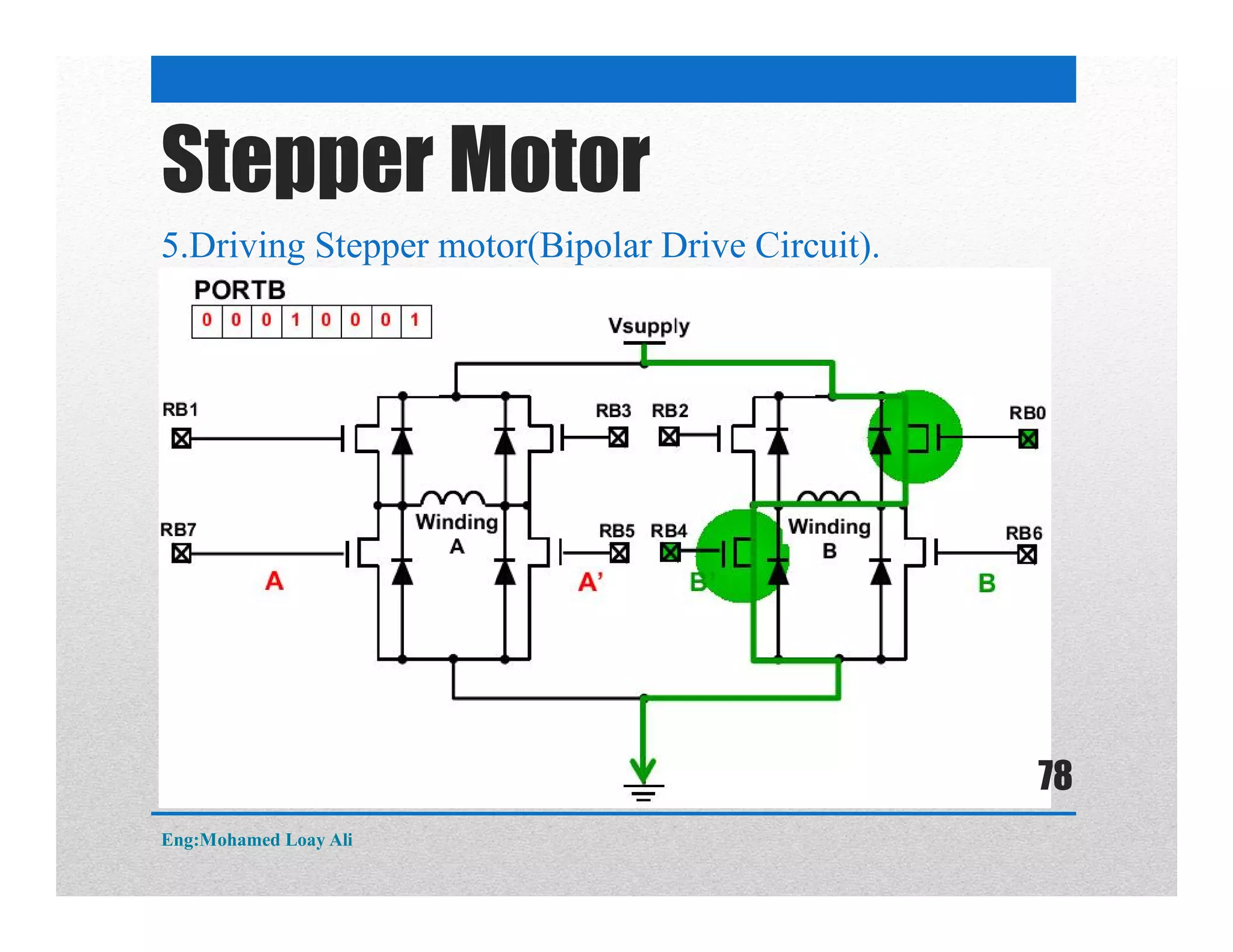
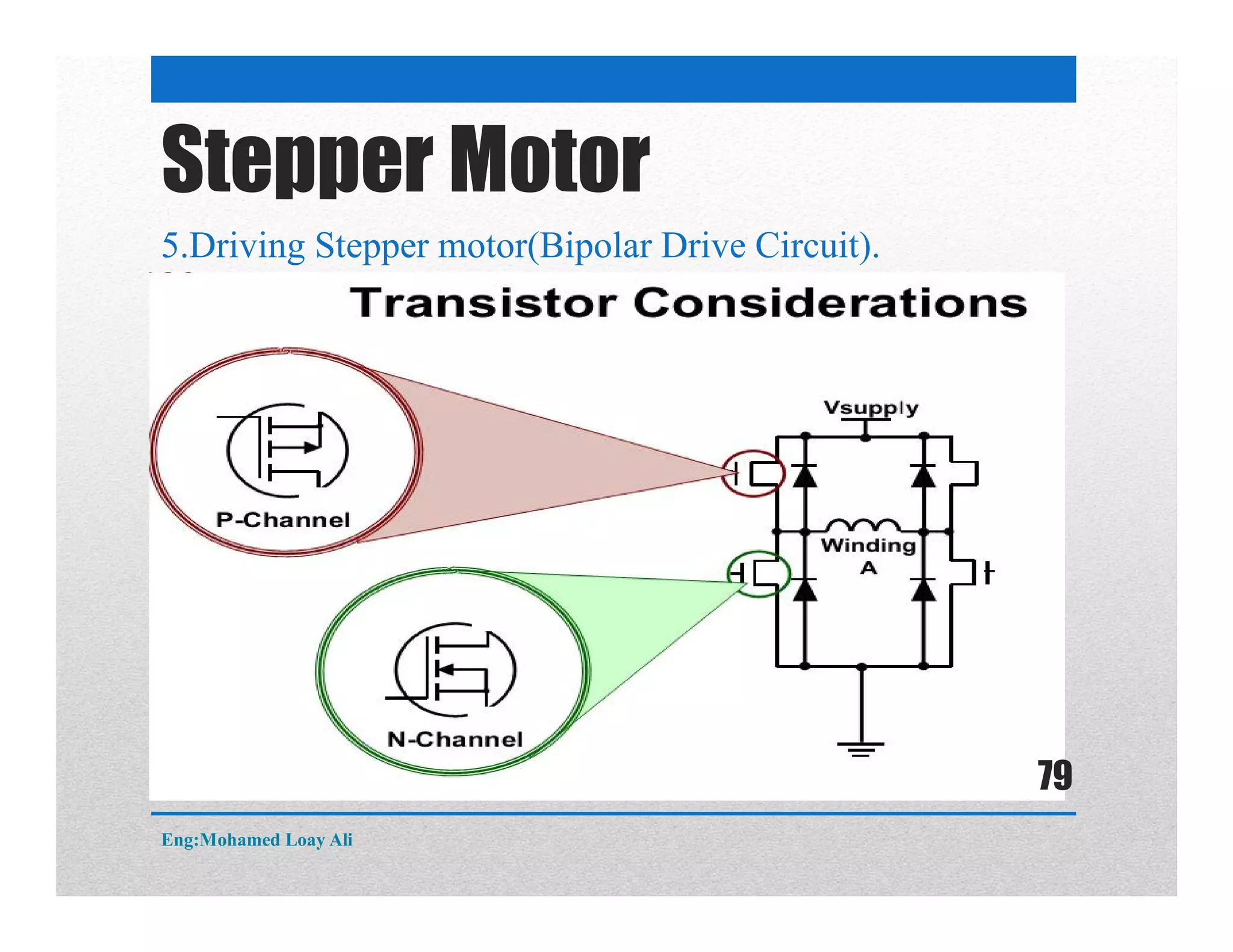
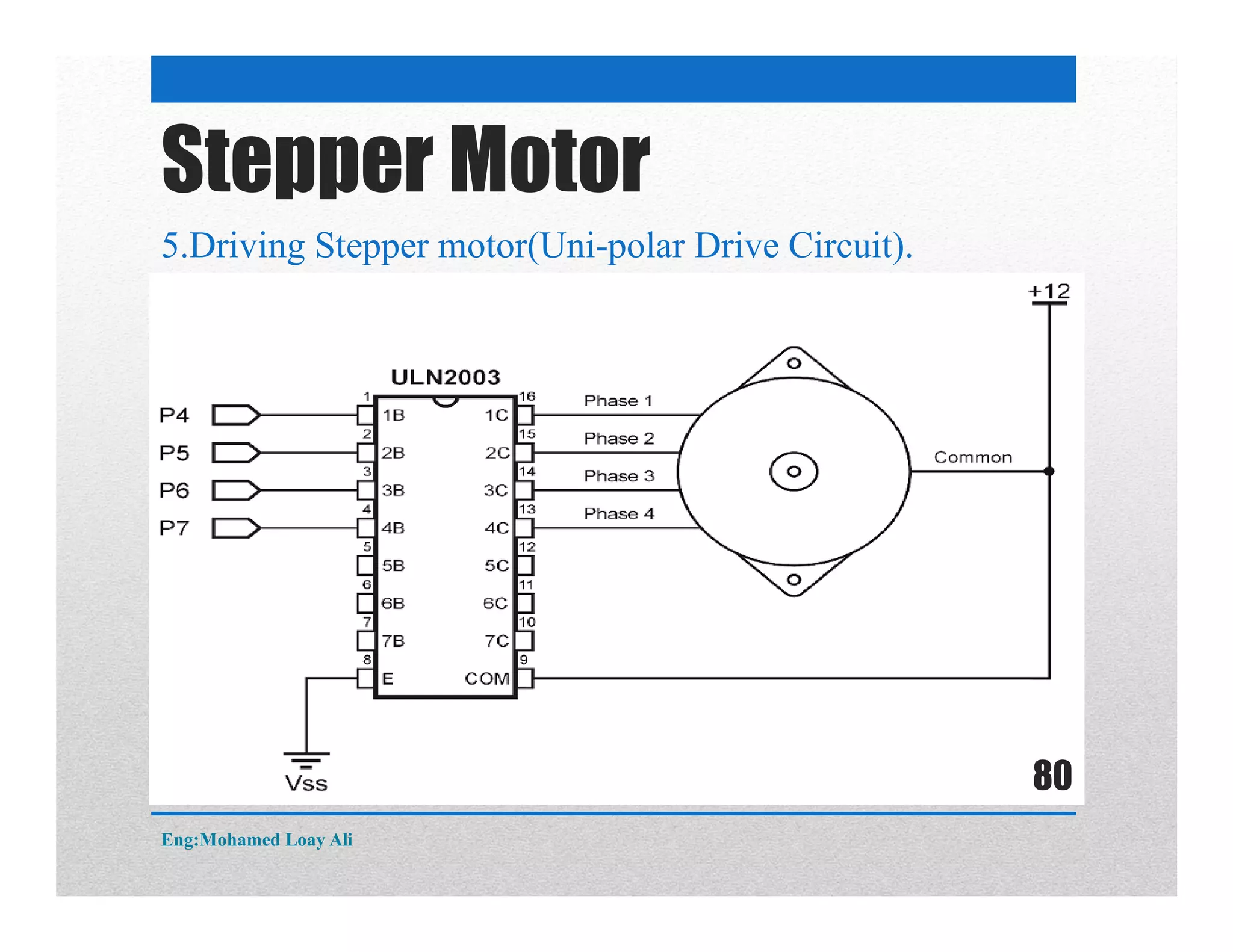
The document discusses various topics related to motor drive and PWM techniques. It covers DC motors, including their parameters and speed control using PWM. It also discusses stepper motors, including their basics, components, types, driving modes for unipolar and bipolar stepper motors, and drive circuits. PWM modes for 8-bit and 16-bit controllers are explained for both DC and stepper motor control applications.