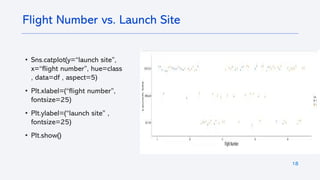
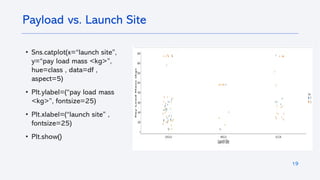
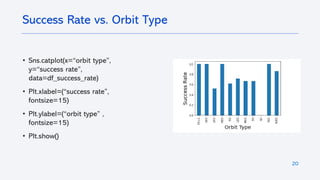
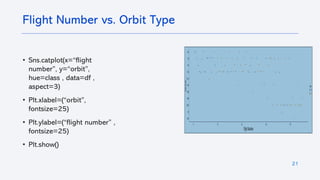
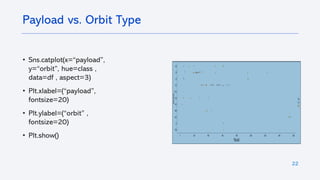
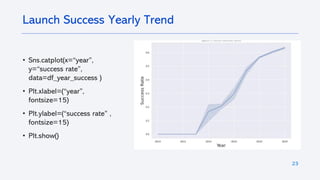
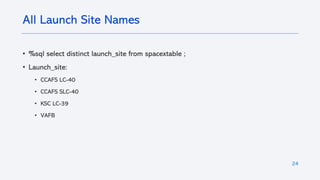
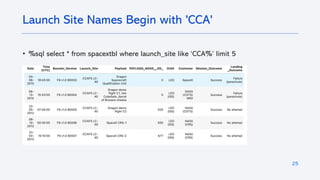
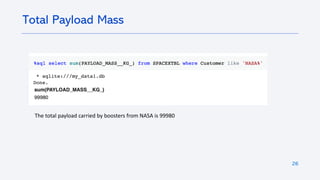
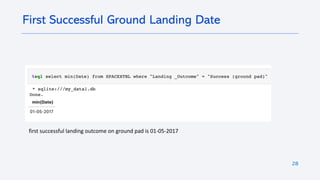
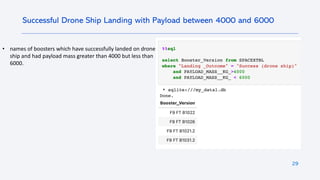
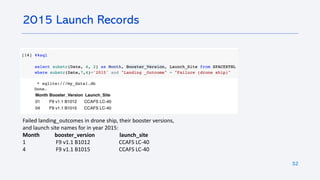
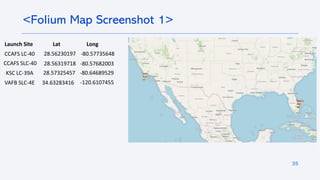
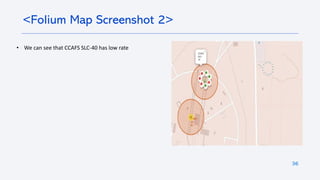
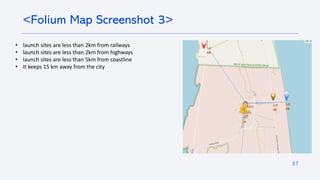
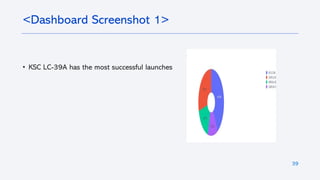
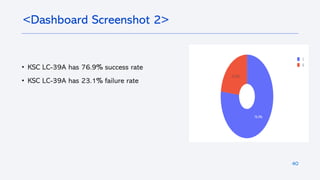
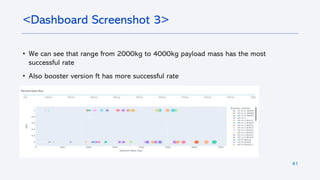
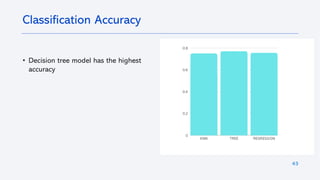
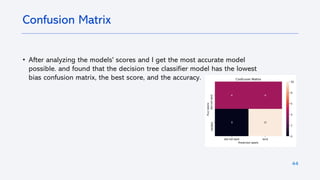
The document outlines a project analyzing the success rate of SpaceX's Falcon 9 first stage landings using data collection methods such as APIs and web scraping. It includes methodologies for data wrangling, exploratory data analysis, and building interactive tools for visualization and predictive analytics. Key findings suggest that the Falcon 9's success rate is influenced by various factors including launch site and payload mass, with decision tree models yielding high accuracy in predicting landing success.