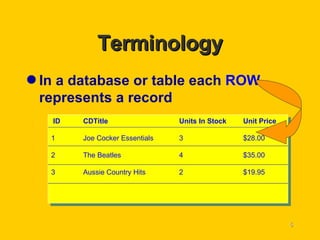
This document provides an introduction to databases, including their basic terminology and concepts. It discusses what a database is, the advantages and disadvantages of computerized databases, and key database terminology such as records, fields, rows, columns, queries, reports, searching, sorting, and forms. It also outlines the important steps for carefully planning a database, including determining what data to store, required operations, listing fields and their descriptions, and creating a sample database table.